上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.1-Basic Concepts

Chap.3 Planar Cartesian Kinematics 3.1 Basic Concepts in Planar Kinematics Body-fixed reference frame:A reference frame that is attached to and moves with the body Rigid body:If movement associated with deformation is small,compared with the overall movement of a body, then the body is considered as a rigid body Mechanism:A collection of rigid bodies that are arranged to allow relative motion Kinematics:The study of position,velocity and acceleration of a system of interconnected bodies that make up a mechanism
3.1 Basic Concepts in Planar Kinematics Body-fixed reference frame: A reference frame that is attached to and moves with the body Rigid body: If movement associated with deformation is small, compared with the overall movement of a body, then the body is considered as a rigid body Mechanism: A collection of rigid bodies that are arranged to allow relative motion Kinematics: The study of position, velocity and acceleration of a system of interconnected bodies that make up a mechanism Chap. 3 Planar Cartesian Kinematics
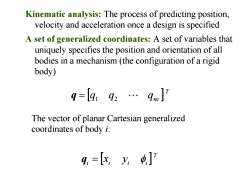
Kinematic analysis:The process of predicting position, velocity and acceleration once a design is specified A set of generalized coordinates:A set of variables that uniquely specifies the position and orientation of all bodies in a mechanism (the configuration of a rigid body) q=[4g2…9c]7 The vector of planar Cartesian generalized coordinates of body i: 4,=[飞,y]
Kinematic analysis: The process of predicting position, velocity and acceleration once a design is specified A set of generalized coordinates: A set of variables that uniquely specifies the position and orientation of all bodies in a mechanism (the configuration of a rigid body) T q q1 q2 qnc The vector of planar Cartesian generalized coordinates of body i: T i i i i q x y
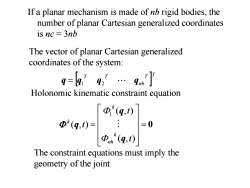
If a planar mechanism is made of nb rigid bodies,the number of planar Cartesian generalized coordinates is nc 3nb The vector of planar Cartesian generalized coordinates of the system: 9=la9.'…467] Holonomic kinematic constraint equation *(q,) Φ(q,t)=: =0 The constraint equations must imply the geometry of the joint
If a planar mechanism is made of nb rigid bodies, the number of planar Cartesian generalized coordinates is nc = 3nb T T nb T T q q1 q2 q Holonomic kinematic constraint equation The vector of planar Cartesian generalized coordinates of the system: 0 ( , ) ( , ) ( , ) 1 t t t k nh k k q q q The constraint equations must imply the geometry of the joint

If the constraint equations are independent,the system is said to have nc-nh degrees of freedom DOF nc-nh=3xnb-nh If DOF independent driving constraints are specified for kinematic analysis ΦP(g,t)=0 Then,the configuration of the system can be determined by solving the constraint equations: mwy-l8ad-t Such a system is called kinematically driven
If the constraint equations are independent, the system is said to have nc – nh degrees of freedom Then, the configuration of the system can be determined by solving the constraint equations: If DOF independent driving constraints are specified for kinematic analysis 0 ( , ) ( , ) ( , ) t t t D k q q q DOF nc nh 3 nb nh ( ,t) 0 D q Such a system is called kinematically driven
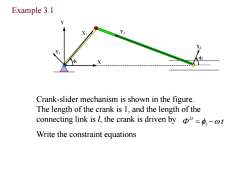
Example 3.1 Y Y2 X Crank-slider mechanism is shown in the figure. The length of the crank is 1,and the length of the connecting link is l,the crank is driven by=-t Write the constraint equations
1 X1 Y1 X2 Y2 2 X Y Example 3.1 Crank-slider mechanism is shown in the figure. The length of the crank is 1, and the length of the connecting link is l, the crank is driven by Write the constraint equations t D 1
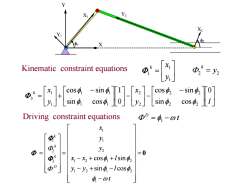
Y Y2 Kinematic constraint equations ,=2 cos2 Driving constraint equations Φ”=功-0t y Φ= y2 =0 -x2+cos +lsin y-y2+sin4-Icos中, 4-0t
1 X1 Y1 X2 Y2 2 X Y Kinematic constraint equations 1 1 1 y k x y l x y x k 0 sin cos cos sin 0 1 sin cos cos sin 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 2 2 y k t D 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 cos sin sin cos k k k D x y y x x l y y l t 0 Driving constraint equations

IfD,is nonsingular,.that isΦ,≠0 Time derivative of equations (g,t)=0I leads to (q,4,)=D,9+④,=0 更,9=-D,=v Time derivative of equations (g,t)=0 leads to 市=④,i+(中,),1+D,i+亚g9+D:=0 Φ,i=Y Y=-(Φ,)m9-2Φ9-Φa TΦ nhx1 nhxnc
Time derivative of equations qt 0 leads to 0 t q,q,t qq Time derivative of equations q q,t 0 leads to 0 t t tt q q q q q q q q q q ( ) q q t tt ( qq)q q 2 q q 1 2 2 nh i tt t 1 nh i t t nh nc j i q q nh nc nc k k k i j q q q 1 q q q q v q t If q is nonsingular, that is q 0
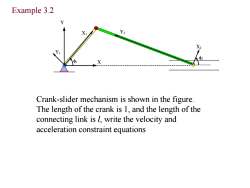
Example 3.2 Y X Y2 X Crank-slider mechanism is shown in the figure. The length of the crank is 1,and the length of the connecting link is l,write the velocity and acceleration constraint equations
1 X1 Y1 X2 Y2 2 X Y Example 3.2 Crank-slider mechanism is shown in the figure. The length of the crank is 1, and the length of the connecting link is l, write the velocity and acceleration constraint equations
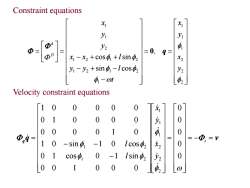
Constraint equations X1 y Φ ] 2 =0,q= x-x2 +cos +lsin y-y2+sing -lcos 4,-ot Velocity constraint equations 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 二 =-①,=y 1 0 -sin o -1 lcosφ2 0 0 coS中, 0 -1 Isin2 0 0 0 0
Constraint equations 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 1 sin cos cos sin y x y x , t y y l x x l y y x D k 0 q Velocity constraint equations q v q t y x y x l l 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 cos 0 1 sin 1 0 sin 1 0 cos 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 2
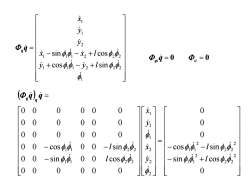
1 少 少2 中,1= 元-sin,4-元2+1cos, Φ,m9=0=0 +cos-i+lsin2 中 (,,9= 00 0 0 0 元1 0 0 0 0 00 0 0 00 0 00 0 0 00 -cos 0 0-Isin 元2 -cos2-Isin 00 -sin 00 Icos 少2 sin+lcos 0 0 0 00 0 可 0
1 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 1 cos sin sin cos y y l x x l y y x qq 0 sin cos cos sin 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 sin 0 0 cos 0 0 cos 0 0 sin 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 2 2 l l y x y x l l q q q q qtq 0 tt 0
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_2014复杂系统动力学试卷.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)邵炜桓.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)第四组-第三次作业-初稿.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)第三次作业要求.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)第一次作业打分表.docx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)周一浩.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)力学仿生第三次作业.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)分组.docx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)仿水黾机器人(第三组).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)二参数温度模型.docx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)9秦源.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)9力学仿生第一次作业_吴靖瑶_鳐鱼水动力学性能在水下推进器及无人机中的应用.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)8吴宇峻.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)8力学仿生第一次作业_沈晓昳_仿猫清洁擦.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)7力学仿生第一次作业_陈志杰_越过山丘,无需白头.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)6陈志杰.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)6力学仿生第一次作业_陈天宇_小型扑翼式无人机.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)5陈天宇.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)5力学仿生第一次作业_曾家雄_虎鹰.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)4吴靖瑶.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.2-Absolute constraints.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.3-Relative Constraint.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.4-Gears.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.5-Driving constraint.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.6-Position, velocity and acceleration analysis.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.6-Position, velocity and acceleration analysis_1.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.7-singularity.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 4_Char4-Numerical methods.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 4_Flow chart for kinematics.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 5_Planar Kinematic Modeling and Analysis.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 5_Modeling for Example 4.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 5_Modeling for Example 5.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 5_Modeling for Example2.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.1-Equations of motion of a planar rigid body.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.2 Virtual work and generalized force.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.2 Virtual work and generalized force.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.3 Equations of motion of constrained planar.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.4 Inverse Dynamics.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.5 Equilibrium Problem.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.6 Constraint reaction forces.ppt
