华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(Food Analysis)Chapter 5 Acidity

Measurement of Acidity
Measurement of Acidity

Contents 1.Definition Total acidity, Effective acidity Volatile acidity acidity in milk(apparent acidity,developed acidity) 2.Effects of acids on food process 3.Source and distribution of acids in food 4.Measurement of acidity
Contents 1. Definition Total acidity, Effective acidity Volatile acidity acidity in milk (apparent acidity, developed acidity) 2. Effects of acids on food process 3. Source and distribution of acids in food 4. Measurement of acidity

Definition Total acidity The total acidity is a measure of all the hydrogen ions (H+)of both the fixed and volatile acids present in food. These included: 1)the potential H+(hydrogen ions)able to be released. 2)Plus those H+already released,existing free H+in food Total acidity is amore accurate representation of the acid concentration than titratable acidity,however it is difficult to measure.Hence,the easier to measure titratable acidity is used to approximate total acidity
Definition Total acidity The total acidity is a measure of all the hydrogen ions (H+) of both the fixed and volatile acids present in food. These included: 1) the potential H+ (hydrogen ions) able to be released. 2) Plus those H+ already released, existing free H+ in food Total acidity is amore accurate representation of the acid concentration than titratable acidity,however it is difficult to measure. Hence, the easier to measure titratable acidity is used to approximate total acidity

Effective acidity The effective acidity in food depends on the concentration of all acids in food as well as their tendency to dissociate hydrogen ions.It is the concentration of H+. Effective acidity is measured as pH
Effective acidity The effective acidity in food depends on the concentration of all acids in food as well as their tendency to dissociate hydrogen ions. It is the concentration of H+ . Effective acidity is measured as pH

Volatile acidity Volatile acidity is often abbreviated to VA Volatile acidity,as the name suggests,refers to the organic acids found in wine,grape juice etc that are more volatile or more easily vaporized than the non-volatile or fixed acids (malic acid) Volatile acids,because their volatility,are able to be steam distilled over,collected and their concentration determined. the main volatile acidity include:acetic acid, butyric acid,etc
Volatile acidity Volatile acidity is often abbreviated to VA Volatile acidity, as the name suggests,refers to the organic acids found in wine, grape juice etc that are more volatile or more easily vaporized than the non-volatile or fixed acids (malic acid) Volatile acids,because their volatility,are able to be steam distilled over, collected and their concentration determined. the main volatile acidity include: acetic acid, butyric acid, etc

Acidity in milk 1) Apparent acidity:derived from the alkali binding properties of casein phosphates,citrates and CO2. Usually it is between 0.15%-0.18%.(lactic acid) 2)Developed acidity:results from the fermentation of milk by lactic acid bacteria.When it is above 0.2%, lactic acid exists. 3)Two ways to express acidity in milk T:the volume of 0.1000mol/l NaOH depleted by 100ml milk sample.The apparent acidity of fresh milk is 16-18 0T the acidity in the milk can be expressed by lactic acid percentage
• Acidity in milk 1) Apparent acidity: derived from the alkali binding properties of casein , phosphates,citrates and CO2. Usually it is between 0.15%-0.18%. (% lactic acid) 2) Developed acidity:results from the fermentation of milk by lactic acid bacteria. When it is above 0.2%, lactic acid exists. 3) Two ways to express acidity in milk 0T: the volume of 0.1000mol/l NaOH depleted by 100ml milk sample. The apparent acidity of fresh milk is 16-18 0T the acidity in the milk can be expressed by lactic acid percentage

