《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷B卷(答案)

Iype I:Singlechoice (1pointforeach, total 40points)AB CL1X×23X4+5+18X9X1011X13X14X1516人17X1819X2021X22X23X24A25X26X27X28x29X313XXUX35X3637x3839XA0x
Type Ⅰ: Single choice (1 point for each, total 40 points). A B C D E 1 × 2 × 3 × 4 × 5 × 6 × 7 × 8 × 9 × 10 × 11 × 12 × 13 × 14 × 15 × 16 × 17 × 18 × 19 × 20 × 21 × 22 × 23 × 24 × 25 × 26 × 27 × 28 × 29 × 30 × 31 × 32 × 33 × 34 × 35 × 36 × 37 × 38 × 39 × 40 ×
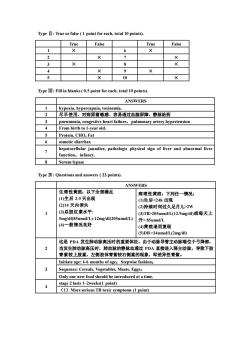
Type II : True orfalse (1 point for each, total 10 points).TrueTrueFalseFalsXType II: Fillin blanks (0.5 point for each, total 10 points).ANSWERShypoxia,hypercapnia, toxinemia尽早使用、对病原菌敏感、容易透过血脑屏障、静脉给药23pneumonia, congestive heart failure, pulmonary artery hypertensionFrom birth to 1-year old.4Protein, CHO, Fatosmotic diarrheahepatocellular jaundice, pathologic physical sign of liver and abnormal liverfunction, infancySerum lypaseType IV: Questions and answers (23 points)ANSWERS生理性黄疽:以下全部满足病理性黄疽:下列任一情况:(I)生后 2-5 天出现(I)生后2W(3)总胆红素水平:(3)TB>205umol/L(12.9mg/dl)或每天上5mg/dl(85umol/L)-12mg/dl(205umol/L)升>85umol/l(4)一般情况良好(4)黄疽退而复现(5)DB>34umol/L(2mg/dl)这是PDA发生肺动脉高压时的重要体征。由于动脉导管主动脉端位于弓降部,当发生肺动脉高压时,肺动脉的静脉血通过 PDA直接进入降主动脉,导致下肢青紫较上肢重,左侧肢体青紫较右侧重的现象,即差异性青紫。Initiate age: 4-6 months of age; Stepwise fashion;Sequence: Cereals, Vegetables, Meats, Eggs;Only one new food should be introduced at atime.stage 2 lasts 1-2weeks(1 point)(1) More serious TB toxic symptoms (I point)
Type Ⅱ: True or false ( 1 point for each, total 10 points). True False True False 1 × 6 × 2 × 7 × 3 × 8 × 4 × 9 × 5 × 10 × Type Ⅲ: Fill in blanks ( 0.5 point for each, total 10 points). ANSWERS 1 hypoxia, hypercapnia, toxinemia. 2 尽早使用、对病原菌敏感、容易透过血脑屏障、静脉给药 3 pneumonia, congestive heart failure,pulmonary artery hypertension 4 From birth to 1-year old. 5 Protein, CHO, Fat 6 osmotic diarrhea 7 hepatocellular jaundice, pathologic physical sign of liver and abnormal liver function,infancy. 8 Serum lypase Type Ⅳ: Questions and answers ( 23 points). ANSWERS 1 生理性黄疸:以下全部满足 (1)生后 2-5 天出现 (2)14 天内消失 (3)总胆红素水平: 5mg/dl(85umol/L)-12mg/dl(205umol/L) (4)一般情况良好 病理性黄疸:下列任一情况: (1)生后2W (3)TB>205umol/L(12.9mg/dl)或每天上 升> 85umol/L (4)黄疸退而复现 (5)DB >34umol/L(2mg/dl) 2 这是 PDA 发生肺动脉高压时的重要体征。由于动脉导管主动脉端位于弓降部, 当发生肺动脉高压时,肺动脉的静脉血通过 PDA 直接进入降主动脉,导致下肢 青紫较上肢重,左侧肢体青紫较右侧重的现象,即差异性青紫。 3 Initiate age: 4-6 months of age;Stepwise fashion; Sequence: Cereals, Vegetables, Meats, Eggs; Only one new food should be introduced at a time. 4 stage 2 lasts 1~2weeks(1 point) (1)More serious TB toxic symptoms (1 point)
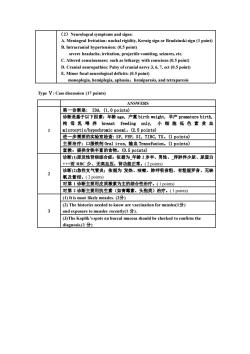
(2)NsigA. Meningeal Irritation: nuchal rigidity, Kernig sign or Brudzinski sign (I point)B. Intracranial hypertension: (0.5 point)severeheadache,irritation,projectilevomiting,seizures,e.C.Altered consciosuch as lethargy with conscious (0.5 point)D.Cranial neeuropathies: Palsy ofcranial nerve3,6,7, ect (0.5 point)E.Minor focal neurological deficits: (0.5 point)monoplegia, hemiplegia,aphasia;hemiparesis, and tetraparesisType V: Case discussion (17 points)ANSWERS第一诊断是:IDA.(1.0points)诊断是基于以下因素:年龄age,产重 birth weight,早产 premature birth,母乳喂养 breastfeeding only,小细胞低色素贫血anemi。(2.5points)cocytic/hypo进一步需要的实验室检查:SF,FEP,SI,TIBC,TS。(1points)主要治疗:口服铁剂 Oral iron,输血 Transfusion。(1 points)宣教:提供含铁丰富的食物。(0.5points)诊断(1)原发性肾病综合症;依据为_年龄2岁半、男性、浮肿伴少尿、尿蛋白而RBC少、无高血压,肾功能正常。(2points诊断(2)急性支气管炎;依据为发热、咳嗽、肺呼吸音粗、有粗湿罗音、无缺氧及紫。(2 points)对第1诊断主要用皮质激素为主的综合性治疗。(1points)对第 2诊断主要用抗生素(如青霉素、头孢类)治疗。(1 points)(1) It is most likely measles. (2分)(2)The histories needed to know arevaccinationformeasles(1分)eto measles recently(1分)ndexposu(3heKoplik'sspot onbuccalmucosa shouldbecheckedtoconfirmthediagnosis.(1分)
