同济大学:《创业学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)03 Opportunities in China

同源大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY Opportunities in China Dr.Pan Xuan School of Economics and Management Tongji University
Opportunities in China Dr. Pan Xuan School of Economics and Management Tongji University
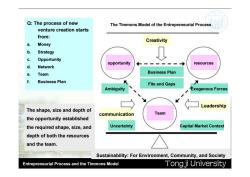
Q:The process of new The Timmons Model of the Entrepreneurial Process venture creation starts from: Creativity a. Money b. Strategy Opportunity resources d opportunity Network 9 Team Business Plan f Business Plan Fits and Gaps Ambiguity Exogenous Forces Leadership The shape,size and depth of communication Team the opportunity established the required shape,size,and Uncertainty Capital Market Context depth of both the resources and the team. Sustainability:For Environment,Community,and Society Entrepreneurial Process and the Timmons Model Tong ji University
Entrepreneurial Process and the Timmons Model The Timmons Model of the Entrepreneurial Process opportunity Q: The process of new venture creation starts from: a. Money b. Strategy c. Opportunity d. Network e. Team f. Business Plan The shape, size and depth of the opportunity established the required shape, size, and depth of both the resources and the team. communication resources Business Plan Fits and Gaps Team Ambiguity Creativity Exogenous Forces Leadership Uncertainty Capital Market Context Sustainability: For Environment, Community, and Society

同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY Definition of Opportunity Summary of Opportunity Spawners and Drivers What will be the main changes In China? Opportunities for Start-up:The world's most intriguing consumer market
Definition of Opportunity Summary of Opportunity Spawners and Drivers What will be the main changes In China? Opportunities for Start-up: The world's most intriguing consumer market

同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY Definition of Opportunity Definition of Opportunity Has the qualities of being attractive,durable,and timely and is Opportunity anchored in a product or service,which creates or adds value for its buyer or end user. A Good Idea is not Necessarily a Good Opportunity For every 100 ideas presented to investors in the form of a business plan or proposal,usually few than_4get funded. ·More than 80 of those rejections occur in the first few hours;another 10-15 are rejected after investors have read the business plan carefully. ·Fewer than 10 attract enough interest to merit a more due diligence thorough review that can take several weeks or months
• Fewer than _______% attract enough interest to merit a more due diligence thorough review that can take several weeks or months. • More than ______% of those rejections occur in the first few hours; another _____________% are rejected after investors have read the business plan carefully. Definition of Opportunity Has the qualities of being attractive, durable, and timely and is anchored in a product or service, which creates or adds value for its buyer or end user. A Good Idea is not Necessarily a Good Opportunity • For every 100 ideas presented to investors in the form of a business plan or proposal, usually few than ______ get funded. Opportunity 4 80 10-15 10 Definition of Opportunity
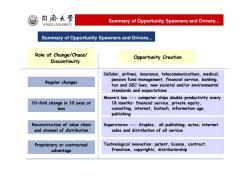
同濟大学 Summary of Opportunity Spawners and Drivers... TONGJI UNIVERSITY Summary of Opportunity Spawners and Drivers... Role of Change/Chaos/ Opportunity Creation Discontinuity Cellular,airlines,insurance,telecommunications,medical, Regular changes pension fund management,financial service,banking. tax and SEC laws,new societal and/or environmental standards and expectations Moore's law---computer chips double productivity every 10-fold change in 10 yeas or 18 months:financial service,private equity, less consulting,internet,biotech,information age, publishing Reconstruction of value chain Superstores ---Staples,all publishing:autos;internet and channel of distribution sales and distribution of all service Proprietary or contractual Technological innovation:patent,license,contract. advantage franchise,copyrights,distributorship
Summary of Opportunity Spawners and Drivers... Role of Change/Chaos/ Discontinuity Regular changes Opportunity Creation Cellular, airlines, insurance, telecommunications, medical, pension fund management, financial service, banking, tax and SEC laws, new societal and/or environmental standards and expectations 10-fold change in 10 yeas or less Moore’s law --- computer chips double productivity every 18 months: financial service, private equity, consulting, internet, biotech, information age, publishing Reconstruction of value chain and channel of distribution Superstores --- Staples, all publishing; autos; internet sales and distribution of all service Proprietary or contractual advantage Technological innovation: patent, license, contract, franchise, copyrights, distributorship Summary of Opportunity Spawners and Drivers

同诱大学 What will be the main changes In China? TONGJI UNIVERSITY What will be the main changes In China?-institutional Land System:from ambiguous to clear,hopefully In the sectors of finance,petroleum,electricity,railway,telecommunication, resource exploitation and public utilities,some investment projects will be open to non-state-owned capital Jiangsu Province Continue and extend the Shanghai Pilot Free-trade-zone Shanghai Zhejiang
What will be the main changes In China? - institutional • In the sectors of finance, petroleum, electricity, railway, telecommunication, resource exploitation and public utilities, some investment projects will be open to non-state-owned capital • Continue and extend the Shanghai Pilot Free-trade-zone What will be the main changes In China? • Land System: from ambiguous to clear, hopefully

