安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Extracellular matrix
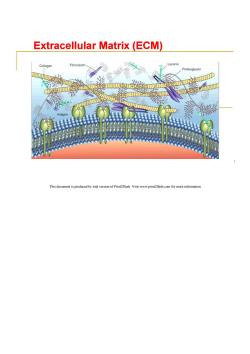
Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Collagen Fibronectin Laminin Proteoglycan D 6d86的 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

ECM Concept:An orderly network outside cells,consisting of secreted protein and polysaccharide by cells. Function:Adhesion,support,regulate the microenvironment of cells,signaling transition,cell proliferation,differentiation, survival,and death. Types:Glycosaminoglycan proteoglycans,collagen elastin, fibronectin laminin,and the plant cell wall. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Contents Extracellular cell matrix 1 Components of ECM Basal lamina 3 Interaction between ECM and cells This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Components of ECM ECM Structure Gel-like matrix Fiber network Molecules GAG PG Collagen elastin fibronectin laminin This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
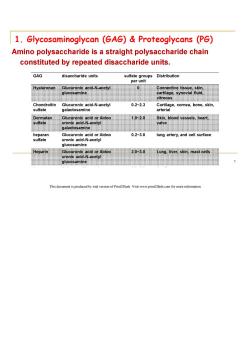
1.Glycosaminoglycan (GAG)&Proteoglycans (PG) Amino polysaccharide is a straight polysaccharide chain constituted by repeated disaccharide units. GAG disaccharide units sulfate groups Distribution per unit Hyaluronan Glucuronic acid-N-acetyl 0 Connective tissue,skin, glucosamine cartilage,synovial fluid vitreous Chondroitin Glucuronic acid-N-acetyl 0.2-2.3 Cartilage,cornea,bone,skin, sulfate galactosamine arterial Dermatan Glucuronic acid or Aidoo 1.0-2.0 Skin,blood vessels,heart, sulfate uronic acid-N-acetyl valve 出到 galactosamine heparan Glucuronic acid or Aidoo 0.2-3.0 lung artery,and cell surface sulfate uronic acid-N-acetyl glucosamine Heparin Glucuronic acid or Aidoo 2.0-3.0 Lung,liver,skin,mast cells uronic acid-N-acetyl glucosamine This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.printflash.com for more information
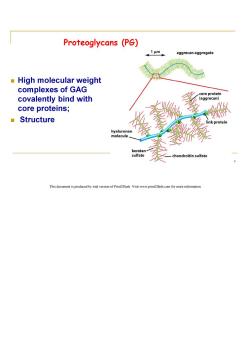
Proteoglycans (PG) 1μm aggrecan aggregate High molecular weight complexes of GAG core protein covalently bind with (aggrecan) core proteins; Structure link protein hyaluronan molecule keratan sulfate chondroitin sulfate This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Proteoglycans (PG) Sythesized and assembled in ER 1)Polysaccharides are assembled to core protein in ER lumen by glycosyltransferases,which in turn add monosaccharide to the specific tetrasaccharide structure on serine; 2)Polymorphology of amino acid sequence and sugar chain; 3)Some PG are integrated members of plasma membrane (Syndecan,蛋白多糖). This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

Function of GAG and PG 1.Make the tissues have flexibility and resistance to stress; 2.Selective permeability of the material transport (glomerulus,.肾小球); 3.Proteoglycans in the cornea()are translucent; 4.Anticoagulant effect; 5.Signal transition; 6.Invovled in tissue aging. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

GAG PG and disease 1.Abnormal degradation-abnormal accumulation- mucopolysaccharidoses(黏多糖贮积病); 2.Change of content ratio-lipid deposition-atherosclerosis (动脉粥样硬化); 3.Secretion increase and level of sulfate reduced-promote tumor cell proliferation and migration -tumor proliferation, invasion,and metastasis. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

2.Collagen and elastin Collagen is the skeleton of ECM The most abundant protein in human. ■ Structure:Triple helix of 3 a-polypeptide strands,the sequence is repeate of Gly-X-Y; There're many types of a strands with different kinds of combination style. Pri-peptide-remove signal peptide-add prepeptide on each ends.—Hydroxylation-—cross link at C terminal(procollagen)-secreted outside-remove prepeptide-self-assembly-mature collagen. This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell signaling.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell junction and cell adhesion.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Nucleus.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cytoskeleton.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Endomembrane system and vesicle transport.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Membrane transport.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell membrane.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)The unity and diversity of cells.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Introduction.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)微丝的形态结构观察.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)细胞内碱性蛋白的显示.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)细胞器的分级分离.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(实践指导,打印版)鸡血细胞的融合.pdf
- 安微医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(实践指导)形态学实验(切片).pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(习题指导,打印版)各章习题集(含参考答案,共二十五章).pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)绪论、人胚发生和早期发育、颜面和四肢的发生、消化系统和呼吸系统的发生、泌尿系统和生殖系统的发生、心血管系统发生.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)消化管、消化腺、呼吸系统、泌尿系统、女性生殖系统、男性生殖系统.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)眼和耳、神经系统、免疫系统、循环系统、内分泌系统、皮肤.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(授课教案,打印版)绪论、上皮组织、结缔组织、血液、淋巴、血细胞发生、软骨与骨、肌组织、神经组织.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(教学大纲,打印版).pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Cell division and cell cycle.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学细胞生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)Programmed cell death and cell senescence.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)01-Introduction to medical genetics.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)02-The Human Genome and the Chromosomal Basis of Heredity.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)05-principles of clinical cytogenetics.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)06-clinical cytogenetics 01 disorders of the autosomes and the sex chromosomes.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)06-clinical cytogenetics 02 disorders of the autosomes and the sex chromosomes.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)08-Genetics of Common Disorders with Complex Inheritance.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)07-patterns of single-gene inheritance.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)09 Genetic Variation in Individuals and Population.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第一章 绪论(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第三章 外源化学物在体内的生物转运与生物转化(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第二章_毒理学基本概念(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第五章 毒作用影响因素(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第六章 外源化学物的一般毒性作用(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第七章 外源化学物致突变作用(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第九章 发育毒性与致畸作用(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第八章_外源化学物致癌作用(含答案).doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)复习题一.doc
- 安徽医科大学:《毒理学基础》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第十一章 管理毒理学(含答案).doc