(2)Neurologcal symptoms and signs: A. Meningeal Irritation: nuchal rigidity, Kernig sign or Brudzinski sign (1 point) B. Intracranial hypertension: (0.5 point) severe headache, irritation, projectile vomiting, seizures, etc. C. Altered consciousness: such as lethargy with conscious (0.5 point) D. Cranial neuropathies: Palsy of cranial nerve 3, 6, 7, ect (0.5 point) E. Minor focal neurological deficits: (0.5 point) monoplegia, hemiplegia, aphasia;hemiparesis, and tetraparesis Type Ⅴ: Case discussion (17 points) ANSWERS 1 第一诊断是: IDA. (1.0 points) 诊断是基于以下因素:年龄 age, 产重 birth weight, 早产 premature birth, 纯 母 乳 喂 养 breast feeding only, 小 细 胞 低 色 素 贫 血 microcytic/hypochromic anemi。(2.5 points) 进一步需要的实验室检查: SF, FEP, SI, TIBC, TS。(1 points) 主要治疗:口服铁剂 Oral iron, 输血 Transfusion。(1 points) 宣教:提供含铁丰富的食物。(0.5 points) 2 诊断(1)原发性肾病综合症;依据为_年龄 2 岁半、男性、_浮肿伴少尿、尿蛋白 +++而 RBC 少、无高血压,肾功能正常。( 2 points) 诊断(2)急性支气管炎;依据为 发热、咳嗽、肺呼吸音粗、有粗湿罗音、无缺 氧及紫绀。( 2 points) 对第 1 诊断主要用皮质激素为主的综合性治疗。( 1 points) 对第 2 诊断主要用抗生素(如青霉素、头孢类)治疗。( 1 points) 3 (1) It is most likely measles. (2分) (2) The histories needed to know are vaccination for measles(1分) and exposure to measles recently(1 分). (3)The Koplik’s spots on buccal mucosa should be checked to confirm the diagnosis.(1 分)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷B卷(试题).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷C卷(试题).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)02 pneumonia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)01 ABO incompatibility of neonates.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)03 congenital heart disease-TOF.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)07 congenital hypothyroidism.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)05 purulent meningitis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)04 iron deficiency anemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)03 congenital heart disease-VSD.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)08 diarrhea.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)06 anute nepheritis-1.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)06 nephrotic syndrome-2.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)01 questions of children healthcare.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)02 questions of neonatal diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)05 questions of blood disorders.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)04 questions of circulatory system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)03 questions of respiratory diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)06 questions of nervous system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)10 questions of infectious diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)09 questions of endocrine disorders.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷C卷(答案).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷A卷(试题).doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(试卷和答案)双语试卷A卷(答案).doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)07 新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病 Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy(HIE).pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)06 新生儿败血症 Neonatal Septicemia.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)21 Chronic Gastritis in Children.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)20 Toxic Bacillary Dysentery.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)27 Inflammation Causes Cholesterol Redistribution by Diverting Cholesterol from Circulation to Tissue Tompartments.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)26 Rotavirus Infection in Children.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)25 Scarlet Fever.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)24 Mumps(Epidemic parotitis).pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)23 Infantile Hepatitis Syndrome.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)22 Infantale Diarrhea and Fluid Therapy.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)19 Pediatric Tuberculosis.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)18 Varicella.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)17 Measles.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)16 Growth Hormone Deficiency.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)15 Congenital Hypothyroidism.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)14 Immunodeficiency.pptx
- 《儿科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)13 Acute Glomerulonephritis,Nephrotic Syndrome.pptx
