重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程课程教学大纲 A Teaching Outline for Pathology Course
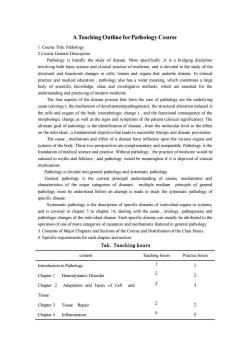
A Teaching Outline for Pathology Course 1.Course Title:Pathology 2.Course General Description Pathology is literally the study of disease.More specifically ,it is a bridging discipline involving both basie science and clinical practice of medicine,and is devoted to the study of the structural and functional changes in cells,tissues and organs that underlie discase.In clinical and medical ducation pathology also hasawide ine wloleed me understanding and practicing of modern medicine. The four aspects of the disease process that form the core of pathology are the underlying cause(etiology),the mechanism of development(pathogenesis),the structural alteration induced in organs of the body (morphologic change and the functionalo ehnse elthend mth tient (lnie cquence of the significance).The ultimate goal of pathology is the identification of disease,from the molecular level to the effect on the individual,a fundamental objective that leads to successful therapy and disease prevention. The cause.mechanism and effect of a disease have influence upon the various organs and ectivesare and inseparable.Pathology is the end practice.Without pathologythe pra ctice of medi ould be reduced to myths and folklore and pathology would be meaningless if it is deprived of clinical implications. Pathology is divided into general pathology and systematic pathology ra pathology is the cuent principal undersadno mechanisms and chara of the diseases multip mediam principle of genera pathology must be understood before an attempt is made to study the systematic pathology of specific disease. Systematic pathology is the description of specific diseases of individual organs or systems, and is covered in chapter 5 to chapter 14.dealing with the cause.etiology.pathogenesis and pathologic changes of the operation of one of more of and mechanisms featured in general pathology 3.Contents of Major Chapters and Sections of the Course and Distribution of the Class Hours. 4.Specific requirements for each chapter and section. Tab.Teaching hours content Teaching hours Practice hours Introduction to Patholog 1 Chapter 1 Hemodynamic Disorder 5 Chapter 2 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and 4 Tissue Chapter 3 Tissue Repai Chapter 4 Inflammation 6
A Teaching Outline for Pathology Course 1. Course Title: Pathology 2.Course General Description Pathology is literally the study of disease. More specifically ,it is a bridging discipline involving both basic science and clinical practice of medicine, and is devoted to the study of the structural and functional changes in cells, tissues and organs that underlie disease. In clinical practice and medical education , pathology also has a wider meaning, which constitutes a large body of scientific knowledge, ideas and investigative methods, which are essential for the understanding and practicing of modern medicine. The four aspects of the disease process that form the core of pathology are the underlying cause (etiology), the mechanism of development(pathogenesis), the structural alteration induced in the cells and organs of the body (morphologic change ) , and the functional consequence of the morphologic change as well as the signs and symptoms of the patient (clinical significance). The ultimate goal of pathology is the identification of disease , from the molecular level to the effect on the individual , a fundamental objective that leads to successful therapy and disease prevention. The cause , mechanism and effect of a disease have influence upon the various organs and systems of the body. These two perspectives are complementary and inseparable. Pathology is the foundation of medical science and practice. Without pathology , the practice of medicine would be reduced to myths and folklore ; and pathology would be meaningless if it is deprived of clinical implications. Pathology is divided into general pathology and systematic pathology. General pathology is the current principal understanding of causes, mechanisms and characteristics of the major categories of diseases. multiple mediam principle of general pathology must be understood before an attempt is made to study the systematic pathology of specific disease. Systematic pathology is the description of specific diseases of individual organs or systems, and is covered in chapter 5 to chapter 14, dealing with the cause , etiology, pathogenesis and pathologic changes of the individual disease. Each specific disease can usually be attributed to the operation of one of more categories of causation and mechanisms featured in general pathology. 3. Contents of Major Chapters and Sections of the Course and Distribution of the Class Hours. 4. Specific requirements for each chapter and section. Tab. Teaching hours content Teaching hours Practice hours Introduction to Pathology 1 1 Chapter 1 Hemodynamic Disorder 5 5 Chapter 2 Adaptation and Injury of Cell and Tissue 4 4 Chapter 3 Tissue Repair 2 2 Chapter 4 Inflammation 6 6
