同济大学:《创业学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)06 The Entrepreneurial Finance

同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY The Entrepreneurial Finance Dr.Pan Xuan School of Economics and Management Tongji University
The Entrepreneurial Finance Dr. Pan Xuan School of Economics and Management Tongji University

同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY How Startup Goes from Idea to IPO? How to Raise Money for Your Startup Entrepreneurial Finance in China
How Startup Goes from Idea to IPO? Entrepreneurial Finance in China How to Raise Money for Your Startup

HOW STARTUP FUNDING WORKS A HYPOTHETICAL STARTUP GOES FROM IDEA TO IPO IPO How Startup Goes from Idea to IPO? 23560的0 100%OF 17%0fA Funding NOTHING IS A LOT LESS THAN BIG COMPANY SERIES A 200,900 Bootstrapping SEED ROUND FAMILY AND FRIENDS .Splitting the Pie and Giving up Pieces COFOUNDER STAGE X受 a1 ·Funding Stages一Idea stage -Co-Founder Stage -Family and Friend Registering the Company -The Angel Round 12 How Funding Works-Cutting the Pie -Venture Capital Round Why Companies Go Public? COFOUNDER FRIENDS ANGEL VENTURE INVESTMENT ANYONE AND FAMILY INVESTORS CAPTAUISTS EMPLOYEES BANKERS Being an Early Employee at a Startup
How Startup Goes from Idea to IPO? Funding Bootstrapping •Splitting the Pie and Giving up Pieces • Funding Stages — Idea stage — Co-Founder Stage — Family and Friend • Registering the Company — The Angel Round • How Funding Works - Cutting the Pie - Venture Capital Round • Why Companies Go Public? • Being an Early Employee at a Startup

同海大学 How to Raise Money for Your Startup TONGJI UNIVERSITY 1.Don't raise money unless you want it and it wants you. Fundraising is not one of the defining qualities of a startup, rapid growth is! (a)taking outside money helps them Most companies in a position grow faster to grow rapidly find that: (b)their growth potential makes it easy to attract such money
1. Don't raise money unless you want it and it wants you. • Fundraising is not one of the defining qualities of a startup, • Most companies in a position to grow rapidly find that: (a) taking outside money helps them grow faster (b) their growth potential makes it easy to attract such money. How to Raise Money for Your Startup rapid growth is!

同濟大学 How to Raise Money for Your Startup TONGJI UNIVERSITY 2.Get introductions to investors. Before you can talk to investors,you have to be introduced to them.If you're presenting at a Demo Day,you'll be introduced to a whole bunch simultaneously. (a)intro from a well-known investor who has just invested in you In phase 2,you have to be introduced,Some investors (b)intro from a founder of a company don't really want startups to they've funded approach them directly (c)intros from other people in the startup community,like lawyers and reporters There are now sites like AngelList,FundersClub,and WeFunder that can introduce you to investors
2. Get introductions to investors. • Before you can talk to investors, you have to be introduced to them. If you're presenting at a Demo Day, you'll be introduced to a whole bunch simultaneously. How to Raise Money for Your Startup • In phase 2, you have to be introduced, Some investors don't really want startups to approach them directly (a) intro from a well-known investor who has just invested in you (b) intro from a founder of a company they've funded (c) intros from other people in the startup community, like lawyers and reporters • There are now sites like AngelList, FundersClub, and WeFunder that can introduce you to investors

同濟大学 How to Raise Money for Your Startup TONGJI UNIVERSITY 3.Do breadth-first search weighted by expected value. Talk to all potential investors in parallel rather than serially,but give higher priority to the more promising ones. Expected value how likely an investor is to say yes X how good it would be if they did. an eminent an obscure angel investor who won't who would invest much,but invest a lot,but will be easy to will be hard to convince convince
3. Do breadth-first search weighted by expected value. • Expected value = how likely an investor is to say yes X how good it would be if they did. How to Raise Money for Your Startup • Talk to all potential investors in parallel rather than serially, but give higher priority to the more promising ones. an eminent investor who would invest a lot, but will be hard to convince an obscure angel who won't invest much, but will be easy to convince

同濟大学 How to Raise Money for Your Startup TONGJI UNIVERSITY 4.Have multiple plans. Store -Salesperson:"How much were you planning to spend?" For they can show you only things that cost the most you'll pay. Investor:"How much you're planning to raise?" plan to raise a It's to see whether you'd be a suitable recipient specific amount for the size of investment they like to make,and also to judge your ambition,reasonableness,and different plans match how far you are along with fundraising. different investors A rule of thumb about the upper limit on what you should raise: the number of people you want to hire X $15k X 18 months. Eg.20 x $15k x 18=$5.4 million
4. Have multiple plans. How to Raise Money for Your Startup It's to see whether you'd be a suitable recipient for the size of investment they like to make, and also to judge your ambition, reasonableness, and how far you are along with fundraising. plan to raise a specific amount different plans match different investors - Salesperson:"How much were you planning to spend?" For they can show you only things that cost the most you'll pay. - Investor: "How much you're planning to raise?" A rule of thumb about the upper limit on what you should raise: the number of people you want to hire X $15k X 18 months. Eg. 20 x $15k x 18 = $5.4 million

