南京大学:《大学物理》课程教学资源(PPT讲座)Plamonics and Metamaterials(李涛)

版象 Nanjing University Plasmonics and Metamaterial Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn Nat.Lab.of Solid State Microstructures Department of Materials Science and Engineering Nanjing University Dielectrie Superlattice Laboratory Nat.Lab.Microstructures Dr.Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
Nanjing University Tao Li taoli@ j n u.edu.cn Nat. Lab. of Solid State Microstructures Department of Materials Science and Engineering Nanjing University Nanjing University Dielectric Superlattice Laboratory Nat. Lab. Microstructures Dr. Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn

Nanjing University 2 Outline Concepts Basic principles Surface pPlasmon Metamaterial Summary Dielectric Superlatice Laboratory Nat. Lab. Microstructures Dr. Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
Nanjing University y C t oncep s y Basic principles y Surface Plasmon y Metamaterial y Summary Dielectric Superlattice Laboratory Nat. Lab. Microstructures Dr. Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn

版象 Nanjing University Optical Properties Light in Condensed Matters Condensed Matter Dielectrie Superlattice Laboratory Nat.Lab.Microstructures Dr.Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
Nanjing University Light Dielectric Superlattice Laboratory Nat. Lab. Microstructures Dr. Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
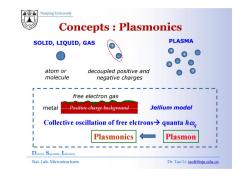
Nanjing University Concepts Plasmonics SOLID,LIQUID,GAS PLASMA atom or decoupled positive and molecule negative charges I free electron gas 1 1 metal Positive charge background Jellium model I I I Collective oscillation of free elctrons>quanta h I 1 Plasmonics Plasmon Dielectric Superlattice Laboratory Nat.Lab.Microstructures Dr.Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
Nanjing University + SOLID, LIQUID, GAS PLASMA - + - + - - + atom or molecule decoupled positive and negative charges + - Positive charge background free electron gas metal Jellium model Collective oscillation of free elctronsÆ quanta hωq Plasmonics Plasmon Dielectric Superlattice Laboratory Nat. Lab. Microstructures Dr. Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn

Nanjing University Concepts Metamaterial METAMATERIAL SOLID,CYSTAL atom artificial atom Notice: >This artificial material (atom)is not exist naturally! “meta'”i迟“beyond'" >The property is with respect to the EM wave, so a key point is the unit cell is sub-wavelength. Light cannot“see”the structure Dielectrie Superlattice Laboratory Nat.Lab.Microstructures Dr.Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
Nanjing University METAMATERIAL SOLID, CYSTAL atom artificial atom Notice: ¾This artificial material (atom) is not exist naturally! “meta” is “beyond” ¾Th t i ith t t th EM The property is with respect to the EM wave, so a key point is the unit cell is sub-wavelength. Light cannot “see” the structure Dielectric Superlattice Laboratory Nat. Lab. Microstructures Dr. Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn Light cannot see the structure