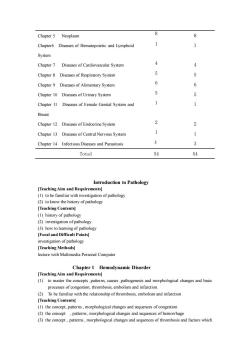
8 Chapter 5 Neoplasm 8 Chapter6 Diseases of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid System Chapter 7 Diseases of Cardiovascular System 4 Chapter 8 Diseases of Respiratory System 5 Chapter9 Diseases of Alimentary System 6 6 Chapter 10 Diseases of Urinary System 5 Chapter 11 Diseases of Female Genital System and 1 Breast Chapter 12 Diseases of Endocrine System 2 Chapter 13 Diseases of Central Nervous System Chapter 14 Infectious Diseases and Parasitosis 3 3 Total 54 54 Introduction to Pathology [Teaching Aim and Requirementsl (1)to be familiar with investigation of pathology (2)to know the history of pathology [Teaching Contents] (1)history of pathology (2)investigation of pathology (3)how to learning of pathology Focal and Difficult Points] investigation of pathology [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 1 Hemodynamic Disorder [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1)to master the concepts,pattern causespathogenesis and morphological hanges and basic processes of congestion,thrombosis,embolism and infarction. (2)To be familiar with the relationship of thrombosis.embolism and infarction [Teaching Contents] (1)the concept.patterns.morphological changes and sequences of congestion (2)the concept .patterns,m logical ch anges and s (3)the hangesand of thrombosis and factors which
Chapter 5 Neoplasm 8 8 Chapter6 Diseases of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid System 1 1 Chapter 7 Diseases of Cardiovascular System 4 4 Chapter 8 Diseases of Respiratory System 5 5 Chapter 9 Diseases of Alimentary System 6 6 Chapter 10 Diseases of Urinary System 5 5 Chapter 11 Diseases of Female Genital System and Breast 1 1 Chapter 12 Diseases of Endocrine System 2 2 Chapter 13 Diseases of Central Nervous System 1 1 Chapter 14 Infectious Diseases and Parasitosis 3 3 Total 54 54 Introduction to Pathology [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) to be familiar with investigation of pathology (2) to know the history of pathology [Teaching Contents] (1) history of pathology (2) investigation of pathology (3) how to learning of pathology [Focal and Difficult Points] investigation of pathology [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 1 Hemodynamic Disorder [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) to master the concepts ,patterns, causes ,pathogenesis and morphological changes and basic processes of congestion, thrombosis, embolism and infarction. (2) To be familiar with the relationship of thrombosis, embolism and infarction [Teaching Contents] (1) the concept, patterns , morphological changes and sequences of congestion (2) the concept , patterns , morphological changes and sequences of hemorrhage (3) the concept , patterns , morphological changes and sequences of thrombosis and factors which

may result in thrombus formation (4)the of embolism moving pathway of embolus,types and of embolism Focal and Difficult Points (1)the concepts,patterns,causes,pathogenesis and morphological changes and basic processes of congestion,thrombosis,embolism and infaretion (2)factors which may result in thrombus formation (3)moving pathway ofembol (4)pulmonary congeston and liver congestion Teaching Methods lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 2 Adaptation and Injury of Celly and Tissu Teaching Aim and Requirements (1)to master the concepts about cell injury,adaptation and repair (2)to master the patterns,causes,pathogenesis and morphological changes of cell injury ITeaching Contentsl (mechanisms of el injury (2)the concepts. patterns,causes pathogenesis and morphological changes of degeneration (3)the concepts,patterns,causes,pathogenesis,morphological changes and sequences of necrosis. (4)the concepts,patterns,causes,pathogenesis,morphological changes and sequences of atrophy. (5) the concepts, patterns.morphological changes of hypertrophy,hyperplasia and metaplasia Focal and Difficult Pointsl (1)the patterns and morphological changes of degeneration and necrosis (2)the mechanisma of fatty change [Teaching Methods] eture with Multimedia Personl Computer Chapter3 Tissue Repair ITeaching Aim and Reguirementsl to be familiar with the morphological changes of adaptation and repair [Teaching Contents] (1)classification of cells by their regenerative potential (2)regenerative processes by different tissue (3)morphology,role of granulation tissue (5)basic proc (6)basic proc ses of wound healing of nerves Focal and Difficult Points (1)classification of cells by their regenerative potential (2)morphology,role of granulation tissue