同濟大学 What will be the main changes In China? TONGJI UNIVERSITY What will be the main changes In China?-Societal Three "100 million"about urbanization --Give 100m migrant peasant workers urban Hukou --transfer 100m from rural to towns and cities in middle and west regions(not to crowded east coastal regions) -reconstruct shantytowns and "village-in-city"for 100m Security Housing Plan:7 million set new start Social Service Service Sector more open: hospital,school,nursing home.... Social WelfareSystem Reform_Pension/medicare/unemployment...:increase the average benefit level,reduce the gap between public sectors and private sectors,urban and rura
What will be the main changes In China? - Societal • Security Housing Plan: 7 million set new start What will be the main changes In China? • Three "100 million" about urbanization -- Give 100m migrant peasant workers urban Hukou -- transfer 100m from rural to towns and cities in middle and west regions (not to crowded east coastal regions) -- reconstruct shantytowns and “village-in-city” for 100 m • Social WelfareSystem Reform_Pension/medicare/unemployment... : increase the average benefit level, reduce the gap between public sectors and private sectors, urban and rura. • Social Service Service Sector more open: hospital, school, nursing home

同海大学 What will be the main changes In China? TONGJI UNIVERSITY What will be the main changes In China?-Economical The growth rate of resident income should be as fast as that of GDP.The goal for per capital Disposable Income Growth Rate is 7%. Financial environment more marketization:interest rate liberalization,IPO decided by the stock market... Convertibility and internationalization of RMB capital account,cross-border investment ·investment ·Exportation .Consumption
What will be the main changes In China? - Economical What will be the main changes In China? • The growth rate of resident income should be as fast as that of GDP. The goal for per capital Disposable Income Growth Rate is 7% . • Financial environment more marketization: interest rate liberalization, IPO decided by the stock market... • Convertibility and internationalization of RMB capital account, cross-border investment • investment • Exportation •Consumption

同济大学 What will be the main changes In China? TONGJI UNIVERSITY What will be the main changes In China?-Demographic Family Planning Policy relaxed:couples where one partner is an only child will now be allowed to have a second child Aging Problem:China is still a demographically young nation,but facing a daunting age wave. While today's developed countries became affluent societies before they aging,China may be the first major country to grow old before it grows rich
What will be the main changes In China? - Demographic What will be the main changes In China? • Family Planning Policy relaxed: couples where one partner is an only child will now be allowed to have a second child • Aging Problem: China is still a demographically young nation, but facing a daunting age wave. While today’s developed countries became affluent societies before they aging, China may be the first major country to grow old before it grows rich

同濟大学 What will be the main changes In China? TONGJI UNIVERSITY One-Child Policy ·Launched in1980 "Baby boomers"entered their childbearing years Population"hawks"argued to tighten policy ·“one-and-a-Half-Child Policy”after1984 In most rural areas,if the first child is a girl,a secondchild allowed,"try for a son" Its implementation delegated to local government It subjects all Chinese households to monitoring of fertility and births
• Launched in 1980 “Baby boomers” entered their childbearing years Population “hawks” argued to tighten policy One-Child Policy • “One-and-a-Half-Child Policy” after 1984 In most rural areas, if the first child is a girl, a secondchild allowed, “try for a son” Its implementation delegated to local government It subjects all Chinese households to monitoring of fertility and births. What will be the main changes In China?
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《创业学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)02 Who are China's New Private Entrepreneur?.pdf
- 同济大学:《创业学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)01 The Entrepreneur and Entrepreneurship(负责人:潘烜).pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Business Model Generation(Alexander Osterwalder & Yves Pigneur)A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Entrepreneurship and China - History of Policy Reforms and Institutional Development.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)ENTREPRENEURSHIP IN CHINA AND RUSSIA COMPARED.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)The development of entrepreneurship in China.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)More Chinese flock to US schools but at steep price.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)The entrepreneur’s business model - toward a unified perspective.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)How to Write a Great Business Plan.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Growth, Institutions, and Entrepreneurial Finance in China - A Survey.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Patterns of venturing financing - The case of Chinese Entrepreneurs.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)10 清蛋白测定.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)09.2 尿素测定.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)09.1 碘-淀粉比色法测定淀粉酶.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)08 GOD法测葡萄糖.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)07 ALT测定教案.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)06 创新性实验设计.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)05 ALP测定.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)01-04方法学评价试验教案.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学资源(理论教案,打印版)第21章 临床毒物检验.pdf
- 同济大学:《创业学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)04 The Business Model Canvas.pdf
- 同济大学:《创业学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)05 Business Plan.pdf
- 同济大学:《创业学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)06 The Entrepreneurial Finance.pdf
- 南京大学:《初级管理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第一章 管理学导论(主讲:李嘉).pdf
- 南京大学:《初级管理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第三章 决策与计划.pdf
- 南京大学:《初级管理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第二章 管理学思想演变.pdf
- 南京大学:《初级管理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第五章 领导与激励.pdf
- 南京大学:《初级管理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第四章 组织与人事.pdf
- 南京大学:《初级管理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第六章 控制.pdf
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第一章 导论(负责人:王秋华).ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十章 组织文化.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十一章 领导者与人力资源开发管理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十二章 二十一世纪的人力资源开发与管理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第二章 工作分析.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第三章 人力资源的吸收.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第四章 绩效考评.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第五章 奖酬与福利.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 员工培训.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第七章 职业发展与管理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 劳动关系.ppt
