南京大学:《高级算法 Advanced Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)08 Greedy and Local Search

Advanced Algorithms Greedy and Local Search 尹一通Nanjing University,2022Fall
尹⼀通 Nanjing University, 2022 Fall Advanced Algorithms Greedy and Local Search
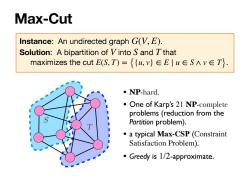
Max-Cut Instance:An undirected graph G(V,E). Solution:A bipartition of V into S and Ithat maximizes the cut E(S,T)={w,v}∈E|u∈S∧v∈T} .NP-hard. One of Karp's 21 NP-complete problems(reduction from the Partition problem). .a typical Max-CSP (Constraint Satisfaction Problem). Greedy is 1/2-approximate
Max-Cut Instance: An undirected graph . Solution: A bipartition of into and that maximizes the cut . G(V, E) V S T E(S, T) = {{u, v} ∈ E ∣ u ∈ S ∧ v ∈ T} T S • NP-hard. • One of Karp’s 21 NP-complete problems (reduction from the Partition problem). • a typical Max-CSP (Constraint Satisfaction Problem). • Greedy is 1/2-approximate
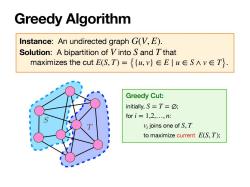
Greedy Algorithm Instance:An undirected graph G(V,E). Solution:A bipartition of Vinto S and Tthat maximizes the cut E(S,T)={w,v}∈E|w∈S∧v∈T}. Greedy Cut: initially,S=T=O; fori=1,2,.,n: Vi joins one of S,T to maximize current E(S,T);
Greedy Algorithm Instance: An undirected graph . Solution: A bipartition of into and that maximizes the cut . G(V, E) V S T E(S, T) = {{u, v} ∈ E ∣ u ∈ S ∧ v ∈ T} T S Greedy Cut: initially, ; for : joins one of to maximize current ; S = T = ∅ i = 1,2,…, n vi S, T E(S, T)
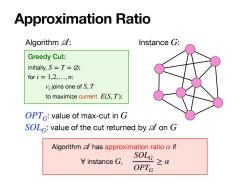
Approximation Ratio Algorithm & Instance G: Greedy Cut: initially,S=T=O; fori=1,2,.,n: Vi joins one of S,T to maximize current E(S,T); OPTG:value of max-cut in G SOLG:value of the cut returned by on G Algorithm has approximation ratio a if SOLG V instance G, ≥ OPTG
Approximation Ratio Greedy Cut: initially, ; for : joins one of to maximize current ; S = T = ∅ i = 1,2,…, n vi S, T E(S, T) Algorithm 𝒜: Instance G: : value of max-cut in : value of the cut returned by on OPTG G SOLG 𝒜 G Algorithm has approximation ratio if instance , 𝒜 α ∀ G SOLG OPTG ≥ α
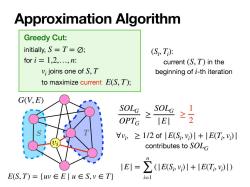
Approximation Algorithm Greedy Cut: initially,S=T=; (S,T: fori=1,2,.,n: current (S,T)in the Vi joins one of S,T beginning of i-th iteration to maximize current E(S,T); G(V,E) SOLG SOLG 1 OPTG ≥ |E1 v≥1/2of|E(S,)川+|E(T)l contributes to SOLG IEI=∑(IES,l+IET,I) E(S,T)={uv∈E|u∈S,v∈T} i=1
Approximation Algorithm E(S, T) = {uv ∈ E ∣ u ∈ S, v ∈ T} Greedy Cut: initially, ; for : joins one of to maximize current ; S = T = ∅ i = 1,2,…, n vi S, T E(S, T) S T vi G(V, E) SOLG OPTG ≥ SOLG |E| , of contributes to ∀vi ≥ 1/2 |E(Si , vi )| + |E(Ti , vi )| SOLG ≥ 1 2 |E| = n ∑ i=1 (|E(Si , vi )| + |E(Ti , vi )|) : current in the beginning of -th iteration (Si , Ti ) (S, T) i
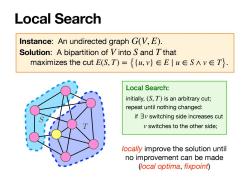
Local Search Instance:An undirected graph G(V,E). Solution:A bipartition of V into S and T that maximizes the cut E(S,T)={w,v}∈Eluw∈S∧v∈T}. Local Search: initially,(S,T)is an arbitrary cut; repeat until nothing changed: if v switching side increases cut v switches to the other side; locally improve the solution until no improvement can be made (local optima,fixpoint)
Local Search Instance: An undirected graph . Solution: A bipartition of into and that maximizes the cut . G(V, E) V S T E(S, T) = {{u, v} ∈ E ∣ u ∈ S ∧ v ∈ T} Local Search: initially, is an arbitrary cut; repeat until nothing changed: if switching side increases cut switches to the other side; (S, T) ∃v v locally improve the solution until no improvement can be made (local optima, fixpoint) T S
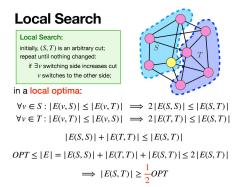
Local Search Local Search: initially,(S,T)is an arbitrary cut; repeat until nothing changed: ifv switching side increases cut v switches to the other side; in a local optima: v∈S:|E(y,S)川≤|E(y,T)川→21E(S,S)川≤|E(S,T)川 v∈T:|E(y,T)川≤IE(y,S)l→2|E(T,T)川≤IE(S,T)l E(S,S)+E(T,T)<E(S,T) OPT≤IE1=IE(S,S)川+IE(T,T)川+IE(S,T)I≤2|E(S,T)I →IE(S,T)I≥二OPT
Local Search Local Search: initially, is an arbitrary cut; repeat until nothing changed: if switching side increases cut switches to the other side; (S, T) ∃v v in a local optima: ∀v ∈ S : |E(v, S)| ≤ |E(v, T)| ⟹ 2|E(S, S)| ≤ |E(S, T)| ∀v ∈ T : |E(v, T)| ≤ |E(v, S)| ⟹ 2|E(T, T)| ≤ |E(S, T)| |E(S, S)| + |E(T, T)| ≤ |E(S, T)| OPT ≤ |E| = |E(S, S)| + |E(T, T)| + |E(S, T)| ⟹ |E(S, T)| ≥ 1 2 OPT ≤ 2|E(S, T)| T S