may result in thrombus formation (4) the concept of embolism; moving pathway of embolus; types and sequences of embolism (5) the concept of infarction ; etiology , types , morphology and sequences of infarction [Focal and Difficult Points] (1) the concepts ,patterns, causes ,pathogenesis and morphological changes and basic processes of congestion, thrombosis, embolism and infarction (2) factors which may result in thrombus formation (3) moving pathway of embolus (4) pulmonary congeston and liver congestion [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 2 Adaptation and Injury of Cell y and Tissue [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) to master the concepts about cell injury , adaptation and repair (2) to master the patterns, causes ,pathogenesis and morphological changes of cell injury [Teaching Contents] (1) causes and mechanisms of cell injury (2) the concepts , patterns , causes pathogenesis and morphological changes of degeneration (3) the concepts , patterns , causes , pathogenesis , morphological changes and sequences of necrosis. (4) the concepts , patterns , causes ,pathogenesis , morphological changes and sequences of atrophy. (5) the concepts , patterns , morphological changes of hypertrophy, hyperplasia and metaplasia. [Focal and Difficult Points] (1) the patterns and morphological changes of degeneration and necrosis (2) the mechanisma of fatty change [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 3 Tissue Repair [Teaching Aim and Requirements] to be familiar with the morphological changes of adaptation and repair [Teaching Contents] (1) classification of cells by their regenerative potential (2) regenerative processes by different tissue (3) morphology , role of granulation tissue (4) basic processes and types of wound healing (5) basic processes of fracture healing (6) basic processes of wound healing of nerves [Focal and Difficult Points] (1) classification of cells by their regenerative potential (2) morphology , role of granulation tissue

ITeaching Methodsl lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 4 Inflammation [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1)to master the concepts about the inflammation (2)tomaster the pathological changes thesite of (3)tomaster the pathogenesis of inflammation (4)to master the common types and morphological characteristics of acute and chronic inflammation (5)to master the local signs and systemic manifestation of inflammation (6)tobe familiar with infammation mediators [Teaching Contents (1)concept and causes of inflammation;basic pathologic changes of inflammation (2)coneept sources and effects of inflammatory mediators (3)clinical manifestation of inflammation (4)morphologic patterns ofacute and chronic inflammation Focal and Difficult Points (1)the concepts about the inflammation,essential pathological changes at the site of inflammation (2)pathogenesis of inflammation and the common types and morphological characteristics of acute and chronic inflammation (3)the local signs and systemic manifestation of infammation (4)inflamm [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 5 Neoplasm [Teaching Aim and Requ rements (1)to master the morphological characteristics of benign and malignant tumors (2)to master atypia of neoplasms (3)to master growth and spread of neoplasms (4)to master concepts and morphology of carcinoma in situ ITeaching contentsl (2)atypia of neoplasms (3)growth and spread of neoplasms (4)characteristics of benign and malignant tumor etion of common tumors (7)carcinoma in sitt (8)clinical features of neoplasia (9)etiology and carcinogenesis Focal and Difficult Points]
[Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 4 Inflammation [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) to master the concepts about the inflammation (2) to master the essential pathological changes at the site of inflammation (3) to master the pathogenesis of inflammation (4) to master the common types and morphological characteristics of acute and chronic inflammation (5) to master the local signs and systemic manifestation of inflammation (6) to be familiar with inflammation mediators [Teaching Contents] (1) concept and causes of inflammation ; basic pathologic changes of inflammation (2) concept,sources and effects of inflammatory mediators (3) clinical manifestation of inflammation (4) morphologic patterns of acute and chronic inflammation [Focal and Difficult Points] (1) the concepts about the inflammation , essential pathological changes at the site of inflammation (2) pathogenesis of inflammation and the common types and morphological characteristics of acute and chronic inflammation (3) the local signs and systemic manifestation of inflammation (4) inflammation mediators [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 5 Neoplasm [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) to master the morphological characteristics of benign and malignant tumors (2) to master atypia of neoplasms (3) to master growth and spread of neoplasms (4) to master concepts and morphology of carcinoma in situ [Teaching Contents] (1) definition , morphology (2) atypia of neoplasms (3) growth and spread of neoplasms (4) characteristics of benign and malignant tumors (5) nomenclature of neoplasms (6) brief introduction of common tumors (7) carcinoma in situ (8) clinical features of neoplasia (9) etiology and carcinogenesis [Focal and Difficult Points]

