上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 4_Char4-Numerical methods

Chapter 4 Numerical Methods in Kinematics Determination of an assembled configuration of a system Giving estimates for the position and orientation of each component Giving the independent constraint equations The use of rapidly convergent and efficient numerical methods to solve the kinematic position equations Solution of the velocity equations Solution of the acceleration equations
• Determination of an assembled configuration of a system § Giving estimates for the position and orientation of each component § Giving the independent constraint equations • The use of rapidly convergent and efficient numerical methods to solve the kinematic position equations • Solution of the velocity equations • Solution of the acceleration equations

4.1 Organization of computations Preprocessor ■ Enter body naming/number Define body connectivity by kinematic joints and drivers Enter geometry of bodies,initial position Enter data that define individual joints Enter data that define period of simulation, numerical methods desired,and error tolerances Enter data that define drivers Geometry of bodies is necessary only for animation
Organization Preprocessor § Enter body naming/number § Define body connectivity by kinematic joints and drivers § Enter geometry of bodies, initial position § Enter data that define individual joints § Enter data that define period of simulation, numerical methods desired, and error tolerances § Enter data that define drivers Geometry of bodies is necessary only for animation

4.1 Organization of computations Kinematic analysis program Construct equations and matrices for kinematic analysis Assemble mechanism or declare infeasible design Identify and eliminate redundant constraint Carry out position,velocity,and acceleration analysis Postprocessor ■ Print alphanumeric results Plot curves Transmit graphic animation to terminal screen
Kinematic analysis program § Construct equations and matrices for kinematic analysis § Assemble mechanism or declare infeasible design § Identify and eliminate redundant constraint § Carry out position, velocity, and acceleration analysis Postprocessor § Print alphanumeric results § Plot curves § Transmit graphic animation to terminal screen 4.1 Organization of computations
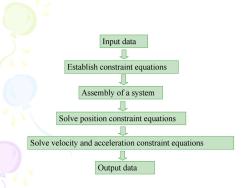
Input data 0 Establish constraint equations 0 Assembly of a system L Solve position constraint equations 见 Solve velocity and acceleration constraint equations Output data
Input data Establish constraint equations Assembly of a system Solve velocity and acceleration constraint equations Output data Solve position constraint equations

4.2 Evaluation of constraint equations and Jacobian Input data Establish constraint equations
4.2 Evaluation of constraint equations and Jacobian Input data Establish constraint equations

Input data Input the body and joint number Input initial position of each body Input joint kind and driving information Q Input inner and outer body number for each joint Input relative position vectors of the joint points Input kinematic coefficients Q Input driving coefficients (only for driving constraints
Input data Input the body and joint number Input initial position of each body Input joint kind and driving information Input inner and outer body number for each joint Input relative position vectors of the joint points Input kinematic coefficients Input driving coefficients (only for driving constraints

Establish constraint equations Derive position constraint equations 见 Calculate Jacobian matrix 夏 Calculate velocity right terms 0 Calculate acceleration right terms
Establish constraint equations Derive position constraint equations Calculate Jacobian matrix Calculate velocity right terms Calculate acceleration right terms
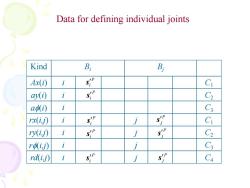
Data for defining individual joints Kind B B Ax(i) i Ci ay(i) i s C2 adi) i C3 rx(ij) i s j Ci ry(i,i) i siP j s C2 r,) C3 rd(i,j) i s j s Ca
Data for defining individual joints i i i i i i i K Bi Bj ind C2 ry(i,j) j C1 rx(i,j) j C4 rd(i,j) j C3 rf(i,j) j af(i) C3 ay C2 (i) Ax C1 (i) P i s P j s P i s P i s P i s P i s P j s P j s
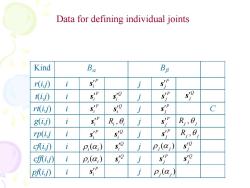
Data for defining individual joints Kind Ba Bp r() i SiP s tij i siP so j s s rt(ij) i P so j C g(ij) i sip R,0 s R,0 rp(ij i s so j R,0 cfij) i p,(c) s0 j p;(a) 59 cffij) i P,(c) S0 j so p叭i) i j p,(a)
Data for defining individual joints i i i i i i i K Ba Bb ind rp(i,j j ) g(i,j) j cf (i,j) j cf(i,j) j rt(i,j) j C t(i,j) j r(i,j) j P i s P j s P j s Ri i , Rj j , Rj j , pf(i,j) Q i s Q j s i j P i s P i s P i s P i s ( ) i ai P j s Q i s Q i s Q i s Q i s P j s P j s P j s ( ) j a j Q j ( ) s i ai P i s ( ) j a j Q j s

4.3 Assembly of a system The objective is to minimize w(q,,r)=q-g)g-g)+rΦ(g,)Φ(g,to) to obtain an assembled configuration 1=q The parameter r>0 is a constant that places relative emphasis on deviation from the initial estimate q"=limg(r) Optimization calculation
The objective is to minimize 4.3 Assembly of a system ( , , ) ( , ) ( , ) 0 0 0 0 0 t r r t t T T q q q q q q q to obtain an assembled configuration a q q The parameter r 0 is a constant that places relative emphasis on deviation from the initial estimate lim (r) r a q q Optimization calculation
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.7-singularity.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.6-Position, velocity and acceleration analysis_1.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.6-Position, velocity and acceleration analysis.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.5-Driving constraint.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.4-Gears.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.3-Relative Constraint.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.2-Absolute constraints.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.1-Basic Concepts.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_2014复杂系统动力学试卷.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)邵炜桓.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)第四组-第三次作业-初稿.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)第三次作业要求.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)第一次作业打分表.docx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)周一浩.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)力学仿生第三次作业.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)分组.docx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)仿水黾机器人(第三组).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)二参数温度模型.docx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)9秦源.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《力学仿生——启示与探索》课程教学资源(讲课讲稿)9力学仿生第一次作业_吴靖瑶_鳐鱼水动力学性能在水下推进器及无人机中的应用.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 4_Flow chart for kinematics.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 5_Planar Kinematic Modeling and Analysis.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 5_Modeling for Example 4.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 5_Modeling for Example 5.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 5_Modeling for Example2.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.1-Equations of motion of a planar rigid body.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.2 Virtual work and generalized force.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.2 Virtual work and generalized force.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.3 Equations of motion of constrained planar.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.4 Inverse Dynamics.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.5 Equilibrium Problem.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.6 Constraint reaction forces.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 7_chap7-Numerical Methods in Dynamics.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 8_Planar Dynamic Modeling and Analysis.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 8_Modeling for Example 4.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 8_Modeling for Example1.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 8_Modeling for Example2.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学上机_双摆动力学仿真说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学上机_双摆动力学逆问题说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学上机_静平衡条件说明.doc
