同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)斜视 STRABISMUS

STRABISMUS occurs when both eyes do not look at the same place at the same time;the eyes are unable to align properly under normal conditions eye(s)may turn in,out,up,or down can be present in one or both eyes often referred to as:cross-eyed,crossed eyes, cockeye,weak eye,wall-eyed,wandering eyes, and or eye turn from:American Optometric Association
STRABISMUS • occurs when both eyes do not look at the same place at the same time; the eyes are unable to align properly under normal conditions • eye(s) may turn in, out, up, or down • can be present in one or both eyes • often referred to as: cross-eyed, crossed eyes, cockeye, weak eye, wall-eyed, wandering eyes, and/or eye turn from: American Optometric Association

CAUSES OF STRABISMUS result of the lack of coordination between the muscles of the eye responsible for eye movement problems with the nerves that transmit information to the eye muscles problems with the control center in the brain that directs eye movement the lack of coordination prevents proper binocular vision and keeps both eyes from gazing at the same point in adults,can be caused by stroke,thyroid problems, brain injury,or other trauma which disrupts the ability of the eye muscles to work properly from:The Cleveland Clinic
CAUSES OF STRABISMUS • result of the lack of coordination between the muscles of the eye responsible for eye movement • problems with the nerves that transmit information to the eye muscles • problems with the control center in the brain that directs eye movement • the lack of coordination prevents proper binocular vision and keeps both eyes from gazing at the same point • in adults, can be caused by stroke, thyroid problems, brain injury, or other trauma which disrupts the ability of the eye muscles to work properly from: The Cleveland Clinic

RISK FACTORS family history-if relatives have strabismus,a person is more likely to develop it refractive errors-extreme farsightedness (hyperopia)can develop strabismus due to the amount of eye focusing necessary to keep vision clear medical conditions-people with Down syndrome or cerebral palsy and people who have suffered a stroke or head injury are at higher risk for developing strabismus from:Strabismus.com
RISK FACTORS • family history—if relatives have strabismus, a person is more likely to develop it • refractive errors—extreme farsightedness (hyperopia) can develop strabismus due to the amount of eye focusing necessary to keep vision clear • medical conditions—people with Down syndrome or cerebral palsy and people who have suffered a stroke or head injury are at higher risk for developing strabismus from: Strabismus.com

TYPES OF STRABISMUS Esotropia-inward turning of the eye Exotropia-outward turning of the eye Hypertropia-upward turning of the eye Hypotropia-downward turning of the eye from:American Optometric Association
TYPES OF STRABISMUS • Esotropia—inward turning of the eye • Exotropia—outward turning of the eye • Hypertropia—upward turning of the eye • Hypotropia—downward turning of the eye from: American Optometric Association

ESOTROPIA The left eye is turned inward-note that the light reflection in the eyes is not symmetric from:Minnesota Department ofHealth
ESOTROPIA The left eye is turned inward—note that the light reflection in the eyes is not symmetric from: Minnesota Department of Health

EXOTROPIA The right eye is turned outward-again,not the light reflection in the eyes is not symmetrical from:Minnesota Department ofHealth
EXOTROPIA The right eye is turned outward—again, not the light reflection in the eyes is not symmetrical from: Minnesota Department of Health

HYPERTROPIA The right eye is turned upward-light reflection not symmetrical from:Minnesota Department ofHealth
HYPERTROPIA The right eye is turned upward—light reflection not symmetrical from: Minnesota Department of Health
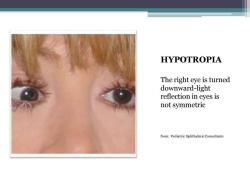
HYPOTROPIA The right eye is turned downward-light reflection in eyes is not symmetric from:Pediatric Ophthalmic Consultants
HYPOTROPIA The right eye is turned downward-light reflection in eyes is not symmetric from: Pediatric Ophthalmic Consultants

ADDITIONAL CLASSIFICATIONS constant or intermittent-the frequency it occurs bilateral-both eyes converge or diverge at the same time unilateral-if it always involves the same eye alternating-when the turning is sometimes the right and other times the left eye from:American Optometric Association
ADDITIONAL CLASSIFICATIONS • constant or intermittent—the frequency it occurs • bilateral—both eyes converge or diverge at the same time • unilateral—if it always involves the same eye • alternating—when the turning is sometimes the right and other times the left eye from: American Optometric Association

WHEN DOES IT OCCUR? congenital-developing during infancy;50%of children with strabismus are born with it acquired-developing in adulthood;can also develop as a result of lack of treatment during childhood from:Strabismus.com
WHEN DOES IT OCCUR? • congenital—developing during infancy; 50% of children with strabismus are born with it • acquired—developing in adulthood; can also develop as a result of lack of treatment during childhood from: Strabismus.com
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)巩膜病 Scleral Disease.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)屈光学 Optics and Refractive errors correction.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)屈光不正 Our eye as a camera Refraction, errors and solutions..ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)泪道疾病 THE WATERING EYE.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)MBBS试题.doc
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)MBBS眼科试卷-B.doc
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)MBBS眼科试卷-A.doc
- 《医学免疫学》课程教学资源(参考资料)医学免疫学常见问题解答.docx
- 广东医科大学:《医学免疫学》课程教学资源(打印版)教学大纲 Medical Immunology(负责人:米娜).pdf
- 《医学免疫学》课程教学资源(参考资料)医学免疫学相关词汇合集.docx
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第十章 内分泌 Endocrine.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第十一章 生殖 Reproduction.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第六章 消化和吸收 Digestion and Absorption.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第八章 尿的生成和排出 Formation and excretion of the urine.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第五章 呼吸 Respiration.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第九章 神经系统的功能 Function of Nervous System.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第四章 血液循环 Blood Circulation.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第三章 血液 Blood.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第二章 细胞的基本功能 Basic functions of cells.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)第一章 绪论 physiology(负责人:张秀娟).pdf
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼眶异常 Disorders of the orbit.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼睑和眼表疾病 The eyelids & ocular surface diseases.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)白内障 Ophthalmology.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)眼科学教学大纲(中文,负责人:徐国彤).doc
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)眼科学教学大纲(英文,Ophthalmology).doc
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼科导论 Introduction(负责人:徐国彤).ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼组织学 Histology of the Eye.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)葡萄膜炎 Disease of the Uvea.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视光学基础 Basic Optics.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视网膜疾病 Retinal Disease.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)视觉系统 Visual Organ.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)角膜病总论 Corneal disease.ppt
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)青光眼 Glaucoma.pptx
- 同济大学:《眼科学》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)眼肿瘤 Ocular trauma.ppt
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Cell Injury.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Inflammation.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Neoplasia.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Thrombosis I-II, Hemodynamics, Atherosclerosis.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Cardiac pathology.pdf
- 同济大学:《病理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题,含答案)Female reproductivepathology.pdf
