同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Aerobic Metabolism II Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation(ETC)

Aerobic Metabolism Il: Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
Aerobic Metabolism II: Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation

-the use of oxygen by aerobes is of great advantage as it provides much more energy than anaerobic fermentation -used by aerobic organisms as a terminal electron acceptor in energy generation
O2 -the use of oxygen by aerobes is of great advantage as it provides much more energy than anaerobic fermentation -used by aerobic organisms as a terminal electron acceptor in energy generation

O2 (cont.) it is suitable for this role because: it is readily available (occurs almost everywhere on the earth) it diffuses easily across cell membranes it is highly reactive and thus readily accepts electrons the use of O,by aerobic organisms is linked to the production of highly destructive ROS (reactive oxygen species)such as:hydrogen peroxide, superoxide radical,hydroxy radical,and singlet oxygen
- it is suitable for this role because: * it is readily available (occurs almost everywhere on the earth) * it diffuses easily across cell membranes * it is highly reactive and thus readily accepts electrons - the use of O2 by aerobic organisms is linked to the production of highly destructive ROS (reactive oxygen species) such as: hydrogen peroxide, superoxide radical, hydroxy radical, and singlet oxygen O2 (cont.)
The Electron Transport Chain(System) consists of a series of redox carriers in the inner membrane of the mitochondria in eukaryotes and the plasma membrane in aerobic prokaryotes that receive electrons from NADH and FADH,which are produced in Glycolysis Fat oxidation Citric Acid Cycle at the end of the pathway,the electrons,along with protons are donated to oxygen to form H,O
The Electron Transport Chain (System) - consists of a series of redox carriers in the inner membrane of the mitochondria in eukaryotes and the plasma membrane in aerobic prokaryotes that receive electrons from NADH and FADH2 which are produced in Glycolysis Fat oxidation Citric Acid Cycle - at the end of the pathway, the electrons, along with protons are donated to oxygen to form H2O

The Electron Transport Chain (cont.) during the transfer of electrons there is a decrease in reduction potential (AE= -0.32V) the energy released is coupled to several endergonic processes such as synthesis of ATP flow of Ca++into the mitochondrial matrix generation of heat in brown adipose tissue
The Electron Transport Chain (cont.) - during the transfer of electrons there is a decrease in reduction potential ( ΔE°ʹ = -0.32V ) - the energy released is coupled to several endergonic processes such as * synthesis of ATP * flow of Ca++ into the mitochondrial matrix * generation of heat in brown adipose tissue
The Electron Transport Chain (cont.) at the end of the pathway,the electrons,along with protons are donated to oxygen to form H,O -during the oxidation of NADH there are 3 steps in which energy loss is sufficient to account for ATP synthesis these steps occur in complexes I,Ill,and IV of the ETC
- at the end of the pathway, the electrons, along with protons are donated to oxygen to form H2O -during the oxidation of NADH there are 3 steps in which energy loss is sufficient to account for ATP synthesis - these steps occur in complexes I, III, and IV of the ETC The Electron Transport Chain (cont.)

Oxidative Phosphorylation is the mechanism by which electron transport is coupled to synthesis of ATP the creation of a proton gradient that accompanies electron transport is the driving force behind synthesis of ATP the complete oxidation of a glucose molecule results in the synthesis of 29.5 to 31 molecules of ATP depending on what other rxs are happening
Oxidative Phosphorylation - is the mechanism by which electron transport is coupled to synthesis of ATP - the creation of a proton gradient that accompanies electron transport is the driving force behind synthesis of ATP - the complete oxidation of a glucose molecule results in the synthesis of 29.5 to 31 molecules of ATP depending on what other rxs are happening
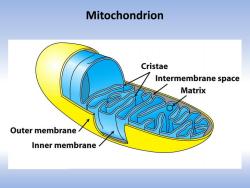
Mitochondrion Cristae Intermembrane space Matrix Outer membrane Inner membrane
Mitochondrion
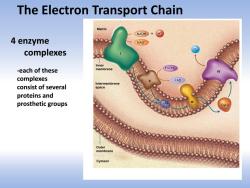
The Electron Transport Chain Matrix NADH+H 4 enzyme NAD 02 complexes Inner -each of these membrane FADH2 么 complexes FAD Intermembrane consist of several space proteins and prosthetic groups Outer membrane Cytosol
The Electron Transport Chain 4 enzyme complexes -each of these complexes consist of several proteins and prosthetic groups
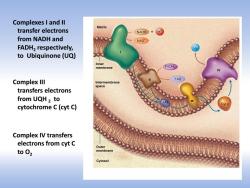
Complexes I and Il Matrix transfer electrons NADH+ from NADH and NAD' FADH2 respectively, to Ubiquinone(UQ) Inner membrane FADH2 么 FAD Complex Ill Intermembrane space transfers electrons from UQH2 to cytochrome C(cyt C) Complex IV transfers electrons from cyt C Outer toO2 membrane Cytosol
Complexes I and II transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2 respectively, to Ubiquinone (UQ) Complex III transfers electrons from UQH 2 to cytochrome C (cyt C) Complex IV transfers electrons from cyt C to O2
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)碳水化合物与碳水化合物代谢 Carbohydrates and Carbohydrate metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)氨基酸代谢 Amino Acid Metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)蛋白质 Proteins.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)细胞生物学(理论).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer——Protein Biosynthesis Translation(翻译).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer(RNA transcription 转录)RNA biosynthesis.pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013 Final term examination for Cellular Biochemistry(无答案).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)中文细胞生化理论留学生教学大纲.docx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)英文细胞生化理论留学生教学大纲 Syllabus for cellular biochemistry.docx
- 同济大学:《环境工程微生物学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)考试试卷及答案.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)The Study of Microbial Structure - Microscopy and Specimen Preparation.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)The History and Scope of Microbiology.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)Microbial Nutrition.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)Microbial Growth.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)Control of Microorganisms by Physical and Chemical Agents.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)The Viruses - Bacteriophages.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)微生物实验室手册(外文版)A Digital Manual for Medical Microbiology Laboratory..pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)认识微生物.pdf
- 南京农业大学:《遗传学实验》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)脂类代谢 Lipids and lipid metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)酶 Enzymes(主讲:王春光).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)脂代谢 Metabolism of Lipids.ppt
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)生物氧化 Biological Oxidation.pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)核苷酸代谢 Metabolism of Nucleotides.ppt
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer——DNA biosynthesis(DNA replication-复制).pptx
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(教学大纲)生物工艺学教学大纲 Bioprocess Technology Fundamentals and Application.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 01 Introduction(主讲:谭天伟).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 02 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 03 Kinetic Models.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 04 Mass Transport in Bioreactor.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 05 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 06 Modes of Process Operation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 07 Scale-up of Aerobic Processes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 08 灭菌 Sterilization.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 09 Immobilization of Biocatalysts.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Fermented Food.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 11 Microbial Energy Conversion Processes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 12 Antibiotics.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 13 Industrial Use of Enzymes.ppt
