对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第三章 工作分析与设计 The Analysis and Design of Work

Chapter 3 -The Analysis and Design of Work ©2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-1
© 2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-1 Chapter 3 The Analysis and Design of Work

Outline of Chapter 3 I.Opening Vignette:Teams Levi's: A Poor Fit? II.Work-Flow Analysis and Organizational Structure III.Job Analysis IV.Management Skills Builder:On the spot interview V.Job Design ©2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-2
© 2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-2 Outline of Chapter 3 I. Opening Vignette: Teams & Levi’s: A Poor Fit? II .Work-Flow Analysis and Organizational Structure III. Job Analysis IV. Management Skills Builder: On the spot interview V. Job Design

Learning Objectives Analyzing a work-flow process. Understand the importance of job analysis in strategic and human resource management. Choose the right job analysis technique for a variety of human resources activities. Understand the different approaches to job design ©2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-3
© 2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-3 Learning Objectives • Analyzing a work-flow process. • Understand the importance of job analysis in strategic and human resource management. • Choose the right job analysis technique for a variety of human resources activities. • Understand the different approaches to job design

I.Opening Vignette: Teams Levi's:A Poor Fit? 3-4
© 2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-4 I. Opening Vignette: Teams & Levi’s: A Poor Fit?

Teams Levi's:A Poor Fit? Throughout the 1990s an increasing number of organizations moved to team-based organizational structures where work is organized and assigned I to groups rather t than individuals.One of the first companies to start this trend was Chrysler,which used "cross-functional platform teams"to cut production time cycles and improve quality and customer satisfaction. Having members of these units swork together simultaneously rather than sequentially smoothed coordination patterns and spawned creativity. ©2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-5
© 2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-5 Teams & Levi’s: A Poor Fit? Throughout the 1990s an increasing number of organizations moved to team-based organizational structures where work is organized and assigned to groups rather than individuals. One of the first companies to start this trend was Chrysler, which used "cross-functional platform teams" to cut production time cycles and improve quality and customer satisfaction. Having members of these units work together simultaneously rather than sequentially smoothed coordination patterns and spawned creativity

A number of organizations tried to mimic Chrysler's success by creating their own work teams,but the results have not always been so positive. For example,in the mid-1990s,Levi's directed its U.S. plants to abandon their individually structured production processes and replace them with team-oriented work designs.In the old piecework system, employees worked alone, performed a single,specialized task (e.g.,attaching a zipper to a pair of jeans),and were paid to the amount of work produced(eg,zippers attached).In the new system,groups of 10 to 25 workers would share all the tasks that go into sewing together a pair of pants and then be paid according to the total number of trousers completed. ©2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-6
© 2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-6 A number of organizations tried to mimic Chrysler's success by creating their own work teams, but the results have not always been so positive. For example, in the mid-1990s, Levi's directed its U.S. plants to abandon their individually structured production processes and replace them with team-oriented work designs. In the old piecework system, employees worked alone, performed a single, specialized task (e.g., attaching a zipper to a pair of jeans), and were paid to the amount of work produced(eg, zippers attached). In the new system, groups of 10 to 25 workers would share all the tasks that go into sewing together a pair of pants and then be paid according to the total number of trousers completed

By 1998,however,it was clear that these supposed benefits of team-based structures were not going to materialize at Levi's.In fact,if anything,this change in the nature of work had just the opposite effects.Instead of increased worker satisfaction,morale actually went down.The new system led to bitter fights between experienced,skilled workers who were formerly doing well with t the individually based bonus system and slower, inexperienced workers who were holding the team back from its group goals..Efficiency,as measured by the quantity of pants produced per hour worked,dropped to 77 percent of preteam levels,while labor and overhead costs increased by 25 percent. ©2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-7
© 2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-7 By 1998, however, it was clear that these supposed benefits of team-based structures were not going to materialize at Levi's. In fact, if anything, this change in the nature of work had just the opposite effects. Instead of increased worker satisfaction, morale actually went down. The new system led to bitter fights between experienced, skilled workers who were formerly doing well with the individually based bonus system and slower, inexperienced workers who were holding the team back from its group goals.. Efficiency, as measured by the quantity of pants produced per hour worked, dropped to 77 percent of preteam levels, while labor and overhead costs increased by 25 percent

CASE Implications -Designing the work to be performed is one of the first tasks of strategy implementation. How to design the job to make the organization more competitive? ©2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-8
© 2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-8 CASE Implications Designing the work to be performed is one of the first tasks of strategy implementation. How to design the job to make the organization more competitive?

