北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 14 Biological Waste Water Treatment

Chapter 14 Biological Waste Water Treatment
Chapter 14 Biological Waste Water Treatment

Main end products of the main waste water impurities in the three main process ypes employed for waste water purification Process type Impurity Aerobic Anoxic Anaerobic Organic carbon CO2+biomass CO2+biomass CO2+CHa+biomass Nitrogen NO3+biomass N2+biomass biomass Phosphorous biomass biomass biomass Heavy metals biomass biomass biomass
Process type Impurity Aerobic Anoxic Anaerobic Organic carbon CO2+biomass CO2 + biomass CO2+CH4+biomass Nitrogen NO3 - +biomass N2+biomass biomass Phosphorous biomass biomass biomass Heavy metals biomass biomass biomass Main end products of the main waste water impurities in the three main process ypes employed for waste water purification
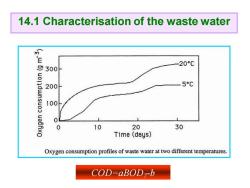
14.1 Characterisation of the waste water (w 6)uondwnsuo -20C 300 200 5C 100 ua6fxo 0 0 10 20 30 Time(days) Oxygen consumption profiles of waste water at two different temperatures. COD=aBODz-b
COD=aBOD7 -b 14.1 Characterisation of the waste water

BOD COD
BOD COD

14.2 Aerobic processes for BOD removal 14.2.1 Microflora of aerobic processes Examples of bacteria often reported from investigations on the microflora of aerobic waste water treatment Organisms Comment Achromobacter Common water and soil bacteria Acinetobacter Utilised for phosphorous removal Alcaligenes Common water and soil bacteria.Important denitrifyer Bacillus Producer of extracellular hydrolytic enzymes Beggiatoa Filamentous bacteria stimulated by high sulphur content Corynebacterium Common water and soil bacteria Escherichia coli Introduced from faeces,together with other enteric bacteria,but not considered important in the process. Flavobacterium Common water and soil bacteria Methanogenic bacteria Obligately anaerobic methane producing bacteria.See Chapter 14.1 Microthrix Filamentous bacteria stimulated by low sludge load and high fatty acid content.May cause sludge bulking. Nitrobacter Obligate aerobe and litoautotroph which oxidises NO2-to NO3- Nitrosomonas Obligate aerobe and litoautotroph which oxidises NH3 to NO2- Nocardia Filamentous actinomycete associated with foaming in the activated sludge process Pseudomonas Important denitrifyer.Utilise a wide spectrum of carbon sources. Sphaerotilus natans Filamentous bacteria that can cause bulking of the sludge. zoogloea ramigera Producer of extracellular polysaccharides. Utilises a wide spectrum of carbon sources Believed to be important for flocculation and biofilm formation
14.2.1 Microflora of aerobic processes 14.2 Aerobic processes for BOD removal
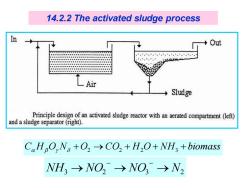
14.2.2 The activated sludge process n Out Air Sludge Principle design of an activated sludge reactor with an aerated compartment (left) and a sludge separator(right). CoHO,Ns+O2>CO2+H2O+NH3 +biomass WH3-→NO2→NO→N2
C H O N + O → CO + H O + NH + biomass 2 2 2 3 NH3 → NO2 → NO3 → N2 − − 14.2.2 The activated sludge process
里 得 , H..co
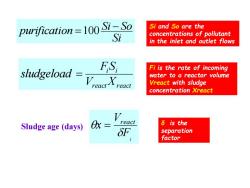
purification =100 Si-So Si and So are the Si concentrations of pollutant in the inlet and outlet flows sludgeload FS, Fi is the rate of incoming water to a reactor volume Vreact with sludge concentration Xreact react Sludge age (days) 脉= δis the SF separation factor
Si Si So purification − =100 react react i i V X FS sludgeload = i F V x react = Si and So are the concentrations of pollutant in the inlet and outlet flows Fi is the rate of incoming water to a reactor volume Vreact with sludge concentration Xreact Sludge age (days) δ is the separation factor
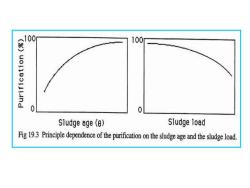
女 100 0 0 Sludge age (e) Sludge load Fig 19.3 Principle dependence of the purification on the sludge age and the sludge load
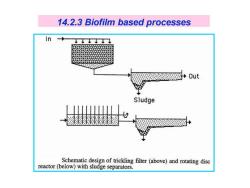
14.2.3 Biofilm based processes Out Sludge Schematic design of trickling filter(above)and rotating disc reactor(below)with sludge separators
14.2.3 Biofilm based processes
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 13 Industrial Use of Enzymes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 12 Antibiotics.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 11 Microbial Energy Conversion Processes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Fermented Food.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 09 Immobilization of Biocatalysts.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 08 灭菌 Sterilization.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 07 Scale-up of Aerobic Processes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 06 Modes of Process Operation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 05 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 04 Mass Transport in Bioreactor.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 03 Kinetic Models.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 02 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 01 Introduction(主讲:谭天伟).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(教学大纲)生物工艺学教学大纲 Bioprocess Technology Fundamentals and Application.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer——DNA biosynthesis(DNA replication-复制).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)核苷酸代谢 Metabolism of Nucleotides.ppt
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)生物氧化 Biological Oxidation.pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)脂代谢 Metabolism of Lipids.ppt
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)酶 Enzymes(主讲:王春光).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)脂类代谢 Lipids and lipid metabolism.pdf
- 《药物生物技术》:新的芯片毛细管电泳及其联用技术研究应用进展(复旦大学:陈执中).pdf
- 三明学院:资源与化工学院生物技术专业本科课程教学大纲(汇编).pdf
- 上海海洋大学:生命学院2011年版课程教学大纲汇编(目录).pdf
- 上海海洋大学:生命学院2011年版课程教学大纲汇编(正文).pdf
- 上海海洋大学:食品学院2018年版课程教学大纲汇编(生物制药专业).pdf
- 山东大学:《细胞生物学》课程教学大纲(共十三章).pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)HIV研究不能误入歧途.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)一种细菌在极端环境下可产氢.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)全方位认识微生物.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)关于农业微生物的应用.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)嗜极菌的应用.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)土壤中放线菌的分离与纯化.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)微生物培养基的配制与灭菌.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)植物感染的真菌及杀菌剂.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)细菌产聚羟基烷酸(PHA).pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)蕈菌.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)蛋白胨.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)革兰氏阴性菌细胞壁外膜组成成分.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)噬菌体侵染大肠杆菌.pdf
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(文献资料,打印版)生活小常识.pdf