版象 Nanjing University Outline Concepts Basic principles ●Surface Plasmon ●Metamaterial ●Summary Dielectrie Superlattice Laboratory Nat.Lab.Microstructures Dr.Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
Nanjing University y C t oncep s y Basic principles y Surface Plasmon y Metamaterial y Summary Dielectric Superlattice Laboratory Nat. Lab. Microstructures Dr. Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
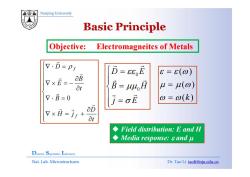
Nanjing University Basic Principle Objective: Electromagneitcs of Metals V.D=p 0=86,E 8=6(0) aB 8t B=44,月 L=I(⊙) 7.B=0 j=cE @=@(k) v×i=j/+ aD 8t Field distribution:E and H Media response:and u Dielectrie Superlattice Laboratory Nat.Lab.Microstructures Dr.Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
Nanjing University Objective: Electromagneitcs of Metals ⎪⎧∇ ⋅ D = f r ρ ⎧D E r r ( ) Objective: Electromagneitcs of Metals ⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨ ∂∂ ∇ × = − ∇ tB ED f r r ρ 00 D E B H εεμμ ⎧ = ⎪⎪⎨ = r r ( ) ( ) ε ε ω μ μ ω == ⎪⎪⎪ ⎪⎨ ∂ ∇ ⋅ = ∂ D B t r r 0 0 j E μμ σ ⎨⎪⎪ = ⎩ r r ( ) ( ) k μ μ ω ω= ⎪⎪⎩ ∂∂ ∇ × = + tD H j f r r Field distribution: E and H Field distribution: E and H Media response: ε and μ Dielectric Superlattice Laboratory Nat. Lab. Microstructures Dr. Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
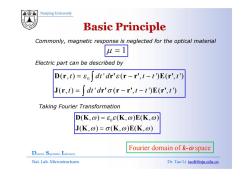
Nanjing University Basic Principle Commonly,magnetic response is neglected for the optical material u=1 Electric part can be described by D(r,t)=8o[dt'dr's(r-r',t-1)E(r',t) J(r,t)=[dt'dr'a(r-r',t-t')E(r',t') Taking Fourier Transformation D(K,0)=6(K,o)E(K,o) J(K,0)=σ(K,⊙)E(K,o) Fourier domain of k-@space Dielectrie Superlattice Laboratory Nat.Lab.Microstructures Dr.Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
Nanjing University Commonly, magnetic response is neglected for the optical material μ = 1 Electric part can be described by 0 ( , ) ' ( , ') ( , ') ( ) ' ( ') ( ') t dt d t t t d d = −− ε ε ∫ ∫ D r r' r r' E r' J ' ' E' ( , t) '( = dt d σ − − , tt t ') ( , ') ∫ J r r' r r' E r' Taking Fourier Transformation 0 ( , ) ( , )( , ) ( ) ( )( ) ω εε ω ω ωσ ω ω = = DK K EK JK K EK JK K EK ( ,ωσ ω ω ) ( = , ) ( , ) Fourier domain of k-ω space Dielectric Superlattice Laboratory Nat. Lab. Microstructures Dr. Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn Fourier domain of k-ω space
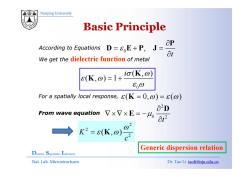
Nanjing University Basic Principle P According to Equations D=E+P,J= Ot We get the dielectric function of metal 8(K.@)-1+io(K.@) 8o0 For a spatially local response,(K=0,)=( From wave equation VxXE= o"D K-c(K) Generic dispersion relation Dielectric Superlattice Laboratory Nat.Lab.Microstructures Dr.Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
Nanjing University According to Equations ε ∂ =+ = P According to Equations D EP J We get the dielectric function of metal 0 , t =+ = ε ∂ D EP J 0 (,) (,)1 iσ ω ε ω ε ω = + K K 0 For a spatially local response, ε ( 0, ) ( ) K = = ω εω 2 ∂ D From wave equation 0 2 t μ ∂ ∇ ×∇× = − ∂ D E 2 2 ω 2 K (,) c ω = ε K ω Generic dispersion relation Dielectric Superlattice Laboratory Nat. Lab. Microstructures Dr. Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn Generic dispersion relation