Questions: WHY are Job Analysis and job Design Very important? Without Job Analysis and proper job design,what would happen? ©2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-9
© 2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-9 Questions: WHY are Job Analysis and job Design Very important? Without Job Analysis and proper job design,what would happen?
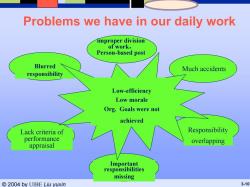
Problems we have in our daily work improper division of work, Person-based post Blurred Much accidents responsibility Low-efficiency Low morale Org.Goals were not achieved Lack criteria of Responsibility performance overlapping appraisal Important responsibilities missing ©2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-10
© 2004 by UIBE Liu yuxin 3-10 Problems we have in our daily work Blurred responsibility Important responsibilities missing Low-efficiency Low morale Org. Goals were not achieved Lack criteria of performance appraisal Much accidents Responsibility overlapping improper division of work, Person-based post
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第二章 战略性人力资源管理 Strategic HR Management.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第一章 人力资源管理——赢得竞争优势.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(作业)Chapter 10 Managing Human Resources Globally.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(作业)Chapter 9 Recognizing Employee Contributions with Pay.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(作业)Chapter 8 Pay Structure Decisions.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(作业)Chapter 7 Training.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(作业)Chapter 6 Appraising and Managing Performance.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(作业)Chapter 5 Personnel Selection and Placement.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(作业)Chapter 4 Human Resource Planning.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(作业)Chapter 3 The Analysis and Design of Work.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(作业)Chapter 2 Strategic Human Resource Management.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(作业)Chapter 1 Human Resource Management:Gaining a Competitive Advantage.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《营销学原理》课程教学资源(教学方案,英文).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《营销学原理》课程教学资源(试题)1997-1998期末考试试卷二(英文,含答案).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《营销学原理》课程教学资源(试题)2001-2002期末考试试卷一(英文,含答案).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《营销学原理》课程教学大纲 Principles of Marketing(英文).pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《国际企业管理 International business management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第五篇 走出去战略 第十章 中国企业跨国经营战略.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《国际企业管理 International business management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第四篇 跨国经营战略篇 第九章 跨国企业的资源寻求战略.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《国际企业管理 International business management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第四篇 跨国经营战略篇 第八章 跨国企业营销战略.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《国际企业管理 International business management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第四篇 跨国经营战略篇 第七章 获得全球竞争优势.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第四章 人力资源规划.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第五章 人员招聘与安置 Personnel Selection & Placement.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第六章 绩效考核 Appraising and Managing Performance.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第七章 员工培训与发展 Training and Developing Employees.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第八章 薪酬方案 Establishing Pay Plans.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第九章 绩效奖励与认可 Recognizing Employee Contributions with Pay.pdf
- 对外经贸大学:《人力资源管理 Human Resource Management》课程教学资源(授课教案)第十章 全球化的人力资源管理 Managing Global Human Resources.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《管理信息系统》课程教学资源(作业)各章习题集.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《管理信息系统》课程教学资源(案例)江铃国际管理信息系统案例分析.pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《管理信息系统》课程教学资源(试题)期末考试试卷(A卷).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《管理信息系统》课程教学资源(试题)期末考试试卷(B卷).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《管理信息系统》课程教学资源(复习要点).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《管理信息系统》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验一 产品销售管理(Access数据库和表的使用).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《管理信息系统》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验一 产品销售管理(查询).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《管理信息系统》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验一 产品销售管理(窗体设计).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《管理信息系统》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验一 产品销售管理(报表).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《管理信息系统》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验二 学生成绩管理(表操作).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《管理信息系统》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验二 学生成绩管理(查询操作).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《管理信息系统》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验二 学生成绩管理(创建报表).pdf
- 对外经济贸易大学:《管理信息系统》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验二 学生成绩管理(窗体的创建与应用).pdf