Effects of acids in food process 1)Color change 2)Food taste 3)Food stability 4)Maturity of fruits 5)Standards of food quality such as:stale oil,meat(PH升高,大于6.7则腐 败);rotten fruits
Effects of acids in food process 1)Color change 2) Food taste 3)Food stability 4) Maturity of fruits 5) Standards of food quality such as: stale oil, meat(PH升高,大于6.7则腐 败); rotten fruits
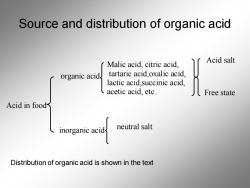
Source and distribution of organic acid Malic acid,citric acid, Acid salt organic acid tartaric acid,oxalic acid, lactic acid,succinic acid, acetic acid,etc Acid in food neutral salt Distribution of organic acid is shown in the text
Source and distribution of organic acid Acid in food organic acid inorganic acid Malic acid, citric acid, tartaric acid,oxalic acid, lactic acid,succinic acid, acetic acid, etc. neutral salt Free state Acid salt Distribution of organic acid is shown in the text

Determination of acidity 1)Determination of total acidity 2)Determination of effective acidity 3)Determination of volatile acidity
Determination of acidity 1)Determination of total acidity 2)Determination of effective acidity 3)Determination of volatile acidity

Determination of total acidity Principle:an acid-base titration RCOOH+NaOH-RCOONa +H2O 食品中的有机酸(弱酸)用标准碱液滴定时,被中和生成盐 类。用酚酞作指示剂,当滴定到终点(pH=8.2,指示剂显 红色)时,根据消耗的标准碱液体积,计算出样品总酸的 含量
Determination of total acidity Principle: an acid-base titration RCOOH + NaOH→ RCOONa +H2O 食品中的有机酸(弱酸)用标准碱液滴定时,被中和生成盐 类。用酚酞作指示剂,当滴定到终点(pH=8.2,指示剂显 红色)时,根据消耗的标准碱液体积,计算出样品总酸的 含量
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(Food Analysis)Chapter 4 Ash and Mineral.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(Food Analysis)Chapter 3 Water Activity.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(Food Analysis)Chapter 2 Physical Methods.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(Food Analysis)Chapter 1 Introduction.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)13 实验方法评价与数据处理下载.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)12 分析质量保证.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)11 食品中有害物质的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)10 食品中限量元素的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)09 食品添加剂的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)08 维生素的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)07 蛋白质及氨基酸分析.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)06 脂类物质的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)05 糖的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)04 酸度的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)03 灰分及矿物质元素.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)02 水分和水分活度的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程教学资源(PPT课件)01 绪论.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《食品安全学》课程教学大纲 Food Safety.pdf
- 《食品安全卫生原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 化学性物质与食品安全.ppt
- 《食品安全卫生原理》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 食品的污染、食源性疾病和食物中毒.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(Food Analysis)Chapter 6 Lipids.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(Food Analysis)Chapter 7 Carbohydrates.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(Food Analysis)Chapter 8 Amino Acid and Protein Analysis.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(Food Analysis)Chapter 9 Vitamins Analysis.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(Food Analysis)Chapter 10 Food Additves Analysis.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(Food Analysis)Chapter 11 Trace Elements Analysis.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(Food Analysis)Chapter 12 Reporting Results and Reliability of Analyses.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(食品营养成分分析实验)实验一 食品中还原糖的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(食品营养成分分析实验)实验二 食品中淀粉的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(食品营养成分分析实验)实验三 食品中脂肪的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(食品营养成分分析实验)实验四 油脂中脂肪酸含量测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(食品营养成分分析实验)实验五 食品中蛋白质含量测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(食品营养成分分析实验)实验六 植物类食品中粗纤维的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(食品营养成分分析实验)实验七 食品中铅、镉、铬的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(食品营养成分分析实验)实验八 食品中维生素C的含量测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(食品营养成分分析实验)实验十 食用植物油脂.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(食品安全性检测实验)实验一 食品中亚硫酸盐含量测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(食品安全性检测实验)实验三 食品中苏丹红染料的测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(食品安全性检测实验)实验四 食品中亚硫酸盐含量测定.ppt
- 华南理工大学:《食品分析》课程PPT教学课件(食品安全性检测实验)实验五 蔬菜中有机磷和氨基甲酸.ppt