同源大学 How to Raise Money for Your Startup TONGJI UNIVERSITY 5.Get the first commitment,and close committed money. The biggest factor in most investors'opinions of you is the opinion of other investors.Once you start getting investors to commit,it becomes increasingly easy to get more to. It's often hard to get the first commitment. 光 IDG SEQUOIA CAPITAL It's not a deal till the money's in the INTERNATIONAL DATA GROUP 红杉资本 bank.Even a day's delay can bring news that causes an investor to change their mind.Even top-tier VC firms will welch on deals. CARLYLE SoftBank GROUP
5. Get the first commitment, and close committed money. How to Raise Money for Your Startup The biggest factor in most investors' opinions of you is the opinion of other investors. Once you start getting investors to commit, it becomes increasingly easy to get more to. It's often hard to get the first commitment. It's not a deal till the money's in the bank. Even a day's delay can bring news that causes an investor to change their mind. Even top-tier VC firms will welch on deals

同濟大学 Entrepreneurial Finance in China TONGJI UNIVERSITY No.1_Not all start-ups need financing By Entrepreneurial Team 7.5% By Family and Friends 4.5% By Government Investment/Subsidy 1.2% By VC 1.0% Financial Support from Incubator 0.3% ¥ Bootstrapping 85.2%
No.1_ Not all start-ups need financing Entrepreneurial Finance in China Bootstrapping 85.2% By Entrepreneurial Team 7.5% By Family and Friends 4.5% By Government Investment/Subsidy 1.2% By VC 1.0% Financial Support from Incubator 0.3%
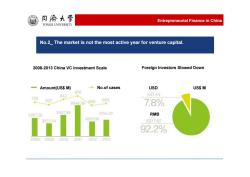
同海大学 Entrepreneurial Finance in China TONGJI UNIVERSITY No.2 The market is not the most active year for venture capital. 2008-2013 China VC Investment Scale Foreign Investors Slowed Down -Amount(US$M) No.of cases USD US$M 976 842 541.44 728 637 608 683 8946.56 7.8% 594799g 52B7.26 4734.47 RMB 4267.06 355754 6377.62 92.2% 200820092010201120122013
No.2_ The market is not the most active year for venture capital. Entrepreneurial Finance in China 2008-2013 China VC Investment Scale Amount(US$ M) No.of cases Foreign Investors Slowed Down USD RMB US$ M
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《创业学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)05 Business Plan.pdf
- 同济大学:《创业学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)04 The Business Model Canvas.pdf
- 同济大学:《创业学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)03 Opportunities in China.pdf
- 同济大学:《创业学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)02 Who are China's New Private Entrepreneur?.pdf
- 同济大学:《创业学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)01 The Entrepreneur and Entrepreneurship(负责人:潘烜).pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Business Model Generation(Alexander Osterwalder & Yves Pigneur)A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Entrepreneurship and China - History of Policy Reforms and Institutional Development.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)ENTREPRENEURSHIP IN CHINA AND RUSSIA COMPARED.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)The development of entrepreneurship in China.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)More Chinese flock to US schools but at steep price.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)The entrepreneur’s business model - toward a unified perspective.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)How to Write a Great Business Plan.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Growth, Institutions, and Entrepreneurial Finance in China - A Survey.pdf
- 《创业学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Patterns of venturing financing - The case of Chinese Entrepreneurs.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)10 清蛋白测定.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)09.2 尿素测定.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)09.1 碘-淀粉比色法测定淀粉酶.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)08 GOD法测葡萄糖.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)07 ALT测定教案.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《临床生物化学及检验》课程教学奖状(实验教案,打印版)06 创新性实验设计.pdf
- 南京大学:《初级管理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第一章 管理学导论(主讲:李嘉).pdf
- 南京大学:《初级管理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第三章 决策与计划.pdf
- 南京大学:《初级管理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第二章 管理学思想演变.pdf
- 南京大学:《初级管理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第五章 领导与激励.pdf
- 南京大学:《初级管理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第四章 组织与人事.pdf
- 南京大学:《初级管理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第六章 控制.pdf
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第一章 导论(负责人:王秋华).ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十章 组织文化.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十一章 领导者与人力资源开发管理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十二章 二十一世纪的人力资源开发与管理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第二章 工作分析.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第三章 人力资源的吸收.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第四章 绩效考评.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第五章 奖酬与福利.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 员工培训.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第七章 职业发展与管理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 劳动关系.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人力资源管理》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第九章 跨文化人力资源管理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《国际商务管理》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2004~2005学年第一学期期末考试(A卷).doc
- 吉林大学:《国际商务管理》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2004~2005学年第一学期期末考试(B卷).doc
