北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 03 Kinetic Models

Chapter 3 Kinetic Models
Kinetic Models Chapter 3
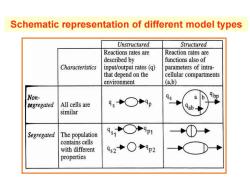
Schematic representation of different model types Unstructured Structured Reactions rates are Reaction rates are described by functions also of Characteristics input/output rates(q) parameters of intra- that depend on the cellular compartments environment (a,b) Non- 9○P9p a segregated All cells are similar Segregated The population 91○P9p1 contains cells with different 92+○9p2 properties
Schematic representation of different model types
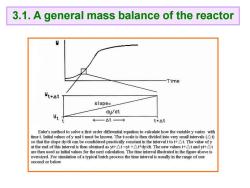
3.1.A general mass balance of the reactor Time Ut+At slope= dy/dt ←—△t→ t+△t Euler's method to solve a first order differential equation to calculate how the variable y varies with time t.Initial values ofy and t must be known.The t-scale is then divided into very small intervals(At) so that the slope dy/dt can be condidered practically constant in the interval t to t+At.The value ofy at the end of this interval is then obtained as yt+At=yt+t*dy/dt.The new values tAt and ytAt are then used as initial values for the next calculation.The time interval illustrated in the figure above is oversized.For simulation of a typical batch process the time interval is usually in the range of one second or below
3.1. A general mass balance of the reactor
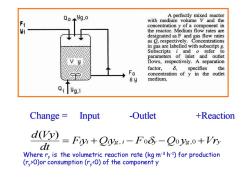
Q0+9g,0 A perfectly mixed reactor with medium volume V and the concentration y of a component in 9 the reactor.Medium flow rates are designated as F and gas flow rates as O,respectively.Concentrations in gas are labelled with subscript g. Subscripts i and o refer to parameters of inlet and outlet V y flows,respectively.A separation factor, 6, specifies the concentration of y in the outlet medium. Qi yg,i Change=Input -Outlet +Reaction d(Vy)=Fy+Qys.-Fo-Qoys.0+Vry dt Where ry is the volumetric reaction rate (kg m-3 h-1)for production (ry>O)or consumption(ry<O)of the component y
Change = Input -Outlet +Reaction Fiyi Qiyg i F y Q yg Vry dt d Vy = + , − 0 − 0 ,0 + ( ) Where ry is the volumetric reaction rate (kg m-3 h -1 ) for production (ry >0)or consumption (ry <0) of the component y
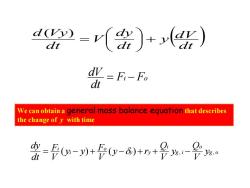
a2=r()+() dⅣ=F:-Fo d We can obtaina general mass balance equation that describes the change of y with time 命=0-0+0-8++号鲁
( ) dt y dV dt dy V dt d Vy + = ( ) Fi Fo dt dV = − g o o g i i y y o i i y V Q y V Q y r V F y y V F dt dy = ( − ) + ( − ) + + , − , We can obtain a general mass balance equation that describes the change of y with time
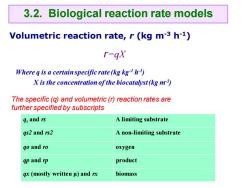
3.2.Biological reaction rate models Volumetric reaction rate,r(kg m-3 h-1) r=gX Where q is a certain specific rate(kg kg) X is the concentration of the biocatalyst(kg m3) The specific(q)and volumetric(r)reaction rates are further specified by subscripts 4s and rs A limiting substrate qs2 and rs2 A non-limiting substrate qo and ro oxygen gp and rp product gx (mostly written u)and rx biomass
Volumetric reaction rate, r (kg m-3 h-1) Where q is a certain specific rate (kg kg-1 h -1 ) X is the concentration of the biocatalyst (kg m-3 ) qs and rs A limiting substrate qs2 and rs2 A non-limiting substrate qo and ro oxygen qp and rp product qx (mostly written μ) and rx biomass 3.2. Biological reaction rate models r=qX The specific (q) and volumetric (r) reaction rates are further specified by subscripts
Model >Substrate consumption model >Cell growth model >Product formation model
Model ➢Substrate consumption model ➢Cell growth model ➢Product formation model
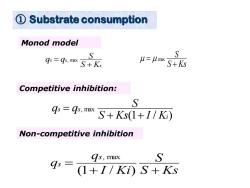
① Substrate consumption Monod model S gs=gs.m S+Ks u=u max S S+Ks Competitive inhibition: S gs =g9s.mx S+Ks(1+1/Ki) Non-competitive inhibition as,max S 9s= (1+I/Ki)S+Ks
① Substrate consumption s s s S K S q q + = , max S Ks S + = max (1 / ) , max i s s S Ks I K S q q + + = S Ks S I Ki q q s s + + = (1 / ) , max Monod model Competitive inhibition: Non-competitive inhibition
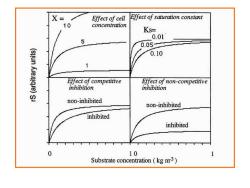
X= Effect of cell Effect of saturation constant 10 concentration Ks= 0.01 0.05 0.10 Effect of competitive Effect of non-competitive inhibition inhibition non-inhibited non-inhibited inhibited inhibited 0 10 Substrate concentration(kg m3)
