同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)脂代谢 Metabolism of Lipids
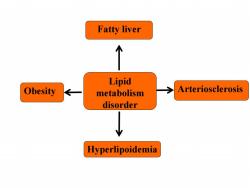
Fatty liver 个 Lipid Obesity metabolism Arteriosclerosis disorder Hyperlipoidemia
Lipid metabolism disorder Obesity Hyperlipoidemia Arteriosclerosis Fatty liver
Contents Concept,classification and structure of lipid Metabolism:Decomposition and biosynthesis The factors regulating lipid metabolism
Contents Concept, classification and structure of lipid Metabolism: Decomposition and biosynthesis The factors regulating lipid metabolism

Section 1 Introduction of lipid > Classfication and structure >Distribution and function >Digestion and absorption
ØClassfication and structure ØDistribution and function ØDigestion and absorption
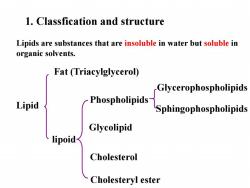
1.Classfication and structure Lipids are substances that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. Fat (Triacylglycerol) Glycerophospholipids Lipid Phospholipids Sphingophospholipids Glycolipid lipoid Cholesterol Cholesteryl ester
Phospholipids lipoid Lipid Glycolipid Fat (Triacylglycerol) Cholesterol Glycerophospholipids Sphingophospholipids 1. Classfication and structure Cholesteryl ester Lipids are substances that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents

Fat Fat:Triacylglycerols(TAG),esters of fatty acids with glycerol .com
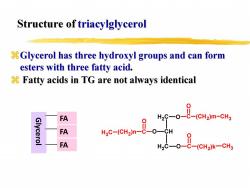
Structure of triacylglycerol Glycerol has three hydroxyl groups and can form esters with three fatty acid. 8 Fatty acids in TG are not always identical FA 2s。总-cr3m-cn Glycerol FA MC-(CMa-8 FA
FAFAFA Glycerol H 2 CC H H 2 C O OO CO (C H 2)m C H 3 CO (C H 2)k C H 3 CO (CH2 H C )n 3
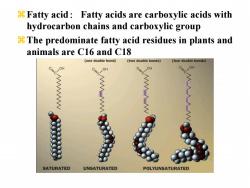
8 Fatty acid:Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with hydrocarbon chains and carboxylic group 8 The predominate fatty acid residues in plants and animals are C16 and C18 (one double bond) (two double bonds】 (four double bonds) OH 0 OH 0 OH OH WWWWWww SATURATED UNSATURATED POLYUNSATURATED
zFatty acid: Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with hydrocarbon chains and carboxylic group zThe predominate fatty acid residues in plants and animals are C16 and C18

Common fatty acid Unsaturated fatty acid 16:1△9℃ CH;(CH);CH=CH(CH2)COOH. Palmitoleic acid 18:1A9℃ CH(CH2)CH=CH(CH2)COOH. Oleic acid 18:2△c,12c CH(CH2)CH=CHCH CH=CH(CH2)COOH.I Linoleic acid 18:3 CH,CH2CH=CHCH CH=CHCH2 CH=CH △9C12C,15C Linolenic acid -(CH2)COOH. 20:4 CH(CH)CH=CHCH CH=CHCH,CH=CH A5C8C,HIC,14C Arachidonic acid -CH2CH=CH(CH)COOH
Common fatty acid Saturated fatty acid Unsaturated fatty acid
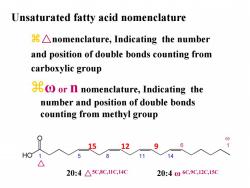
Unsaturated fatty acid nomenclature 8Anomenclature,Indicating the number and position of double bonds counting from carboxylic group or n nomenclature,Indicating the number and position of double bonds counting from methyl group 9 6 HO 8 11 14 20:4△5C,8C,1C,14C 20:406C,9C,12C,15C
z△nomenclature, Indicating the number and position of double bonds counting from carboxylic group zω or n nomenclature, Indicating the number and position of double bonds counting from methyl group 15 12 9 △ Unsaturated fatty acid nomenclature 20:4 △5C,8C,11C,14C 20:4 ω 6C,9C,12C,15C

Essential Fatty Acids(EFA): Some fatty acids that are necessary for human nutrition,but can't synthesis in the body,must obtain from food Including: Linoleic acid (18:2) Linolenic acid (18:3)
Some fatty acids that are necessary for human nutrition, but can’t synthesis in the body, must obtain from food . Including: Essential Fatty Acids(EFA): (18:2) (18:3)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)酶 Enzymes(主讲:王春光).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)脂类代谢 Lipids and lipid metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Aerobic Metabolism II Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation(ETC).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)碳水化合物与碳水化合物代谢 Carbohydrates and Carbohydrate metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)氨基酸代谢 Amino Acid Metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)蛋白质 Proteins.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)细胞生物学(理论).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer——Protein Biosynthesis Translation(翻译).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer(RNA transcription 转录)RNA biosynthesis.pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013 Final term examination for Cellular Biochemistry(无答案).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)中文细胞生化理论留学生教学大纲.docx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)英文细胞生化理论留学生教学大纲 Syllabus for cellular biochemistry.docx
- 同济大学:《环境工程微生物学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)考试试卷及答案.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)The Study of Microbial Structure - Microscopy and Specimen Preparation.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)The History and Scope of Microbiology.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)Microbial Nutrition.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)Microbial Growth.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)Control of Microorganisms by Physical and Chemical Agents.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)The Viruses - Bacteriophages.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)生物氧化 Biological Oxidation.pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)核苷酸代谢 Metabolism of Nucleotides.ppt
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer——DNA biosynthesis(DNA replication-复制).pptx
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(教学大纲)生物工艺学教学大纲 Bioprocess Technology Fundamentals and Application.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 01 Introduction(主讲:谭天伟).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 02 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 03 Kinetic Models.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 04 Mass Transport in Bioreactor.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 05 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 06 Modes of Process Operation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 07 Scale-up of Aerobic Processes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 08 灭菌 Sterilization.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 09 Immobilization of Biocatalysts.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Fermented Food.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 11 Microbial Energy Conversion Processes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 12 Antibiotics.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 13 Industrial Use of Enzymes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 14 Biological Waste Water Treatment.ppt
- 《药物生物技术》:新的芯片毛细管电泳及其联用技术研究应用进展(复旦大学:陈执中).pdf
- 三明学院:资源与化工学院生物技术专业本科课程教学大纲(汇编).pdf
