同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼眶异常 Disorders of the orbit

Disorders of the orbit
Disorders of the orbit
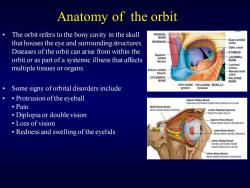
Anatomy of the orbit The orbit refers to the bony cavity in the skull FRONTAL BONE SPHENOID Supra-orbital that houses the eye and surrounding structures. notch Optic canal Diseases of the orbit can arise from within the ETHMOID orbit or as part of a systemic illness that affects LACRIMAL multiple tissues or organs. Inferior orbital nssure PALATINE 日ONE infra-orbital infra-orbital MAXILLA Some signs oforbital disorders include: groove foramen Protrusion of the eyeball ·Pain Diplopia or double vision ·Loss of vision Redness and swelling of the eyelids
Anatomy of the orbit • The orbit refers to the bony cavity in the skull that houses the eye and surrounding structures. Diseases of the orbit can arise from within the orbit or as part of a systemic illness that affects multiple tissues or organs. • Some signs of orbital disorders include: • • Protrusion of the eyeball • Pain • Diplopia or double vision • Loss of vision • Redness and swelling of the eyelids
Orbital diseases 。Thyroid eye disease Orbital infection and inflammations ·Orbital tumors Congenital orbital malformations
Orbital diseases • Thyroid eye disease • Orbital infection and inflammations • Orbital tumors • Congenital orbital malformations
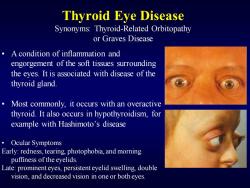
Thyroid Eye Disease Synonyms:Thyroid-Related Orbitopathy or Graves Disease A condition of inflammation and engorgement of the soft tissues surrounding the eyes.It is associated with disease of the thyroid gland. Most commonly,it occurs with an overactive thyroid.It also occurs in hypothyroidism,for example with Hashimoto's disease ·Ocular Symptoms Early:redness,tearing,photophobia,and morning puffiness of the eyelids. Late:prominent eyes,persistenteyelid swelling,double vision,and decreased vision in one or both eyes
Thyroid Eye Disease Synonyms: Thyroid-Related Orbitopathy or Graves Disease • A condition of inflammation and engorgement of the soft tissues surrounding the eyes. It is associated with disease of the thyroid gland. • Most commonly, it occurs with an overactive thyroid. It also occurs in hypothyroidism, for example with Hashimoto’s disease • Ocular Symptoms Early: redness, tearing, photophobia, and morning puffiness of the eyelids. Late: prominent eyes, persistent eyelid swelling, double vision, and decreased vision in one or both eyes

Pathology Activated T cells infiltrate orbital contents and stimulate fibroblasts,leading to: 1.Enlargement of extraocular muscles 2.Cellular infiltration of interstitial tissues 3.Proliferation of orbital fat and connective tissue
Pathology Activated T cells infiltrate orbital contents and stimulate fibroblasts, leading to: 1.Enlargement of extraocular muscles 2.Cellular infiltration of interstitial tissues 3.Proliferation of orbital fat and connective tissue
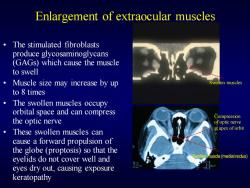
Enlargement of extraocular muscles The stimulated fibroblasts produce glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)which cause the muscle to swell Muscle size may increase by up Swollen muscles to 8 times The swollen muscles occupy orbital space and can compress Compression the optic nerve ofoptic nerve These swollen muscles can at apex oforbit cause a forward propulsion of the globe (proptosis)so that the eyelids do not cover well and Swollen muscle(medialrectus) eyes dry out,causing exposure keratopathy
Enlargement of extraocular muscles • The stimulated fibroblasts produce glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) which cause the muscle to swell • Muscle size may increase by up to 8 times • The swollen muscles occupy orbital space and can compress the optic nerve • These swollen muscles can cause a forward propulsion of the globe (proptosis) so that the eyelids do not cover well and eyes dry out, causing exposure keratopathy Swollen muscles Compression of optic nerve at apex of orbit Swollen muscle (medial rectus)

