北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 12 Antibiotics

Chapter 12 Antibiotics
Chapter 12 Antibiotics
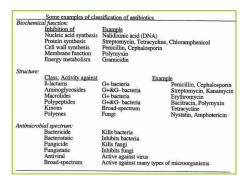
Some examples of classification of antibiotics Biochemical function: Inhibition of Example Nucleic acid synthesis Nalidixinic acid (DNA) Protein synthesis Streptomycin,Tetracycline,Chloramphenicol Cell wall synthesis Penicillin,Cephalosporin Membrane function Polymyxin Energy metabolism Gramicidin Structure: Class:Activity against Example B-lactams G+bacteria Penicillin,Cephalosporin Aminoglycosides G+&G-bacteria Streptomycin,Kanamycin Macrolides G+bacteria Erythromycin Polypeptides G+&G-bacteria Bacitracin,Polymyxin Kinons Broad-spectrum Tetracycline Polyenes Fungi Nystatin,Amphotericin Antimicrobial spectrum: Bactericide Kills bacteria Bacteristatic Inhibits bacteria Fungicide Kills fungi Fungistatic Inhibits fungi Antiviral Active against virus Broad-spectrum Active against many types of microorganisms
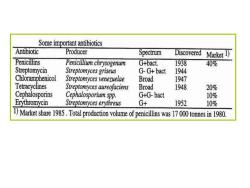
Some important antibiotics Antibiotic Producer Spectrum Discovered Market 1) Penicillins Penicillium chrysogenum G+bact. 1938 40% Streptomycin Streptomyces griseus G-G+bact 1944 Chloramphenicol Streptomyces venezuelae Broad 1947 Tetracyclines Streptomyces aureofaciens Broad 1948 20% Cephalosporins Cephalosporium spp. G+G-bact 10% Erythromycin Streptomyces erythreus G+ 1952 10% 1)Market share 195.Total production voume of penicillins was 17000tones in1980
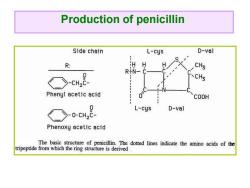
Production of penicillin Side chain L-cys D-val R: RiN- CHs -, 、CH Phenyl acetic acid COOH L-cys D-val Phenoxy acetic acid The basic structure of penicillin.The dotted lines indicate the amino acids of the tripeptide from which the ring structure is derived
Production of penicillin

Penicillin G:benzylpenicillin Penicillin V:phenoxymethypenicillin Strain: Penicillium notatum (1940s) Penicillium chrysogenum 6-APA
Penicillin G: benzylpenicillin Penicillin V: phenoxymethypenicillin Strain: Penicillium notatum (1940s) Penicillium chrysogenum 6-APA
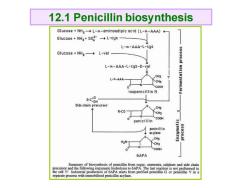
12.1 Penicillin biosynthesis Glucose NH-L-o-aminoadipic acid (L-a-AAA)+ Glucose NH3+S02--L-cys L-a-AAA-L-cys Glucose+NH3→L-Val L-a-AAA-L-cys-D-val CH3 L-a-AAA CH3 COOH isopenicillin N RCOH Side chein precursor R-CO CH3 COOH penicillin penicillin acylase CH3 H2 CH3 COOH 6APA 兰 Summary of biosynthesis of penicillin from ammoni,sulphate and side chain separate process with immobilised penicillin acylase
12.1 Penicillin biosynthesis
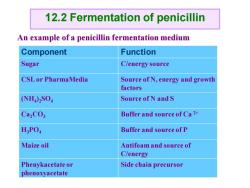
12.2 Fermentation of penicillin An example of a penicillin fermentation medium Component Function Sugar C/energy source CSL or PharmaMedia Source of N,energy and growth factors NH4)2S04 Source ofN and S Ca2CO3 Buffer and source of Ca2+ H;PO Buffer and source of P Maize oil Antifoam and source of C/energy Phenykacetate or Side chain precursor phenoxyacetate
An example of a penicillin fermentation medium Component Function Sugar C/energy source CSL or PharmaMedia Source of N, energy and growth factors (NH4 )2SO4 Source of N and S Ca2CO3 Buffer and source of Ca 2+ H3PO4 Buffer and source of P Maize oil Antifoam and source of C/energy Phenykacetate or phenoxyacetate Side chain precursor 12.2 Fermentation of penicillin
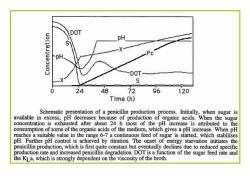
DOT PH DOT- s 24 48 72 96 120 Time(h) Schematic presentation of a penicillin production process.Initially,when sugar is available in excess,pH decreases because of production of organic acids.When the sugar concentration is exhausted after about 24 h most of the pH increase is attributed to the consumption of some of the organic acids of the medium,which gives a pH increase.When pH reaches a suitable value in the range 6-7 a continuous feed of sugar is started,which stabilises pH.Further pH control is achieved by titration.The onset of energy starvation initiates the penicillin production,which is first quite constant but eventually declines due to reduced specific production rate and increased penicillin degradation.DOT is a function of the sugar feed rate and the KL a,which is strongly dependent on the viscosity of the broth
