安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cytoskeleton
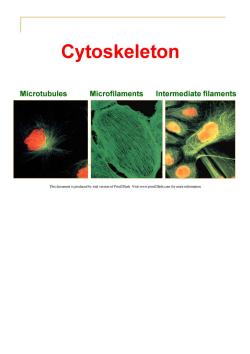
Cytoskeleton Microtubules Microfilaments Intermediate filaments This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Concept of Cytoskeleton (Narrow sense) The cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments in eukaryotic cells.It provide structural integrity dynamics for cells; helps to move organelles and materials throughout cell;helps to move chromosomes during cell division. There are 3 basic components of the cytoskeleton: Microtubules(MT)(微管); Microfilaments(MF)(微丝); Intermediate filaments(lF)(中间纤维). This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
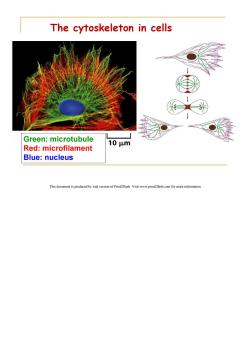
The cytoskeleton in cells Green:microtubule 10 um Red:microfilament Blue:nucleus This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
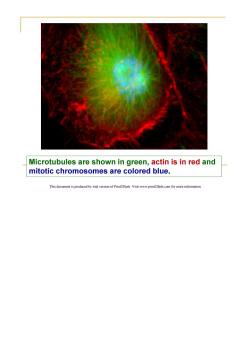
Microtubules are shown in green,actin is in red and mitotic chromosomes are colored blue. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more informatior
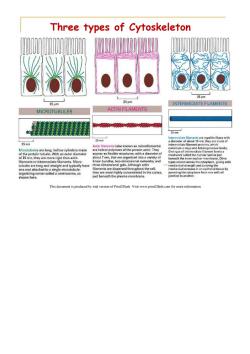
Three types of Cytoskeleton 254m 254m 25m INTERMEDIATE FILAMENTS MICROTUBULES ACTIN FILAMENTS P您p0n般畅 25m Intermediate lilaments are ropelike fibers with 25 nm a diameter of about 10 nm;they are made of 25 nm Actin filamants (also known as microfilaments) intermediate filament proteins,which Microtubules are long,hollow cylinders made are helical polymers of the protein actin.They constitute a large and heterogeneous family of the protein tubulin.With an outer diameter appear as flexible structures,with a diameter of One type of intermediate filament forms a meshwork called the nuclear lamina just of 25 nm,they are more rigid than actin about 7 nm,that are organized into a variety of beneath the inner nuclear mombrane.Other filaments or intermediate filaments.Micro- linear bundles,two-dimensional networks,and types extend across the cytoplasm,giving cells tubules are long and straight and typically have three-dimensional gels.Although actin mechanical strength and carrying the one end attached to a single microtubule- filaments are dispersed throughout the cell, mechanical stresses in an epithelial tissue by organizing center called a centrosome,as they are most highly concentrated in the cortex, spanning the cytoplasm from one cell-cell shown here. iust beneath the plasma membrane. junction to another. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
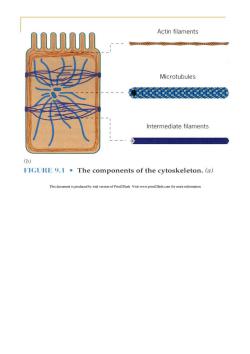
Actin filaments M 092o95029925P Microtubules Intermediate filaments (b) FIGURE 9.1 The components of the cytoskeleton.(a) This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
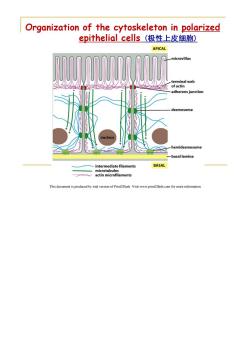
Organization of the cytoskeleton in polarized epithelial cells(极性上皮细胞) APICAL microvillus terminal web of actin adherens junction desmosome nucleus hemidesmosome basal lamina intermediate filaments BASAL microtubules actin microfilaments This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
Section 1.Microtubule(MT) (微管) Interphase This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Microtubules Hollow cylindrical structure composed of microtubule proteins and microtubule associated proteins. Presented in cytosol. a Control of the membranous organelle positioning and intracellular material transport; take part in the assembly of flagella(鞭毛), cilia(纤毛),centrosomes(中心体),spindle(纺锤体); regulate cell motility,cell division and cell morphology. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.printflash.com for more information
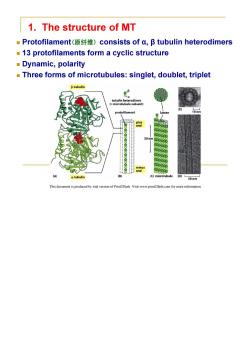
1.The structure of MT Protofilament(原纤维)consists of a,阝tubulin heterodimers 13 protofilaments form a cyclic structure Dynamic,polarity Three forms of microtubules:singlet,doublet,triplet B-tubulin g。 tubulin heterodimer (=microtubule subunit) protofilament 10 nm plus end 50nm minus end (A) a-tubulin (B) (C)microtubule 50nm This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Endomembrane system and vesicle transport.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Membrane transport.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell membrane.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)The unity and diversity of cells.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Introduction.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)微丝的形态结构观察.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)细胞内碱性蛋白的显示.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)细胞器的分级分离.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)鸡血细胞的融合.pdf
- 安微医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(实践指导)形态学实验(切片).pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(习题指导,打印版)各章习题集(含参考答案,共二十五章).pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)绪论、人胚发生和早期发育、颜面和四肢的发生、消化系统和呼吸系统的发生、泌尿系统和生殖系统的发生、心血管系统发生.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)消化管、消化腺、呼吸系统、泌尿系统、女性生殖系统、男性生殖系统.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)眼和耳、神经系统、免疫系统、循环系统、内分泌系统、皮肤.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)绪论、上皮组织、结缔组织、血液、淋巴、血细胞发生、软骨与骨、肌组织、神经组织.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(教学大纲,打印版).pdf
- 川北医学院:《医学微生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)颈动脉窦和主动脉弓压力感受性反射 Carotid sinus and aortic arch Baroreceptor Reflex.pdf
- 川北医学院:《医学微生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一篇 细菌学 第一章 细菌的形态与结构 Morphology and Structure of Bacteria.pdf
- 遵义医科大学第一临床学院:《核医学 Nuclear Medicine》课程教学资源(教学大纲)实验教学大纲(影像).rtf
- 遵义医科大学第一临床学院:《核医学 Nuclear Medicine》课程教学资源(教学大纲)实验教学大纲(影像技术).rtf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Nucleus.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell junction and cell adhesion.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell signaling.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Extracellular matrix.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell division and cell cycle.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Programmed cell death and cell senescence.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)01-Introduction to medical genetics.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)02-The Human Genome and the Chromosomal Basis of Heredity.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)05-principles of clinical cytogenetics.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)06-clinical cytogenetics 01 disorders of the autosomes and the sex chromosomes.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)06-clinical cytogenetics 02 disorders of the autosomes and the sex chromosomes.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)08-Genetics of Common Disorders with Complex Inheritance.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)07-patterns of single-gene inheritance.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)09 Genetic Variation in Individuals and Population.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第一章 绪论(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第三章 外源化学物在体内的生物转运与生物转化(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第二章_毒理学基本概念(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第五章 毒作用影响因素(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第六章 外源化学物的一般毒性作用(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第七章 外源化学物致突变作用(含答案).doc