Five Main Clinical Manifestations 1. Soft Tissue Involvement 2. Eyelid Retraction 3. Proptosis 4. Optic Neuropathy Exposure Keratopathy 5. Fibrosed Muscles/ Restrictive myopathy
Five Main Clinical Manifestations 1. Soft Tissue Involvement 2. Eyelid Retraction 3. Proptosis 4. Optic Neuropathy / Exposure Keratopathy 5. Fibrosed Muscles/ Restrictive myopathy
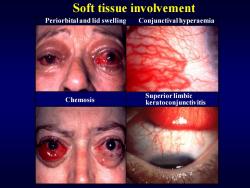
Soft tissue involvement Periorbitaland lid swelling Conjunctival hyperaemia Superior limbic Chemosis keratoconjunctivitis
Soft tissue involvement Periorbital and lid swelling Chemosis Conjunctival hyperaemia Superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis
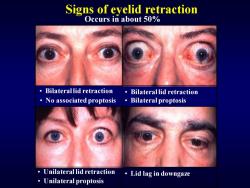
Signs of eyelid retraction Occurs in about 50% Bilaterallid retraction Bilaterallid retraction No associated proptosis.Bilateral proptosis Unilateral lid retraction ·Lid lag in downgaze Unilateral proptosis
Signs of eyelid retraction Occurs in about 50% • Bilateral lid retraction • No associated proptosis • Bilateral lid retraction • Bilateral proptosis • Lid lag in downgaze • Unilateral lid retraction • Unilateral proptosis
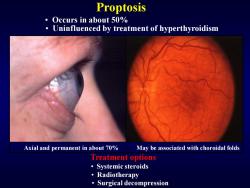
Proptosis Occurs in about 50% Uninfluenced by treatment of hyperthyroidism Axial and permanent in about 70% May be associated with choroidal folds Treatment options ·Systemic steroids ·Radiotherapy Surgical decompression
Proptosis Treatment options • Systemic steroids • Radiotherapy • Surgical decompression • Occurs in about 50% • Uninfluenced by treatment of hyperthyroidism Axial and permanent in about 70% May be associated with choroidal folds
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)斜视 STRABISMUS.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)巩膜病 Scleral Disease.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)屈光学 Optics and Refractive errors correction.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)屈光不正 Our eye as a camera Refraction, errors and solutions..ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)泪道疾病 THE WATERING EYE.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)MBBS试题.doc
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)MBBS眼科试卷-B.doc
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)MBBS眼科试卷-A.doc
- 《医学免疫学》课程教学资源(参考资料)医学免疫学常见问题解答.docx
- 广东医科大学:《医学免疫学》课程教学资源(打印版)教学大纲 Medical Immunology(负责人:米娜).pdf
- 《医学免疫学》课程教学资源(参考资料)医学免疫学相关词汇合集.docx
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第十章 内分泌 Endocrine.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第十一章 生殖 Reproduction.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第六章 消化和吸收 Digestion and Absorption.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第八章 尿的生成和排出 Formation and excretion of the urine.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第五章 呼吸 Respiration.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第九章 神经系统的功能 Function of Nervous System.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第四章 血液循环 Blood Circulation.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第三章 血液 Blood.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第二章 细胞的基本功能 Basic functions of cells.pdf
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼睑和眼表疾病 The eyelids & ocular surface diseases.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)白内障 Ophthalmology.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)眼科学教学大纲(中文,负责人:徐国彤).doc
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)眼科学教学大纲(英文,Ophthalmology).doc
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼科导论 Introduction(负责人:徐国彤).ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼组织学 Histology of the Eye.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)葡萄膜炎 Disease of the Uvea.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视光学基础 Basic Optics.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视网膜疾病 Retinal Disease.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视觉系统 Visual Organ.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)角膜病总论 Corneal disease.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)青光眼 Glaucoma.pptx
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼肿瘤 Ocular trauma.ppt
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Cell Injury.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Inflammation.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Neoplasia.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Thrombosis I-II, Hemodynamics, Atherosclerosis.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Cardiac pathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Female reproductivepathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)GIpathology.pdf