(1)the morphological characteristics of benign and malignant tumors of neoplasms (4)carcinoma in situ (5)the process and mechanisms of tumor invasion and metastasis (6)carcinogenesis [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 6 Diseases of Hematopoietic and Lvmphoid System [Teaching Aim and Requirements] to be familiar with regular categories of malignant lymphoma and their morphology Teaching Contents oma and Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma Focal and Difficult Points Hodgkin's lymphoma [Teaching Methodsl ecture with Multimedia Personal Compute Chapter 7 Diseases of Cardiovascular System ITeaching Aim and Requirementsl (1)to master the basic pathologic changes of atherosclerosis,especially for ischemic heart diseases (coronary heart disease)and its harmfuness (2)t naster the hasic ch anges of hypertension and the pathologic changes of each chief organs (3)to master the basic pathologic changes of rheumatic fever and heart disease;to master the basic pathologic changes,clinical course and prognosis of rheumatic heart disease.To master the morphologic characteristics and the affection on bloodstream dynamics of chronic valyular diseas (4)Tobe familiar with the characteristics of (5)To be familiar with the characteristics of myocardits and cardiomyopathy ITeaching Contentsl (1)etiology.pathogenesis.morphology and clinicopathologic correlation of atherosclerosis (2)ischemic heart diseases (coronary heart disease)including angina pectoris,myocardial and sudden cardiac de ()etiology,pathogenesis,morphology of hypertension;the characteristics of malignant hypertension (4)etiology,pathogenesis,morphology and clinicopathologic correlation of rheumatic fever and heart disease rphologic characteristics of valvular heartis the affection on (6)the characteristics of infective endocarditis (7)the characteristics of myocardits and cardiomyopathy [Focal and Difficult Points]
(1) the morphological characteristics of benign and malignant tumors (2) atypia of neoplasms (3) growth and spread of neoplasms (4) carcinoma in situ (5) the process and mechanisms of tumor invasion and metastasis (6) carcinogenesis [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 6 Diseases of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid System [Teaching Aim and Requirements] to be familiar with regular categories of malignant lymphoma and their morphology [Teaching Contents] Hodgkin’s lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma [Focal and Difficult Points] Hodgkin’s lymphoma [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Compute Chapter 7 Diseases of Cardiovascular System [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) to master the basic pathologic changes of atherosclerosis, especially for ischemic heart diseases (coronary heart disease) and its harmfulness (2) to master the basic pathologic changes of hypertension and the pathologic changes of each chief organs (3) to master the basic pathologic changes of rheumatic fever and heart disease; to master the basic pathologic changes ,clinical course and prognosis of rheumatic heart disease. To master the morphologic characteristics and the affection on bloodstream dynamics of chronic valvular disease. (4) To be familiar with the characteristics of infective endocarditis (5) To be familiar with the characteristics of myocardits and cardiomyopathy [Teaching Contents] (1) etiology, pathogenesis, morphology and clinicopathologic correlation of atherosclerosis (2) ischemic heart diseases (coronary heart disease) including angina pectoris ,myocardial infarction, ischemic cardiomyopathy and sudden cardiac death (3) etiology, pathogenesis , morphology of hypertension ; the characteristics of malignant hypertension (4) etiology , pathogenesis, morphology and clinicopathologic correlation of rheumatic fever and heart disease (5) pathogenesis and the morphologic characteristics of valvular heart disease; the affection on bloodstream dynamics of chronic valvular disease (6) the characteristics of infective endocarditis (7) the characteristics of myocardits and cardiomyopathy [Focal and Difficult Points]

(1)pathogenesis basic morphologic changes of atherosclerosis (2)ischemic heart diseases (rary heart disease)angina infarctior (3)pathogenesis,morphology of hypertensior (4)morphology of rheumatic fever and heart disease (5)the morphologic characteristics of valvular heart disease,the affection on bloodstream dynamics of chronic valvular disease Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 8 Diseases of Respiratory System ITeaching Aim and Requirementsl (1)to master the morphological changes and pathogenesis of chronic bronchitis,emphysema and cor pulmonale (2)to master the pathological changes and clinical association of lobar pneumonia,to master the morphological characteristics of the lobular pneumonia (3)To be familiar with the pathological changes of bronchiectasis and interstitial pneumonia (4)to master the basic pathology of tuberculosis and the cours of development in tuberculosis (5)to be familiar vith the rphological changes and path ogen licosis (7)to know SARS and bird flu ITeaching Contentsl (1)etiology pathogenesis.morphology.clinical pathologic correlation (2)etiology pathogenesis,types morphology,clinical pathologic comrelation of pulmonary (3)pathogenesis,morphology and clinical pathologic correlation of bronchiectasis (4)etiology,morphology,clinical pathologic correlation and complications of lobar pneumonia (5)morphological changes characteristics of the lobular pneumonia and interstitial pneumonia (6)changes and pathogenesis of s and m nholo of cor pulmonal (8)the basic pathology of tuberculosis and the coursof development in tuberculosis (9)etiology,pathogenesis.basic morphology of tuberculosis:the transition rule of basic morphology of tuberculosis.primary pulmonary tuberculosis and secondary pulmonary tuberculosis,extrapulmonary tuberculosis noma and nasopharyngeal carcinom (1)the morphological changes and pathogenesis of chronic bronchitis emphysema and cor pulmonale (2)the pathological changes and clinical association of lobar pneumonia (3)the morphological cha arteriicsofthelobulhrpmeumon ()morphology of r the nsition rule of basic morphology of tuberculosis,primary pulmonary tuberculosis and secondary pulmonary tuberculosis ITeaching Methodsl lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer
(1) pathogenesis, basic morphologic changes of atherosclerosis (2) ischemic heart diseases (coronary heart disease) - angina pectoris ,myocardial infarction (3) pathogenesis , morphology of hypertension (4) morphology of rheumatic fever and heart disease (5) the morphologic characteristics of valvular heart disease; the affection on bloodstream dynamics of chronic valvular disease [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 8 Diseases of Respiratory System [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) to master the morphological changes and pathogenesis of chronic bronchitis , emphysema and cor pulmonale (2) to master the pathological changes and clinical association of lobar pneumonia; to master the morphological characteristics of the lobular pneumonia (3) To be familiar with the pathological changes of bronchiectasis and interstitial pneumonia (4) to master the basic pathology of tuberculosis and the cours of development in tuberculosis (5) to be familiar with the morphological changes and pathogenesis of silicosis (6) to be familiar eith the pathological changes of carcinoma of the lung and nasopharyngeal (7) to know SARS and bird flu [Teaching Contents] (1) etiology,pathogenesis , morphology, clinical pathologic correlation (2) etiology , pathogenesis , types , morphology, clinical pathologic correlation of pulmonary emphysema (3) pathogenesis ,morphology and clinical pathologic correlation of bronchiectasis (4) etiology, morphology , clinical pathologic correlation and complications of lobar pneumonia (5) morphological changes characteristics of the lobular pneumonia and interstitial pneumonia (6) etiology, morphological changes and pathogenesis of silicosis (7) etiology ,pathogenesis and morphology of cor pulmonale (8) the basic pathology of tuberculosis and the cours of development in tuberculosis (9) etiology , pathogenesis, basic morphology of tuberculosis; the transition rule of basic morphology of tuberculosis; primary pulmonary tuberculosis and secondary pulmonary tuberculosis; extrapulmonary tuberculosis (10)morphology of lung carcinoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma [Focal and Difficult Points] (1) the morphological changes and pathogenesis of chronic bronchitis , emphysema and cor pulmonale (2) the pathological changes and clinical association of lobar pneumonia (3) the morphological characteristics of the lobular pneumonia (4) pathogenesis, basic morphology of tuberculosis; the transition rule of basic morphology of tuberculosis; primary pulmonary tuberculosis and secondary pulmonary tuberculosis [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer

Chapter 9 Diseases ofAlimentary System Teaching Aim and Requirements (1)to master the etiology,pathogenesis,pathological changes and clinical association of chronic gastuitis,peptic ulcers (2)to master the etiology.pathogenesis,pathological changes and clinical association of viral hepatitis cirrhosis (3)to be familiar with the morphological characteristics of cinoma,ston ch carcinoma,colorectal carcinoma and liver carcinoma [Teaching Contents] (1)the etiology,pathogenesis,pathological changes and clinical association of chronic gastuitis, peptic ulcers (2)the etiology,pathogenesis,pathological changes and clinical association of viral hepatitis (3)the morphological characteristics of alcoholicliver disease (4)definition of the early essophageal carcinoma.stomach carcinoma,colorectal carcinoma and liver carcinoma morphological characteristics of essophageal carcinoma,stomach carcinoma colorectal carcinoma and liver carcinoma Focal and Difficult Points] (1)pathogenesis ogical changes and clinical association of chronic gastuitis,peptic ulcers (2)pathogenesis. pathological changes and clinical association of viral hepatitis,cirrhosis (3)definition of the early essophageal