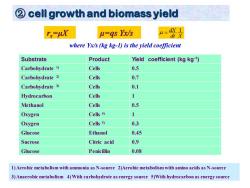
cell growth and biomass yield rx=uX u=gs Yx/s H=dX I dt X where Yx/s (kg kg-1)is the yield coefficient Substrate Product Yield coefficient(kg kg-1) Carbohydrate 1) Cells 0.5 Carbohydrate 2) Cells 0.7 Carbohydrate 3) Cells 0.1 Hydrocarbon Cells 1 Methanol Cells 0.5 Oxygen Cells 1 Oxygen Cells 5) 0.3 Glucose Ethanol 0.45 Sucrose Citric acid 0.9 Glucose Penicillin 0.08 1)Aerobic metabolism with ammonia as N-source 2)Aerobic metabolism with amino acids as N-source 3)Anaerobic metabolism 4)With carbohydrate as energy source 5)With hydrocarbon as energy source
② cell growth and biomass yield dt X dX 1 = Substrate Product Yield coefficient (kg kg-1 ) Carbohydrate 1) Cells 0.5 Carbohydrate 2) Cells 0.7 Carbohydrate 3) Cells 0.1 Hydrocarbon Cells 1 Methanol Cells 0.5 Oxygen Cells 4) 1 Oxygen Cells 5) 0.3 Glucose Ethanol 0.45 Sucrose Citric acid 0.9 Glucose Penicillin 0.08 1) Aerobic metabolism with ammonia as N-source 2)Aerobic metabolism with amino acids as N-source 3) Anaerobic metabolism 4) With carbohydrate as energy source 5)With hydrocarbon as energy source rx=μX μ=qs Yx/s where Yx/s (kg kg-1) is the yield coefficient
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 02 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 01 Introduction(主讲:谭天伟).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(教学大纲)生物工艺学教学大纲 Bioprocess Technology Fundamentals and Application.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer——DNA biosynthesis(DNA replication-复制).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)核苷酸代谢 Metabolism of Nucleotides.ppt
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)生物氧化 Biological Oxidation.pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)脂代谢 Metabolism of Lipids.ppt
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)酶 Enzymes(主讲:王春光).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)脂类代谢 Lipids and lipid metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Aerobic Metabolism II Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation(ETC).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)碳水化合物与碳水化合物代谢 Carbohydrates and Carbohydrate metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)氨基酸代谢 Amino Acid Metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)蛋白质 Proteins.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)细胞生物学(理论).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer——Protein Biosynthesis Translation(翻译).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer(RNA transcription 转录)RNA biosynthesis.pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013 Final term examination for Cellular Biochemistry(无答案).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)中文细胞生化理论留学生教学大纲.docx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)英文细胞生化理论留学生教学大纲 Syllabus for cellular biochemistry.docx
- 同济大学:《环境工程微生物学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)考试试卷及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 04 Mass Transport in Bioreactor.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 05 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 06 Modes of Process Operation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 07 Scale-up of Aerobic Processes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 08 灭菌 Sterilization.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 09 Immobilization of Biocatalysts.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Fermented Food.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 11 Microbial Energy Conversion Processes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 12 Antibiotics.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 13 Industrial Use of Enzymes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 14 Biological Waste Water Treatment.ppt
- 《药物生物技术》:新的芯片毛细管电泳及其联用技术研究应用进展(复旦大学:陈执中).pdf
- 三明学院:资源与化工学院生物技术专业本科课程教学大纲(汇编).pdf
- 上海海洋大学:生命学院2011年版课程教学大纲汇编(目录).pdf
- 上海海洋大学:生命学院2011年版课程教学大纲汇编(正文).pdf
- 上海海洋大学:食品学院2018年版课程教学大纲汇编(生物制药专业).pdf
- 山东大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学大纲(共十三章).pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)HIV研究不能误入歧途.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)一种细菌在极端环境下可产氢.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)全方位认识微生物.pdf