Scheduling
Scheduling
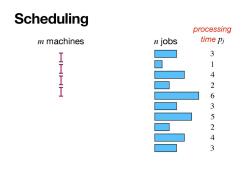
Scheduling processing m machines n jobs time pj 3 HH 9 1 4 HH 2 6 3 5 2 4 3
Scheduling m machines n jobs processing time pj 3 1 4 2 6 3 5 2 4 3
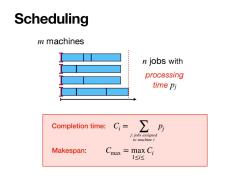
Scheduling m machines n jobs with processing time Pj Completion time: C=∑ j:jobs assigned to machine i Makespan: max ma <Ci 1≤i达
Scheduling n jobs m machines processing time pj with Completion time: Makespan: Ci = j: job ∑ s assigned to machine i pj Cmax = max 1≤i≤ Ci
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《高级算法 Advanced Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)07 Lovász Local Lemma.pdf
- 南京大学:《高级算法 Advanced Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)06 Dimension Reduction.pdf
- 南京大学:《高级算法 Advanced Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)05 Concentration of measure.pdf
- 南京大学:《高级算法 Advanced Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 Hashing and Sketching.pdf
- 南京大学:《高级算法 Advanced Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)03 Balls into Bins.pdf
- 南京大学:《高级算法 Advanced Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)02 Fingerprinting.pdf
- 南京大学:《高级算法 Advanced Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)01 Introduction - Min-Cut and Max-Cut(尹⼀通).pdf
- 南京大学:《高级算法 Advanced Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)03 Balls-into-Bins Model and Chernoff Bounds.pptx
- 《量子计算》课程教学资源(阅读文献)Lecture Notes on Quantum Algorithms(Andrew M. Childs).pdf
- 《量子计算》课程教学资源(阅读文献)Quantum Computation and Quantum Information(10th Anniversary Edition,Michael A. Nielsen & Isaac L. Chuang).pdf
- 《理论计算机科学》课程教学资源(阅读文献)Computational Complexity - A Modern Approach.pdf
- 《理论计算机科学》课程教学资源(阅读文献)Approximation via Correlation Decay when Strong Spatial Mixing Fails(HIS).pdf
- 《理论计算机科学》课程教学资源(阅读文献)Galton–Watson process - Branching.pdf
- 《理论计算机科学》课程教学资源(阅读文献)Analysis Of Boolean Functions(Ryan O’Donnell).pdf
- 南京大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 14 假设检验.pptx
- 南京大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 13 区间估计(参数估计).pptx
- 南京大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 12 点估计(参数估计).pptx
- 南京大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 11 统计量与抽样分布.pptx
- 南京大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 10 极限理论.pptx
- 南京大学:《概率论与数理统计 Probability and Statistics》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 09 典型二维连续型随机变量、相关系数.pptx
- 南京大学:《高级算法 Advanced Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)09 Rounding Dynamic Programs.pdf
- 南京大学:《高级算法 Advanced Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)10 Rounding Linear Programs.pdf
- 南京大学:《高级算法 Advanced Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)11 The Primal-Dual Schema.pdf
- 南京大学:《高级算法 Advanced Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)12 SDP-Based Algorithms.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(教学大纲,杨春).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)01 图论简介、图的定义及其相关概念、图的同构.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)02 完全图、偶图与补图、顶点的度与图的度序列.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)03 子图的相关概念、几种典型的图运算、路与连通性.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 图的代数表示、最短路算法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)05 邻接谱、邻接代数与图空间、托兰定理.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)06 树的概念与应用、树的性质、树的中心与形心.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)07 生成树的概念与性质、生成树的计数、回路系统简介.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)08 克鲁斯克尔算法、管梅谷的破圈法、Prim算法、根树简介.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)09 图的连通性(割边、割点和块).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)10 网络的容错性参数.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)11 图的宽直径简介.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)12 欧拉图与哈密尔顿图(欧拉图与中国邮路问题).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)13 哈密尔顿图.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)14 度极大非哈密尔顿图与TSP问题.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《图论及其应用 Graph Theory and its Applications》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)15 超哈密尔顿图与超可迹图问题.pdf