Nanjing University Basic Principle Dielectric function of free electron gas We have dynamic equation of an electron of plasma sea in an external E field mx+myx=-eE Plasma frequency e x(t)= E() 2 Ne2 m(@2+iyo) (o)=1- +iyo Eomo ne2 P=- E m(o2+iyo) (o)=1- D=61- )E If neglecting the loss @-+iy@ Drude Model o2=o6+K2c2 Dispersion of volume plasmons Dielectric Superlattice Laboratory Nat.Lab.Microstructures Dr.Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
Nanjing University Dielectric function of free electron gas W h d i ti f l t f l i mm e && & x xE + γ = − We have dynamic equation of an electron of plasma sea in an external E field Plasma frequency 2 2 () () ( ) e t t m i ω γω = + x E 2 2 () 1 Pi ω ε ω ω γω = − + 2 2 0 0 p N em ω ε = 2 2 2 ( ) ne m i ω γω = − + P E 2 2 () 1 P ω γωi ω ε ω ω + = − 2 0 2 (1 ) Pi ω ε ω γω = − + D E Drude Model ω If neglecting the loss 2 2 22 ω ω= +P K c Dispersion of volume plasmons Dielectric Superlattice Laboratory Nat. Lab. Microstructures Dr. Tao Li taoli@nju.edu.cn
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 电磁波的传播 Propagation of Electromagnetic Wave.pdf
- 南京大学:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 狭义相对论 Special Theory of Relativity.pdf
- 南京大学:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 电磁波的辐射 Electromagnetic Wave Radiation.pdf
- 南京大学:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 静磁场 Magnetostatic field.pdf
- 南京大学:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 静电场 Electrostatic field.pdf
- 南京大学:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 电磁现象的普遍规律 Universal Law of Electromagnetic Phenomenon.pdf
- 南京大学:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)预备知识——矢量场论复习(李涛)Preliminary Knowledge - Revise in the Vector Field Theory.pdf
- 南京大学:《电动力学 Electrodynamics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)引言 Introduction.pdf
- 惠州学院:《大学物理》课程教学资源(电子教案)第44讲 衍射光栅、X射线衍射.pdf
- 惠州学院:《大学物理》课程教学资源(电子教案)大学物理B(主讲:叶凡).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高等电磁场理论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 球坐标系中的场与波 Spherical Wave Functions.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高等电磁场理论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 柱坐标系中的场与波 Cylindrical Wave Functions.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高等电磁场理论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 直角坐标系中的场与波(标量波函数理论 Plane Wave Functions).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高等电磁场理论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 电磁定理和原理 Electromagnetic Theorems and Principles.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高等电磁场理论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 平面波简述 Introduction to Plane Waves.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高等电磁场理论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 基本电磁理论 Basic Electromagnetic Theory.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高等电磁场理论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)绪论 Advanced Electromagnetic Field Theory.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高等电磁场理论》课程教学资源(教学大纲,负责人:熊江、梁锋).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《铁磁学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 金属磁性的能带模型理论.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《铁磁学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 自发磁化的交换作用理论.pdf
- 南京大学:《大学物理》课程教学资源(PPT讲座)等离激元光子学 Part A(背景与基本原理).pdf
- 南京大学:《大学物理》课程教学资源(PPT讲座)等离激元光子学 Part B(物理效应和应用).pdf
- 南京大学:《大学物理》课程教学资源(PPT讲座)Beam, beam, beam——无衍射光束的产生与调控.pdf
- 南京大学:《光学》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)量子电子学与光学工程简介(光电信息工程专业简介).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,有限差分法)第1章 绪论(主讲:王秉中).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,有限差分法)第2章 有限差分法 2.1 差分运算的基本概念 2.2 边值问题(静态场)的差分计算.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,有限差分法)第2章 有限差分法 2.3 特征值问题(时谐场)的差分计算.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,有限差分法)第3章 频域有限差分法 3.1 FDFD基本原理 3.2 吸收边界条件 3.3 总场/散射场体系和近远场变换 3.4 数值算例(1).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,有限差分法)第3章 频域有限差分法 3.4 数值算例(2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,有限差分法)第4章 时域有限差分法 I 4.1 FDTD基本原理 4.2 解的稳定性条件 4.3 非均匀网格 4.4 共形网格 4.5 半解析数值模型 4.6 良导体中的差分格式.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,有限差分法)第5章 时域有限差分法 II 5.1 Beyliss-Turkel吸收边界条件 5.2 Engquist-Majda吸收边界条件 5.3 廖氏吸收边界条件 5.4 Berenger完全匹配层 5.5 Gedney完全匹配层.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,有限差分法)第6章 时域有限差分法 III 6.1 激励源技术 6.2 集总参数电路元件的模拟 6.3 数字信号处理技术 6.4 应用举例(I).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,有限差分法)第6章 时域有限差分法 III 6.4 应用举例(II).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,有限差分法)第7章 无条件稳定的FDTD方法 7.1 ADI-FDTD法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,矩量法)第8章 矩量法基本原理 8.1 矩量法原理.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,矩量法)第8章 矩量法基本原理 8.2 静电场中的矩量法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,矩量法)第9章 空域差分-时域矩量法 9.1 空域差分-时域矩量法 9.2 Laguerre-FDTD法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,矩量法)第10章 积分方程 10.1 积分方程和格林函数.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,矩量法)第10章 积分方程 10.2 磁矢量位和远场近似 10.3 表面积分方程.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《计算电磁学 Computational Electronmagentics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,矩量法)第10章 积分方程 10.4 细导线的线积分方程、第11章 矩量法应用 11.1 一维线天线的辐射(1/2).pdf