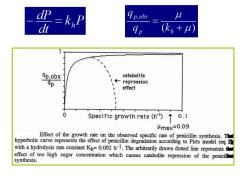
= 4p.obs 9p (k+ ap,obs catabolite ←repres3ion effect 1 0 Specific growth rate(h1)0.1 max≈0.09 Effect of the growth rate on the observed specific rate of penicillin synthesis.The hyperbolic curve represents the effect of penicillin degradation according to Pirts model (eq 2 with a hydrolysis rate constant Kh=0.002 h-1.The arbitrarily drawn dotted line representsh effect of too high sugar concentration which causes catabolite repression of the penicilF synthesis
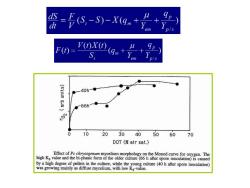
会=--xg* em F()= V(t)X(t S (9m+y (silun que 40h 66h 0 10 2030405060 70 DOT air sat.) Effect of Pc chrysogenumn mycelium morphology on the Monod curve for oxygen.The high Ks value and the bi-phasic form of the older culture(66 h after spore inoculation)is caused by a high degree of pellets in the culture,while the young culture(40 h after spore inoculation) was growing mainly as diffuse mycelium,with low Ks-value
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 11 Microbial Energy Conversion Processes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Fermented Food.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 09 Immobilization of Biocatalysts.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 08 灭菌 Sterilization.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 07 Scale-up of Aerobic Processes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 06 Modes of Process Operation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 05 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 04 Mass Transport in Bioreactor.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 03 Kinetic Models.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 02 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 01 Introduction(主讲:谭天伟).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(教学大纲)生物工艺学教学大纲 Bioprocess Technology Fundamentals and Application.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer——DNA biosynthesis(DNA replication-复制).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)核苷酸代谢 Metabolism of Nucleotides.ppt
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)生物氧化 Biological Oxidation.pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)脂代谢 Metabolism of Lipids.ppt
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)酶 Enzymes(主讲:王春光).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)脂类代谢 Lipids and lipid metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Aerobic Metabolism II Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation(ETC).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)碳水化合物与碳水化合物代谢 Carbohydrates and Carbohydrate metabolism.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 13 Industrial Use of Enzymes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 14 Biological Waste Water Treatment.ppt
- 《药物生物技术》:新的芯片毛细管电泳及其联用技术研究应用进展(复旦大学:陈执中).pdf
- 三明学院:资源与化工学院生物技术专业本科课程教学大纲(汇编).pdf
- 上海海洋大学:生命学院2011年版课程教学大纲汇编(目录).pdf
- 上海海洋大学:生命学院2011年版课程教学大纲汇编(正文).pdf
- 上海海洋大学:食品学院2018年版课程教学大纲汇编(生物制药专业).pdf
- 山东大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学大纲(共十三章).pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)HIV研究不能误入歧途.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)一种细菌在极端环境下可产氢.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)全方位认识微生物.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)关于农业微生物的应用.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)嗜极菌的应用.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)土壤中放线菌的分离与纯化.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)微生物培养基的配制与灭菌.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)植物感染的真菌及杀菌剂.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)细菌产聚羟基烷酸(PHA).pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)蕈菌.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)蛋白胨.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)革兰氏阴性菌细胞壁外膜组成成分.pdf
