北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 06 Modes of Process Operation

CHAPTER 6 Modes of Process Operation
Chapter 6 Modes of Process Operation

办=0-)+(0-)++i yg.o i)the batch mode,where F;=F=0 dy =r+GTR dt ii)the fed-batch mode,where F=0 and Fi=F>0 产-0-++GR iii)the continuous mode,where Fi=Fo=F>0 答=会0w-8)+5+G7R
i) the batch mode, where Fi=Fo=0 ii) the fed-batch mode, where Fo=0 and Fi=F>0 iii) the continuous mode, where Fi=Fo=F>0 g o o g i i y o i i y V Q y V Q y y r V F y y V F dt dy = ( − ) + ( − ) + + , − , r GTR dt dy = y + y y r GTR V F dt dy = ( i − ) + y + y y r GTR V F dt dy = ( i − ) + y +
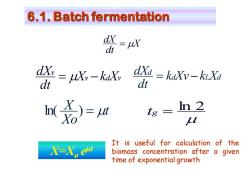
6.1.Batch fermentation =uX dt dX=jKy-kaXv dXd=kaXv-kiXa dt dt M名)=a tg= In 2 L It is useful for calculation of the X=Xoem biomass concentration after a given time of exponential growth
6.1. Batch fermentation X dt dX = v d v v X k X dt dX = − d L d d k Xv k X dt dX = − t Xo X ln( ) = ln 2 tg = X=Xo e μt It is useful for calculation of the biomass concentration after a given time of exponential growth
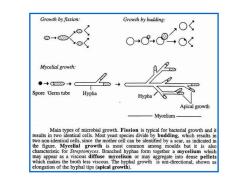
Growth by fission: Growth by budding: $+88 Mycelial growth: ●+Q8→ Spore Germ tube Hypha Hypha Apical growth Mycelium Main types of microbial growth.Fission is typical for bacterial growth and it results in two identical cells.Most yeast species divide by budding,which results in two non-identical cells,since the mother cell can be identified by a scar,as indicated in the figure.Mycelial growth is most common among moulds but it is also characteristic for Streptomyces.Branched hyphae form together a mycelium which may appear as a viscous diffuse mycelium or may aggregate into dense pellets which makes the broth less viscous.The hyphal growth is uni-directional,shown as elongation of the hyphal tips(apical growth)
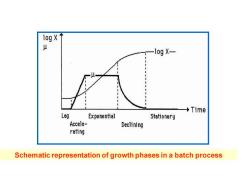
gx y -log X- +Time Lag Exponential Stationary Accele- Declining rating Schematic representation of growth phases in a batch process
Schematic representation of growth phases in a batch process

A simple modelfor an increasing specific growth rate during a lag phase is ='mx(-exp(-tt》 tL (h):the constant related to the length of the lag phase
A simple model for an increasing specific growth rate during a lag phase is μ=μmax (I-exp(-t/tL )) tL (h) : the constant related to the length of the lag phase
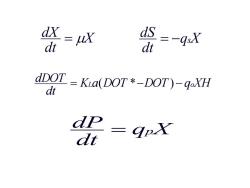
dx dt =uX d dt =-4X dDOT=Kia(DOT *-DOT)-qoXH dt dp=qox dt
X dt dX = q X dt dS = − s K a DOT DOT q XH dt dDOT = L ( *− ) − o q X dt dP = p

10 20 100 D01 216012nS (8)100 0 of 0 -0.5 ogx DOT Time (h) 10 Simulation of batch processes onentially until the C/energy substrate(S) 18℃0n气2<4 Constants used:qs.max=I h1:Ks.s=0.05 kg m-3:Ks.o=5 air sat; Yx/s 0.5 kg:Yo/s=0.5 kg kg-1.KLa 500 h-1 (250 h-1 in the middle curve)
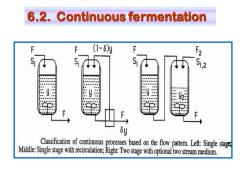
6.2.Continuous fermentation F (1-6y F2 8y Classification of continuous processes based on the flow patter.Left:Single stag Middle:Single stage with recirculation;Right:Two stage with optional two stream medium
6.2. Continuous fermentation
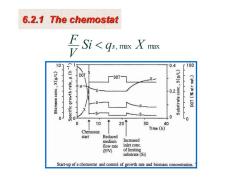
6.2.1 The chemostat Si<qs,mx X max 101 0.4 r100 DOT DOT- X 0.2 (3=51m5)101 0 0 Lo 0 10 20 30 40 Time (h) Chemostat start Reduced medium Increased flow rate inlet conc (F/V) of limiting substrate (Si) Start-up of a chemostat and control of growth rate and biomass concentration
Si q , max X max V F s 6.2.1 The chemostat
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 05 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 04 Mass Transport in Bioreactor.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 03 Kinetic Models.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 02 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 01 Introduction(主讲:谭天伟).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(教学大纲)生物工艺学教学大纲 Bioprocess Technology Fundamentals and Application.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer——DNA biosynthesis(DNA replication-复制).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)核苷酸代谢 Metabolism of Nucleotides.ppt
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)生物氧化 Biological Oxidation.pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)脂代谢 Metabolism of Lipids.ppt
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)酶 Enzymes(主讲:王春光).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)脂类代谢 Lipids and lipid metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Aerobic Metabolism II Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation(ETC).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)碳水化合物与碳水化合物代谢 Carbohydrates and Carbohydrate metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)氨基酸代谢 Amino Acid Metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)蛋白质 Proteins.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)细胞生物学(理论).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer——Protein Biosynthesis Translation(翻译).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer(RNA transcription 转录)RNA biosynthesis.pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013 Final term examination for Cellular Biochemistry(无答案).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 07 Scale-up of Aerobic Processes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 08 灭菌 Sterilization.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 09 Immobilization of Biocatalysts.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Fermented Food.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 11 Microbial Energy Conversion Processes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 12 Antibiotics.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 13 Industrial Use of Enzymes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 14 Biological Waste Water Treatment.ppt
- 《药物生物技术》:新的芯片毛细管电泳及其联用技术研究应用进展(复旦大学:陈执中).pdf
- 三明学院:资源与化工学院生物技术专业本科课程教学大纲(汇编).pdf
- 上海海洋大学:生命学院2011年版课程教学大纲汇编(目录).pdf
- 上海海洋大学:生命学院2011年版课程教学大纲汇编(正文).pdf
- 上海海洋大学:食品学院2018年版课程教学大纲汇编(生物制药专业).pdf
- 山东大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学大纲(共十三章).pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)HIV研究不能误入歧途.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)一种细菌在极端环境下可产氢.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)全方位认识微生物.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)关于农业微生物的应用.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)嗜极菌的应用.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)土壤中放线菌的分离与纯化.pdf
