安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Membrane transport

4-2 Membrane Transport Outline Principles of membrane transport; Passive transport and active transport; Two main classes of membrane transport proteins:carriers and channels: The ion transport systems; Endocytosis and phagocytosis:cellular uptake of macromolecules and particles. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Principles of membrane transport 1.The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier.It allows for separation and exchange of materials across the plasma membrane. 2.The protein-free lipid bilayers are highly impermeable to ions. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
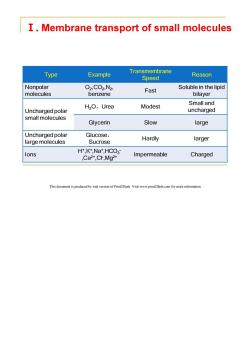
I.Membrane transport of small molecules Type Example Transmembrane Speed Reason Nonpolar O2,C02,N2, Fast Soluble in the lipid molecules benzene bilayer Small and H2O,Urea Modest Uncharged polar uncharged small molecules Glycerin Slow large Uncharged polar Glucose, large molecules Sucrose Hardly larger H+,K+,Na*,HCO3 lons Ca2+,CF,Mg2+ Impermeable Charged This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
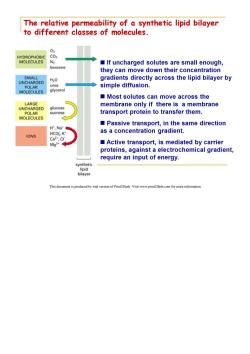
The relative permeability of a synthetic lipid bilayer to different classes of molecules. 03 HYDROPHOBIC CO2 MOLECULES N2 If uncharged solutes are small enough, benzene they can move down their concentration SMALL gradients directly across the lipid bilayer by UNCHARGED H2O POLAR urea simple diffusion. MOLECULES glycerol Most solutes can move across the LARGE glucose membrane only if there is a membrane UNCHARGED POLAR sucrose transport protein to transfer them. MOLECULES Passive transport,in the same direction H',Na" HCO K' as a concentration gradient. IONS Ca2,CI Mg2+ Active transport,is mediated by carrier proteins,against a electrochemical gradient, require an input of energy. synthetic lipid bilayer This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

1.Simple diffusion (passive diffusion) 简单扩散(被动扩散) The concentration differs between both sides of membrane; Low molecular weight,fat-soluble; Does not require membrane transport proteins. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
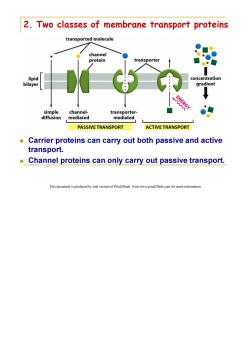
2.Two classes of membrane transport proteins transported molecule channel protein transporter lipid concentration bilayer gradient simple channel- transporter- diffusion mediated mediated PASSIVE TRANSPORT ACTIVE TRANSPORT Carrier proteins can carry out both passive and active transport. Channel proteins can only carry out passive transport. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
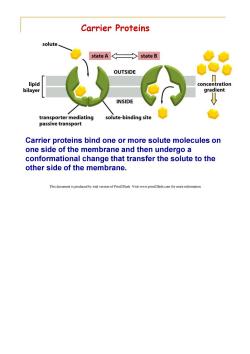
Carrier Proteins solute stateA state B OUTSIDE lipid concentration bilayer gradient INSIDE transporter mediating solute-binding site passive transport Carrier proteins bind one or more solute molecules on one side of the membrane and then undergo a conformational change that transfer the solute to the other side of the membrane. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Carrier Proteins Carrier protein-mediated: Facilitated diffusion: 1)Bind with solute specifically and change the conformation; 2)Diffusion rate is influenced by the concentration gradient and the number of carrier protein; 3)Downhill,does not need ATP. Active transport: 1)Uphill,need ATP; 2)The carrier has the specificity and variability. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
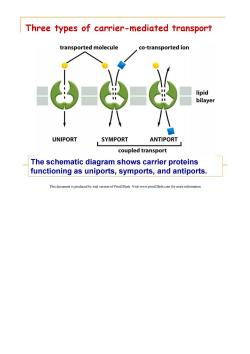
Three types of carrier-mediated transport transported molecule co-transported ion lipid bilayer UNIPORT SYMPORT ANTIPORT coupled transport The schematic diagram shows carrier proteins functioning as uniports,symports,and antiports. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
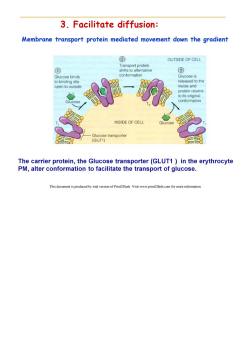
3.Facilitate diffusion: Membrane transport protein mediated movement down the gradient ② OUTSIDE OF CELL Transport protein ① shifts to altemative ③ Glucose binds conformation Glucose is to binding site released to the open to outside inside and protein returns to its original Glucose conformation INSIDE OF CELL Glucose Glucose transporter (GluT1) The carrier protein,the Glucose transporter(GLUT1 )in the erythrocyte PM,alter conformation to facilitate the transport of glucose. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell membrane.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)The unity and diversity of cells.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Introduction.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)微丝的形态结构观察.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)细胞内碱性蛋白的显示.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)细胞器的分级分离.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)鸡血细胞的融合.pdf
- 安微医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(实践指导)形态学实验(切片).pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(习题指导,打印版)各章习题集(含参考答案,共二十五章).pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)绪论、人胚发生和早期发育、颜面和四肢的发生、消化系统和呼吸系统的发生、泌尿系统和生殖系统的发生、心血管系统发生.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)消化管、消化腺、呼吸系统、泌尿系统、女性生殖系统、男性生殖系统.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)眼和耳、神经系统、免疫系统、循环系统、内分泌系统、皮肤.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)绪论、上皮组织、结缔组织、血液、淋巴、血细胞发生、软骨与骨、肌组织、神经组织.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(教学大纲,打印版).pdf
- 川北医学院:《医学微生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)颈动脉窦和主动脉弓压力感受性反射 Carotid sinus and aortic arch Baroreceptor Reflex.pdf
- 川北医学院:《医学微生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一篇 细菌学 第一章 细菌的形态与结构 Morphology and Structure of Bacteria.pdf
- 遵义医科大学第一临床学院:《核医学 Nuclear Medicine》课程教学资源(教学大纲)实验教学大纲(影像).rtf
- 遵义医科大学第一临床学院:《核医学 Nuclear Medicine》课程教学资源(教学大纲)实验教学大纲(影像技术).rtf
- 遵义医科大学第一临床学院:《核医学 Nuclear Medicine》课程教学资源(教学大纲)理论课教学大纲(影像技术).doc
- 遵义医科大学第一临床学院:《核医学 Nuclear Medicine》课程教学资源(教学大纲)理论课教学大纲(影像).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Endomembrane system and vesicle transport.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cytoskeleton.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Nucleus.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell junction and cell adhesion.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell signaling.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Extracellular matrix.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell division and cell cycle.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Programmed cell death and cell senescence.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)01-Introduction to medical genetics.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)02-The Human Genome and the Chromosomal Basis of Heredity.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)05-principles of clinical cytogenetics.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)06-clinical cytogenetics 01 disorders of the autosomes and the sex chromosomes.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)06-clinical cytogenetics 02 disorders of the autosomes and the sex chromosomes.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)08-Genetics of Common Disorders with Complex Inheritance.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)07-patterns of single-gene inheritance.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)09 Genetic Variation in Individuals and Population.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第一章 绪论(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第三章 外源化学物在体内的生物转运与生物转化(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第二章_毒理学基本概念(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第五章 毒作用影响因素(含答案).doc