carcinoma,stomach carcinoma,colorectal carcinoma and liver carcinoma Teaching Methods lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 10 Diseases of Urinary System ITeaching Aim and Requirementsl (1)to master the etiology,pathogenesis,pathological changes and clinical association of (2)to master the morphological characteristics and and clinical association of pyelonephritis (3)tobe familiar with the morphological characteristics of renal cell carcinoma and bladder transitional cell carcinoma ITeaching Contentsl (1)the etioloy,pathogenesis pathological changes and clinical association of endocapillary proliferative glomeru lonephrittis crescentic glomeruonephritis,membranou glomeruonephritis.membranoproliferative glomeruonephritis.Goodpasture's syndrome.IgA nephropathy.minimal change disease.mesangial proliferative glomeruonephritis and sclerosing glomeruonephritis (2)the and clinical association of acute and chronic pyelonephritis (3)the morphological characteristics of renal cell carcinoma and bladder transitional cell carcinoma Focal and Difficult Points]
Chapter 9 Diseases of Alimentary System [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) to master the etiology, pathogenesis , pathological changes and clinical association of chronic gastuitis, peptic ulcers (2) to master the etiology, pathogenesis , pathological changes and clinical association of viral hepatitis , cirrhosis (3) to be familiar with the morphological characteristics of alcoholic liver disease , essophageal carcinoma, stomach carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma and liver carcinoma [Teaching Contents] (1) the etiology, pathogenesis , pathological changes and clinical association of chronic gastuitis, peptic ulcers (2) the etiology, pathogenesis , pathological changes and clinical association of viral hepatitis , cirrhosis (3) the morphological characteristics of alcoholic liver disease (4) definition of the early essophageal carcinoma, stomach carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma and liver carcinoma ; morphological characteristics of essophageal carcinoma, stomach carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma and liver carcinoma [Focal and Difficult Points] (1) pathogenesis , pathological changes and clinical association of chronic gastuitis, peptic ulcers (2) pathogenesis , pathological changes and clinical association of viral hepatitis , cirrhosis (3) definition of the early essophageal carcinoma, stomach carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma and liver carcinoma [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 10 Diseases of Urinary System [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) to master the etiology, pathogenesis , pathological changes and clinical association of common glomeruonephritis (2) to master the morphological characteristics and and clinical association of pyelonephritis (3) tobe familiar with the morphological characteristics of renal cell carcinoma and bladder transitional cell carcinoma [Teaching Contents] (1) the etiology, pathogenesis , pathological changes and clinical association of endocapillary proliferative glomeru lonephrittis , crescentic glomeruonephritis,membranous glomeruonephritis, membranoproliferative glomeruonephritis, Goodpasture’s syndrome, IgA nephropathy, minimal change disease, mesangial proliferative glomeruonephritis and sclerosing glomeruonephritis (2) the morphological characteristics and clinical association of acute and chronic pyelonephritis (3) the morphological characteristics of renal cell carcinoma and bladder transitional cell carcinoma [Focal and Difficult Points]

(1)the etiology.pathogenesis of glomeruonephritis (2)the pathological changes and in of endocapillary proliferative glomeru lonephrittis,crescentic glomeruonephritis and sclerosing glomeruonephritis (3)the morphological characteristics of and clinical association of acute and chronic pyelonephritis [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 11 Diseases of Female Genital System and Breast ITeaching Aim and Requirementsl (1)to master the pathological changes and clinical features of cervix and breast carcinoma (2)to be familiar with the pathological changes and clinical features of hydatidiform mole (3)to be familiar with the pathological changes of condyloma acuminatum |Teaching Contents] (1)etiology,morphology and clinicopathological correlations of cervix and breast carcinoma (2)etiology,morphology and clinicopathological correlations of hydatidiform mole,invasive nd cho (3)he paholo ocarcinom ogical changes of Focal and Difficult Points (1)morphology of cervix and breast carcinoma (2)morphology of hydatidiform mole.invasive mole and choriocarcinoma [Teaching Methods] ecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 12 Diseases of Endocrine System [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1)to master the pathological features of thyroid papillary carcinom ()to be famil eatures and clinicopathologica correlations of diffus nontoxic goiter and diffuse toxic goiter (3)to be familiar with thethe pathological features of thyroid adenoma and pituitary adenoma [Teaching Contents] (1)the etiology.pathogenesis,pathological changes and clinicopathological correlations of diffuse n ter and diffusetox ()the features of thyroid (3)the the pathological features of pituitary adenoma Focal and Difficult Points (1)pathogenesis.pathological changes and clinicopathological correlations of diffuse nontoxic oiteranddifusetoxicgoiter [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 13 Diseases of Central Nervous System
(1) the etiology, pathogenesis of glomeruonephritis (2) the pathological changes and clinical association of endocapillary proliferative glomeru lonephrittis , crescentic glomeruonephritis and sclerosing glomeruonephritis (3) the morphological characteristics of and clinical association of acute and chronic pyelonephritis [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 11 Diseases of Female Genital System and Breast [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) to master the pathological changes and clinical features of cervix and breast carcinoma (2) to be familiar with the pathological changes and clinical features of hydatidiform mole, invasive mole and choriocarcinoma (3) to be familiar with the pathological changes of condyloma acuminatum. [Teaching Contents] (1) etiology , morphology and clinicopathological correlations of cervix and breast carcinoma (2) etiology , morphology and clinicopathological correlations of hydatidiform mole, invasive mole and choriocarcinoma (3) he pathological changes of condyloma acuminatum [Focal and Difficult Points] (1) morphology of cervix and breast carcinoma (2) morphology of hydatidiform mole, invasive mole and choriocarcinoma [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 12 Diseases of Endocrine System [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) to master the pathological features of thyroid papillary carcinoma (2) to be familiar with the the pathological features and clinicopathological correlations of diffuse nontoxic goiter and diffuse toxic goiter (3) to be familiar with the the pathological features of thyroid adenoma and pituitary adenoma [Teaching Contents] (1) the etiology, pathogenesis, pathological changes and clinicopathological correlations of diffuse nontoxic goiter and diffuse toxic goiter (2) the pathological features of thyroid carcinoma and thyroid adenoma (3) the the pathological features of pituitary adenoma [Focal and Difficult Points] (1) pathogenesis, pathological changes and clinicopathological correlations of diffuse nontoxic goiter and diffuse toxic goiter (2) the pathological features of thyroid carcinoma and thyroid adenoma [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 13 Diseases of Central Nervous System

[Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1)to master the etiology,morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis and epidemic encephalitis B (2)to be familiar with the pathological features of poliomyelitis,glioma and meningioma [Teaching Contents] (1)The etiology,morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis (2)The etiology morphology and clinicopathological comrelations and complicaton of epidemic encephalitis B (3)the pathological features of poliomyelitis (4)the pathological features of glioma and meningioma [Focal and Difficult Points] the etiology,morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis and epidemic encephalitis B [Teaching Methods lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 14 Infectious Diseases and Parasitosis [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1)to master the etiology,pathogenesis,morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of typhoid fever,bacillary dysentery (2)to master the etiology,pathogenesis,morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of amoebiasis (3)to master the etiology,pathogenesis,morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of schistosomiasis (4)to be familiar with the pathological features of AIDS (5)to know the pathological features of clonorchiasis sinensis [Teaching Contents] (1)the etiology,pathogenesis,morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of typhoid fever,bacillary dysentery (2)the etiology,pathogenesis,morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of intestinal amoebiasis and ectraintestinal amoebiasis (3)the etiology,pathogenesis,morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of schistosomiasis (4)the pathological features of clonorchiasis sinensis (5)the etiology,pathological features of AIDS [Focal and Difficult Points] (1)the etiology,pathogenesis,morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of typhoid fever,bacillary dysentery and intestinal amoebiasis (2)the etiology,pathogenesis,morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of schistosomiasis [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer
[Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) to master the etiology , morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis and epidemic encephalitis B (2) to be familiar with the pathological features of poliomyelitis , glioma and meningioma [Teaching Contents] (1) The etiology , morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis (2) The etiology , morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of epidemic encephalitis B (3) the pathological features of poliomyelitis (4) the pathological features of glioma and meningioma [Focal and Difficult Points] the etiology , morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis and epidemic encephalitis B [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer Chapter 14 Infectious Diseases and Parasitosis [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) to master the etiology , pathogenesis , morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of typhoid fever, bacillary dysentery (2) to master the etiology , pathogenesis, morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of amoebiasis (3) to master the etiology , pathogenesis , morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of schistosomiasis (4) to be familiar with the pathological features of AIDS (5) to know the pathological features of clonorchiasis sinensis [Teaching Contents] (1) the etiology , pathogenesis , morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of typhoid fever, bacillary dysentery (2) the etiology , pathogenesis, morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of intestinal amoebiasis and ectraintestinal amoebiasis (3) the etiology , pathogenesis , morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of schistosomiasis (4) the pathological features of clonorchiasis sinensis (5) the etiology ,pathological features of AIDS [Focal and Difficult Points] (1) the etiology , pathogenesis , morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of typhoid fever, bacillary dysentery and intestinal amoebiasis (2) the etiology , pathogenesis , morphology and clinicopathological correlations and complicaton of schistosomiasis [Teaching Methods] lecture with Multimedia Personal Computer
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程理论教学大纲(供七年制和五年制使用).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)传染病与寄生虫病(infectious desease and parasitosis).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)神经系统疾病(Diseases of the CNS).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)内分泌系统疾病.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)女性生殖系统疾病(disease of female reproductive system and breast).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)泌尿系统疾病 Diseases of urinary system.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)消化系统疾病 Digestive system disease.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)呼吸系统疾病.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)心血管疾病 Diseases of Cardiovascular system.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)肿瘤(tumor, neoplasm).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)炎症 inflammation.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)局部血液循环障碍.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)绪论、细胞和组织的适应与损伤、损伤的修复.ppt
- 《病理学》课程作业习题(含参考答案).pdf
- 《病理学》课程实习指导 Guidance of Pathology.pdf
- 《病理学》课程教学大纲(五年制临床、儿科、麻醉、基础、预防、口腔医学专业使用;七年制临床、儿科、检验、物理专业使用).docx
- 《遗传与优生学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 遗传咨询(genetic counseling).pdf
- 《遗传与优生学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 肿瘤遗传学.pdf
- 《遗传与优生学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 分子病(molecular disease).pdf
- 《遗传与优生学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 染色体病 Chromosomal Disorder(染色体异常综合征 Chromosomal Aberration Syndrome).pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学实习指导(英文).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程作业习题(英文,无答案).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程英文试卷(试题).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程英文试卷(答案).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)infectious disease.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)the Diseases of female genital system.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)disease of nevous system_1.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)disease of nevous system_2.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)diseases of cardiovascular system.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)diseases of respiratory system.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)disease of alimentary system.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)disease of urinary system.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)cell adaptation and injury, repair.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)tumor.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)Introduction and hemodynamic rearangment.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)inflammation.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)内分泌系统疾病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)传染和寄生虫病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)女性生殖系统疾病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(授课教案)神经系统疾病.doc
