同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)蛋白质 Proteins

CHAPTER 1 Proteins Overview Amino acid structures Four levels of organization in proteins -02 binding proteins:myoglobin and hemoglobin 2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate function in RBC protein physical-chemical properties and purifications methods Clinical correlations:Prion disease,Scurvy, Methemoglobinemia
CHAPTER 1 Proteins – Amino acid structures – Four levels of organization in proteins – O2 binding proteins: myoglobin and hemoglobin – 2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate function in RBC – protein physical-chemical properties and purifications methods – Clinical correlations: Prion disease, Scurvy, Methemoglobinemia Overview
Section Molecular Composition of Proteins life is maintained by molecular network system Protein make up about 15%of the cell Proteins play key roles in a living system Enzymes,Structural,Transport,Motor Storage,Signaling,Receptors,Gene regulation Special functions (antibody)
• life is maintained by molecular network system • Protein make up about 15% of the cell • Proteins play key roles in a living system Enzymes, Structural, Transport, Motor Storage, Signaling, Receptors, Gene regulation Special functions (antibody) ………. ……….. ………… Molecular Composition of Proteins Section 1
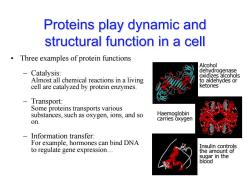
Proteins play dynamic and structural function in a cell Three examples of protein functions Alcohol Catalysis: dehydrogenase oxidizes alcohols Almost all chemical reactions in a living to aldehydes or cell are catalyzed by protein enzymes. ketones -Transport: Some proteins transports various substances,such as oxygen,ions,and so Haemoglobin on. carries oxygen Information transfer: For example,hormones can bind DNA Insulin controls to regulate gene expression... the amount of sugar in the blood
Proteins play dynamic and structural function in a cell • Three examples of protein functions – Catalysis: Almost all chemical reactions in a living cell are catalyzed by protein enzymes. – Transport: Some proteins transports various substances, such as oxygen, ions, and so on. – Information transfer: For example, hormones can bind DNA to regulate gene expression… Alcohol dehydrogenase oxidizes alcohols to aldehydes or ketones Haemoglobin carries oxygen Insulin controls the amount of sugar in the blood

Alcohol acts as a central nervous system depressant alcohol abuse

The Chemical Breakdown of Alcohol CH CH,OH_ADH>CHaCHO ALDH>CH COO- Acetaldehyde Acetate The chemical name for alcohol is ethanol(CH3CH2OH).The body processes and eliminates ethanol in separate steps.Chemicals called enzymes help to break apart the ethanol molecule into other compounds (or metabolites),which can be processed more easily by the body.Some of these intermediate metabolites can have harmful effects on the body. Most of the ethanol in the body is broken down in the liver by an enzyme called alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH),which transforms ethanol into a toxic compound called acetaldehyde(CH3CHO),a known carcinogen.However,acetaldehyde is generally short-lived; it is quickly broken down to a less toxic compound called acetate (CHaCOO)by another enzyme called aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH).Acetate then is broken down to carbon dioxide and water. mainly in tissues other than the liver
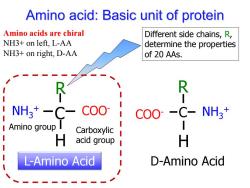
Amino acid:Basic unit of protein Amino acids are chiral Different side chains,R, NH3+on left.L-AA determine the properties NH3+on right,D-AA of 20 AAs. C- NH虜*一C- C00 COO--C-NH3+ I Amino group I Carboxylic H acid group H L-Amino Acid D-Amino Acid
Amino acid: Basic unit of protein NH COO- 3 + C R H L-Amino Acid Different side chains, R, determine the properties of 20 AAs. Amino group Carboxylic acid group Amino acids are chiral NH3+ on left, L-AA NH3+ on right, D-AA COO- NH3 + C R H D-Amino Acid
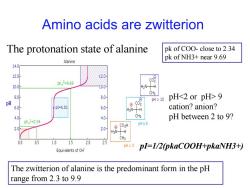
Amino acids are zwitterion The protonation state of alanine pk of COO-close to 2.34 pk of NH3+near 9.69 Alanine 14.0 12.0h pK2=9.69 10.0 H2N-H CH3 8.0 8.0- pH>10 pH9 02 6.0 =601 6.0- HgN-H cation?anion? 4.0 4.0 CH3 pH between 2 to 9? pKg1=2.34 pH≈6 2.0 2.0 9C02H H3N-H CH3 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 <2 Equivalents of OH" pl=1/2(pkaCOOH+pkaNH3+) The zwitterion of alanine is the predominant form in the pH range from 2.3 to 9.9
Amino acids are zwitterion The zwitterion of alanine is the predominant form in the pH range from 2.3 to 9.9 pk of COO- close to 2.34 pk of NH3+ near 9.69 pH 9 cation? anion? pH between 2 to 9? The protonation state of alanine pI=1/2(pkaCOOH+pkaNH3+)
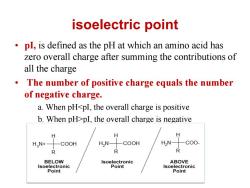
isoelectric point pl,is defined as the pH at which an amino acid has zero overall charge after summing the contributions of all the charge 。 The number of positive charge equals the number of negative charge. a.When pHpI,the overall charge is negative H HaN+- COOH H,N COOH HN- -C00- R R R BELOW Isoelectronic ABOVE Isoelectronic Point Isoelectronic Point Point
isoelectric point • pI, is defined as the pH at which an amino acid has zero overall charge after summing the contributions of all the charge • The number of positive charge equals the number of negative charge. a. When pHpI, the overall charge is negative c. When pH=pI, there is no overall charge
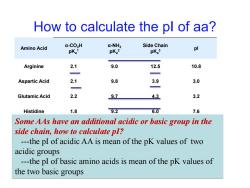
How to calculate the pl of aa? Amino Acid a-CO>H a-NH3 Side Chain pKa1 pKa2 pKa3 pl Arginine 2.1 9.0 12.5 10.8 Aspartic Acid 2.1 9.8 3.9 3.0 Glutamic Acid 2.2 97 43 3.2 Histidine 1.8 9.2 6.0 7.6 Some AAs have an additional acidic or basic group in the side chain,how to calculate pI? ---the pI of acidic AA is mean of the pK values of two acidic groups ---the pI of basic amino acids is mean of the pK values of the two basic groups
How to calculate the pI of aa? Amino Acid α-CO2H pKa 1 α-NH3 pKa 2 Side Chain pKa 3 pI Arginine 2.1 9.0 12.5 10.8 Aspartic Acid 2.1 9.8 3.9 3.0 Glutamic Acid 2.2 9.7 4.3 3.2 Histidine 1.8 9.2 6.0 7.6 Some AAs have an additional acidic or basic group in the Lysine 2.2 9.0 10.5 9.8 side chain, how to calculate pI? ---the pI of acidic AA is mean of the pK values of two acidic groups ---the pI of basic amino acids is mean of the pK values of the two basic groups

What's the significance of zwitterion property? Ionizable groups stabilize the pH value of the solution against external disturbances. Any ionizable group buffers the pH of the solution at pH value close to its pK. The buffering capacity of ionizable groups helps human maintain a constant in body fluid. A contribution to homeostatsis
What’s the significance of zwitterion property? • Ionizable groups stabilize the pH value of the solution against external disturbances. • Any ionizable group buffers the pH of the solution at pH value close to its pK. • The buffering capacity of ionizable groups helps human maintain a constant in body fluid. A contribution to homeostatsis
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)细胞生物学(理论).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer——Protein Biosynthesis Translation(翻译).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer(RNA transcription 转录)RNA biosynthesis.pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-2013 Final term examination for Cellular Biochemistry(无答案).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)中文细胞生化理论留学生教学大纲.docx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)英文细胞生化理论留学生教学大纲 Syllabus for cellular biochemistry.docx
- 同济大学:《环境工程微生物学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)考试试卷及答案.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)The Study of Microbial Structure - Microscopy and Specimen Preparation.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)The History and Scope of Microbiology.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)Microbial Nutrition.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)Microbial Growth.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)Control of Microorganisms by Physical and Chemical Agents.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)The Viruses - Bacteriophages.pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)微生物实验室手册(外文版)A Digital Manual for Medical Microbiology Laboratory..pdf
- 《环境微生物学与实验》课程教学资源(文献资料)认识微生物.pdf
- 南京农业大学:《遗传学实验》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 南京农业大学:《动植物野外实习》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 南京农业大学:《细胞遗传学(双语)》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 南京农业大学:《前沿生命科学的奥秘》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)氨基酸代谢 Amino Acid Metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)碳水化合物与碳水化合物代谢 Carbohydrates and Carbohydrate metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Aerobic Metabolism II Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation(ETC).pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)脂类代谢 Lipids and lipid metabolism.pdf
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)酶 Enzymes(主讲:王春光).pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)脂代谢 Metabolism of Lipids.ppt
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)生物氧化 Biological Oxidation.pptx
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)核苷酸代谢 Metabolism of Nucleotides.ppt
- 同济大学:《细胞的生物化学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Genetic information transfer——DNA biosynthesis(DNA replication-复制).pptx
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(教学大纲)生物工艺学教学大纲 Bioprocess Technology Fundamentals and Application.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 01 Introduction(主讲:谭天伟).ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 02 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 03 Kinetic Models.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 04 Mass Transport in Bioreactor.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 05 Reactor Design and Instrumentation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 06 Modes of Process Operation.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 07 Scale-up of Aerobic Processes.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 08 灭菌 Sterilization.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 09 Immobilization of Biocatalysts.ppt
- 北京化工大学:《生物工艺学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Fermented Food.ppt
