安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell junction and cell adhesion
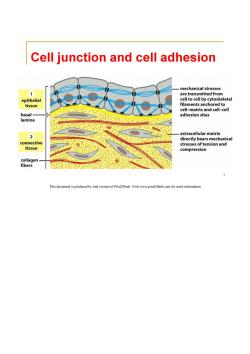
Cell junction and cell adhesion mechanical stresses 1 are transmitted from epithelial cell to cell by cytoskeletal tissue filaments anchored to cell-matrix and cell-cell basal- adhesion sites lamina extracellular matrix directly bears mechanical connective stresses of tension and tissue compression collagen fibers 1 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
Contents Cell junction and cell adhesion Cell junction 2 Cell adhesion molecules 2 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
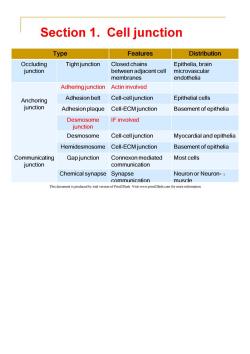
Section 1.Cell junction Type Features Distribution Occluding Tight junction Closed chains Epithelia,brain junction between adjacent cell microvascular membranes endothelia Adhering junction Actin involved Anchoring Adhesion belt Cell-cell junction Epithelial cells junction Adhesion plaque Cell-ECM junction Basement of epithelia Desmosome IF involved junction Desmosome Cell-cell junction Myocardial and epithelia Hemidesmosome Cell-ECM junction Basement of epithelia Communicating Gap junction Connexon mediated Most cells junction communication Chemical synapse Synapse Neuron or Neuron-3 communication muscle This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
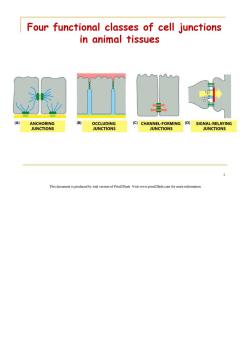
Four functional classes of cell junctions in animal tissues (A ANCHORING (B) OCCLUDING (C)CHANNEL-FORMING (D) SIGNAL-RELAYING JUNCTIONS JUNCTIONS JUNCTIONS JUNCTIONS This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
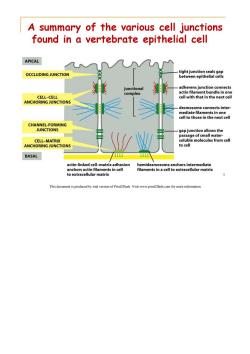
A summary of the various cell junctions found in a vertebrate epithelial cell APICAL OCCLUDING JUNCTION tight junction seals gap between epithelial cells junctional adherens junction connects complex actin filament bundle in one CELL-CELL cell with that in the next cell ANCHORING JUNCTIONS desmosome connects inter- mediate filaments in one cell to those in the next cell CHANNEL-FORMING JUNCTIONS gap junction allows the passage of small water- CELL-MATRIX soluble molecules from cell ANCHORING JUNCTIONS to cell BASAL actin-linked cell-matrix adhesion hemidesmosome anchors intermediate anchors actin filaments in cell filaments in a cell to extracellular matrix to extracellular matrix 5 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
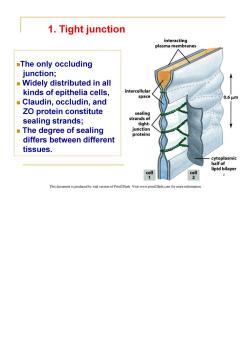
1.Tight junction interacting plasma membranes The only occluding junction; Widely distributed in all kinds of epithelia cells, intercellular space 0.6um Claudin,occludin,and ZO protein constitute sealing sealing strands; strands of tight- The degree of sealing junction proteins differs between different tissues. cytoplasmic half of lipid bilayer cell cell 6 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
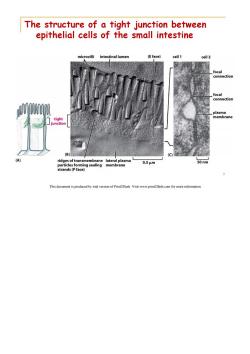
The structure of a tight junction between epithelial cells of the small intestine microvilli intestinal lumen (E face) cell 1 cell 2 focal connection focal connection plasma tight membrane junction (B) (A) ridges of transmembrane lateral plasma 0.5um 50nm particles forming sealing membrane strands(P face) 7 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more informatior

A model of a tight junction cell 1 UF UU cell 2 claudin occludin tight-junction proteins 8 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Function of tight junction Seal the gap between epithelia,isolate the tissue and outside,prevent material transition,ensure the environmental stability within the organization. The barrier to prevent lateral diffusion of membrane lipids and protein,keep the polarity of epithelial cells. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
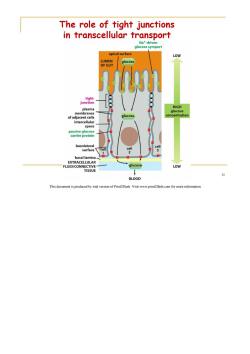
The role of tight junctions in transcellular transport Na+-driven glucose symport apical surface LOW LUMEN glucose OF GUT tight junction HIGH plasma glucose membranes of adjacent cells glucose concentration intercellular space passive glucose carrier protein basolateral cell surface cell cell basal lamina EXTRACELLULAR FLUID/CONNECTIVE glucose LOW TISSUE BLOOD This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Nucleus.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cytoskeleton.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Endomembrane system and vesicle transport.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Membrane transport.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell membrane.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)The unity and diversity of cells.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Introduction.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)微丝的形态结构观察.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)细胞内碱性蛋白的显示.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)细胞器的分级分离.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)鸡血细胞的融合.pdf
- 安微医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(实践指导)形态学实验(切片).pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(习题指导,打印版)各章习题集(含参考答案,共二十五章).pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)绪论、人胚发生和早期发育、颜面和四肢的发生、消化系统和呼吸系统的发生、泌尿系统和生殖系统的发生、心血管系统发生.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)消化管、消化腺、呼吸系统、泌尿系统、女性生殖系统、男性生殖系统.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)眼和耳、神经系统、免疫系统、循环系统、内分泌系统、皮肤.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)绪论、上皮组织、结缔组织、血液、淋巴、血细胞发生、软骨与骨、肌组织、神经组织.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(教学大纲,打印版).pdf
- 川北医学院:《医学微生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)颈动脉窦和主动脉弓压力感受性反射 Carotid sinus and aortic arch Baroreceptor Reflex.pdf
- 川北医学院:《医学微生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一篇 细菌学 第一章 细菌的形态与结构 Morphology and Structure of Bacteria.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell signaling.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Extracellular matrix.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell division and cell cycle.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Programmed cell death and cell senescence.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)01-Introduction to medical genetics.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)02-The Human Genome and the Chromosomal Basis of Heredity.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)05-principles of clinical cytogenetics.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)06-clinical cytogenetics 01 disorders of the autosomes and the sex chromosomes.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)06-clinical cytogenetics 02 disorders of the autosomes and the sex chromosomes.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)08-Genetics of Common Disorders with Complex Inheritance.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)07-patterns of single-gene inheritance.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)09 Genetic Variation in Individuals and Population.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第一章 绪论(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第三章 外源化学物在体内的生物转运与生物转化(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第二章_毒理学基本概念(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第五章 毒作用影响因素(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第六章 外源化学物的一般毒性作用(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第七章 外源化学物致突变作用(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第九章 发育毒性与致畸作用(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第八章_外源化学物致癌作用(含答案).doc
