上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.5 Equilibrium Problem
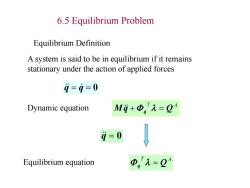
6.5 Equilibrium Problem Equilibrium Definition A system is said to be in equilibrium if it remains stationary under the action of applied forces i=9=0 Dynamic equation M9+Φ,'=2 i=0 Equilibrium equation D,九=
q q 0 T A Mq q Q T A q Q A system is said to be in equilibrium if it remains stationary under the action of applied forces Equilibrium Definition Dynamic equation Equilibrium equation q 0 6.5 Equilibrium Problem
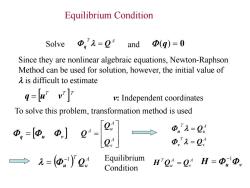
Equilibrium Condition Solve Φ,2=04 and 1Φ(q)=0 Since they are nonlinear algebraic equations,Newton-Raphson Method can be used for solution,however,the initial value of A is difficult to estimate q=u'v v:Independent coordinates To solve this problem,transformation method is used 0,=②。中]0 Φ1=2 e Φ,九=2, →=(西,0 Equilibrium Condition H'Q=2,H=ΦΦ
Equilibrium Condition Solve T A q Q and (q) 0 Since they are nonlinear algebraic equations, Newton-Raphson Method can be used for solution, however, the initial value of is difficult to estimate To solve this problem, transformation method is used q u v A v T A u T Q Q v u A u T u Q 1 A v A u A Q Q Q A v A u T H Q Q H u v 1 Equilibrium Condition v: Independent coordinates T T T q u v
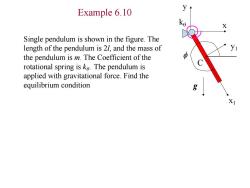
Example 6.10 X Single pendulum is shown in the figure.The length of the pendulum is 21,and the mass of the pendulum is m.The Coefficient of the rotational spring is ke.The pendulum is applied with gravitational force.Find the equilibrium condition g X1
Example 6.10 x1 y1 C x y f g kq Single pendulum is shown in the figure. The length of the pendulum is 2l, and the mass of the pendulum is m. The Coefficient of the rotational spring is kq . The pendulum is applied with gravitational force. Find the equilibrium condition
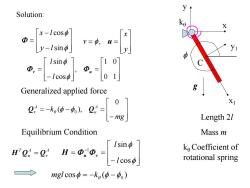
Solution: X x-lcosφ Φ= -1sn v=0,u= y 10 Generalized applied force g e-wse-l Length 21 Equilibrium Condition Mass m [lsinφ I2:-Q:H-losd ko Coefficient of rotational spring mgl cos中=-kg(p-中)
x1 y1 C x y f g Length 2l Mass m kq kqCoefficient of rotational spring 0 1 1 0 , cos sin v u f f l l f f sin cos y l x l y x v f, u Equilibrium Condition A v A u T H Q Q Generalized applied force mg k A u A v 0 ( ), Q q f f 0 Q f f cos sin 1 l l H u v cos ( ) f q f f 0 mgl k Solution:
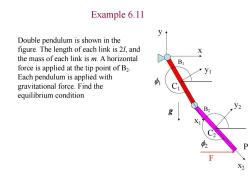
Example 6.11 Double pendulum is shown in the figure.The length of each link is 27,and X the mass of each link is m.A horizontal Br force is applied at the tip point of B2 y1 Each pendulum is applied with gravitational force.Find the 中1 equilibrium condition g X 2 p2 F X2
Example 6.11 x1 y1 C1 x y f1 g x2 y2 C2 f2 F P Double pendulum is shown in the figure. The length of each link is 2l, and the mass of each link is m. A horizontal force is applied at the tip point of B2 . Each pendulum is applied with gravitational force. Find the equilibrium condition B2 B1
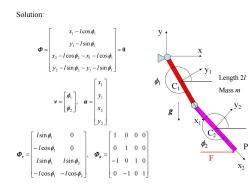
Solution: x-Icos y-Isin Φ= =0 X x2-lcos中2-x1-1cos中1 y2-Isin2-y,-lsin中, yi 1 Length 2/ XI Mass m y v= l 中2」 X2 g y2 X Ising 0 1 00 0 -1c0sφ1 0 0 100 P ①,= Φ.= Ising Isin2 -1 010 F X2 -lcos中,-Icos2 0-101
x1 y1 C1 x y f1 g x2 y2 C2 f2 Length 2l Mass m F P 0 2 2 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 sin sin cos cos sin cos f f f f f f y l y l x l x l y l x l 2 2 1 1 2 1 , y x y x v u f f 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 , cos cos sin sin cos 0 sin 0 1 2 1 2 1 1 v u f f f f f f l l l l l l Solution:

Isin 0 「10 00 -Icos 0 010 0 。= Isin Isin2 一1 010 -1cos41-1cosφ2 0-101 lsinφ1 0 -1cos 0 H=DΦ。= 21sin Isin -21cos -Icos
0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 , cos cos sin sin cos 0 sin 0 1 2 1 2 1 1 v u f f f f f f l l l l l l 1 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 cos cos 2 sin sin cos 0 sin 0 f f f f f f l l l l l l H u v
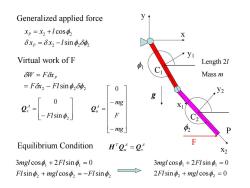
Generalized applied force xp=x2 +lcos X δxp=δx2-Isin2δ冲2 Virtual work of F Length 2/ δW=Fxp Mass m =Fx2-Flsin2δp2 0 g eLa -mg 2= X F -mg 2 Equilibrium Condition F H2=2,4 3mgl coso +2FIsin=0 3mgl coso +2FIsin=0 FIsin2 +mgl cos,=-FIsin2 2FIsin2 mgl cos2=0
Generalized applied force x1 y1 C1 x y f1 g x2 y2 C2 f2 Length 2l Mass m F P 2 2 2 2 2 sin cos f f f x x l x x l P P 2 2 2 sinf f F x Fl W F xP 2 sin 0 Fl f A Qv Virtual work of F A v A u T Equilibrium Condition H Q Q mg F mg A u 0 Q 2 2 2 1 1 sin cos sin 3 cos 2 sin 0 f f f f f Fl mgl Fl mgl Fl 2 sin cos 0 3 cos 2 sin 0 2 2 1 1 f f f f Fl mgl mgl Fl

Problem Equation Φ,'=Q4 is computationally feasible However A good estimate of the equilibrium position is needed as a starting point for iterative computation The difficulty associated with unstable equilibrium configuration The principle of minimum total potential energy is employed in order to avoid the difficulty
• A good estimate of the equilibrium position is needed as a starting point for iterative computation • The difficulty associated with unstable equilibrium configuration is computationally feasible T A Equation q Q However The principle of minimum total potential energy is employed in order to avoid the difficulty Problem

Stable Equilibrium Condition For conservative systems,the condition that defines a state qo of stable equilibrium is that the total potential energy be minimized 4=9=0 and TPE(qO)≤TPE(q) for all q such that (q-qa)'(q-go)≤ε TPE Stable equilibrium state q 90
Stable Equilibrium Condition ( ) ( ) q q 0 and TPE q0 TPE q for all q such that q q0 q q0 T For conservative systems, the condition that defines a state q0 of stable equilibrium is that the total potential energy be minimized q TPE q0 Stable equilibrium state
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.4 Inverse Dynamics.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.3 Equations of motion of constrained planar.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.2 Virtual work and generalized force.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.2 Virtual work and generalized force.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.1-Equations of motion of a planar rigid body.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 5_Modeling for Example2.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 5_Modeling for Example 5.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 5_Modeling for Example 4.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 5_Planar Kinematic Modeling and Analysis.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 4_Flow chart for kinematics.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 4_Char4-Numerical methods.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.7-singularity.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.6-Position, velocity and acceleration analysis_1.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.6-Position, velocity and acceleration analysis.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.5-Driving constraint.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.4-Gears.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.3-Relative Constraint.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.2-Absolute constraints.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 3_CHAP3.1-Basic Concepts.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_2014复杂系统动力学试卷.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 6_Char6.6 Constraint reaction forces.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 7_chap7-Numerical Methods in Dynamics.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 8_Planar Dynamic Modeling and Analysis.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 8_Modeling for Example 4.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 8_Modeling for Example1.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_Chapter 8_Modeling for Example2.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学上机_双摆动力学仿真说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学上机_双摆动力学逆问题说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学上机_静平衡条件说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_动力学附加题.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_双摆动力学仿真说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_双摆动力学逆问题说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_运动学上机_运动学计算流程图.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_运动学计算流程图.doc
- 上海交通大学:《复杂系统动力学计算机辅助分析》课程教学资源_静平衡条件说明.doc
- 上海交通大学:《人体生物力学》课程教学资源(讲义)人体生物力学概论(梁夫友).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《人体生物力学》课程教学资源(讲义)心血管生物力学及其在疾病诊疗方面的应用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《人体生物力学》课程教学资源(讲义)运动生物力学及组织损伤机理、计算机辅助手术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《人体生物力学》课程教学资源(讲义)生物力学的发展前景.pdf
- 《力学改变生活》课程教学资源(文献资料)The First Sounds of Merging Black Holes.pdf
