长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 2 Probablisitic Limit States Design Method

JPKIC 结构计原黑 Chapter 2 Principle of Structure Design and Calculation Based on Probabilostic Limit State Method
Chapter 2 Principle of Structure Design and Calculation Based on Probabilostic Limit State Method

JPKIC Main content 箱构设计原黑 History and basic concept of methods for calculation and design Functional requirement of structure Conception of limit state,probabilistic limit state design method Design method,principles,expressions and factors of existing Codes Strength of Materials,action classifications,action combination
Main content ⚫ History and basic concept of methods for calculation and design ⚫ Functional requirement of structure ⚫ Conception of limit state, probabilistic limit state design method ⚫ Design method, principles, expressions and factors of existing Codes ⚫ Strength of Materials, action classifications, action combination

JPKIC 结构设计原理 §2.0 Introduction hepniiplestncturedesgn 1,The Purpose of Structural Design Design structures meeting functional requirements, comparing the action effects from outside environment and its resistance to reach the objectives of safety and economy Specifically,Design is to determine cross-sectional size, area of reinforcing bar and construction requirements
§2.0 Introduction 1、The Purpose of Structural Design Design structures meeting functional requirements, comparing the action effects from outside environment and its resistance to reach the objectives of safety and economy Specifically, Design is to determine cross-sectional size, area of reinforcing bar and construction requirements

JPKIC 2.History of structural design 结构热试原得】 From Gelieo age to present,300 years,the design can be summarized from two aspects: 1)structural design theory, theory of elasticity limit state theory 2)Structural design method deterministic design method probabilistic design method
2、History of structural design From Gelieo age to present, 300 years, the design can be summarized from two aspects: 1) structural design theory, theory of elasticity limit state theory 2) Structural design method deterministic design method probabilistic design method

JIPKIC 结构线其原黑 3,Theory and method of structural design and calculation Allowable stress method ](1860 year) ●Fracture design method」(l932year) Multi-factor limit state design method(1970 year) Probabilistic limit state design method based on reliability theory,this is a objective for engineers
3、Theory and method of structural design and calculation ⚫ Allowable stress method ](1860 year) ⚫ Fracture design method ](1932year) ⚫ Multi-factor limit state design method(1970 year) ⚫ Probabilistic limit state design method based on reliability theory, this is a objective for engineers

2.0.1 Allowable stress method JIPKIC 结构盘计原课 l、Basic concepts Allowable [stress method ]-a maximum stress of a section reach or exceed allowable stress,and then element fails o s[o]= strengthof material safety factor o.≤o.]=A concrete stress RC member Steel stress Where :k and k are stafey factors
safety factor strength o f material = c c c c k f = s s s s k f = RC member: concrete stress Steel stress Where : are stafey factors. s k and k c 1、Basic concepts §2.0.1 Allowable stress method Allowable [stress method ]—a maximum stress of a section reach or exceed allowable stress, and then element fails
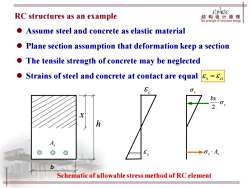
JPKIC RC structures as an example 结构设计原理 jhepniheipledstucturedesgn Assume steel and concrete as elastic material Plane section assumption that deformation keep a section The tensile strength of concrete may be neglected ● Strains of steel and concrete at contact are equal &=8 E bx h A b Schematic of allowable stress method of RC element
c RC structures as an example ⚫ Assume steel and concrete as elastic material ⚫ Plane section assumption that deformation keep a section ⚫ The tensile strength of concrete may be neglected ⚫ Strains of steel and concrete at contact are equal b x h s s As c c bx 2 As Schematic of allowable stress method of RC element s ci =

JPKIC 2、features 结构设计原黑 1,safety factor K>1,a lager k will have a higher safety and more material. 2.Without consideration of diversity of function 1 )load-carrying capacity. 2)service performance,crack and deformation. 3,The determination of safety is by experience judgment and no scientific basis. 3,applicable condition Non-line-shape structures,such dam,spatial shell structures. No equations in code.So elastic mechanism method is a useful tool
2、features 1、safety factor K >1, a lager k will have a higher safety and more material. 2、Without consideration of diversity of function 1)load-carrying capacity. 2) service performance, crack and deformation . 3、The determination of safety is by experience judgment and no scientific basis. 3、applicable condition Non-line-shape structures, such dam, spatial shell structures. No equations in code. So elastic mechanism method is a useful tool

JPKIC 结构计原黑 S 2.0.2 Fracture design method -1930s l、basic concept The inner force reaches ultimate inner force under loading, and then element fails.Taking flexural RC element as an example,as M≤M./k where is the inner force of section,is ultimate inner force of a cross section,k is a safety factor
§2.0.2 Fracture design method ——1930s 1、basic concept Mu M M k u M The inner force reaches ultimate inner force under loading, and then element fails. Taking flexural RC element as an example, as where is the inner force of section, is ultimate inner force of a cross section, k is a safety factor
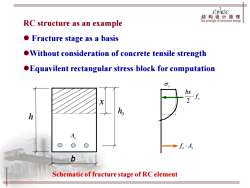
JIPKIC 结构设计原理 RC structure as an example The principle of structure design Fracture stage as a basis Without consideration of concrete tensile strength Equavilent rectangular stress block for computation bx h A Schematic of fracture stage of RC element
b x h As 0 h s As f c c f bx 2 Schematic of fracture stage of RC element RC structure as an example ⚫ Fracture stage as a basis ⚫Without consideration of concrete tensile strength ⚫Equavilent rectangular stress block for computation
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of RC Structures.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 0 General Introduction.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第9讲 受弯构件受力全过程和破坏特点.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第10讲 单筋矩形截面强度计算公式及其应用.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第8讲 受弯构件受力全过程和破坏特点.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第7讲 受弯构件截面形式和构造特点.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第6讲 作用、作用代表值和作用效应组合.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第5讲 概率极限状态设计法的基本原则.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第4讲 钢筋基本力学性能.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第3讲 混凝土基本力学性能.docx
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第2讲 钢筋混凝土结构基本概念.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第四讲 钢筋基本力学性能.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第十讲 受弯构件强度计算公式及其应用.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第六讲 作用、作用代表值和作用效应组合.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第八讲 受弯构件受力全过程和破坏特点.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第五讲 概率极限状态设计法的基本原则.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第二讲 钢筋混凝土结构基本概念.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第九讲 受弯构件正截面承载力计算的基本原则.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第三讲 混凝土基本力学性能.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第七讲 受弯构件截面形式和构造要求.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 4 Shear Strength of Inclined Section in Flexure(Shear strength of RC beams).ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 6 Carrying Capacity of Members under Axial Loading 轴心受压构件承载力计算.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 7 Load-Carrying Capacity of Normal Section of Members under Eccentric Loads.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 9 Crack width.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《水工钢筋混凝土结构》课程教学资源(教案大纲)水工钢筋混凝土结构教学大纲 Water Power Engineering Reinforced Concrete Structure (负责人:任宜春).pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《水工钢筋混凝土结构》课程教学资源(教案大纲)水工钢筋混凝土结构教案.pdf
- 《水工钢筋混凝土结构》课程教学资源(参考资料)中华人民共和国水利行业标准(SL191-2008)水工混凝土结构设计规范 Design code for hydraulic concrete structures.pdf
- 《水工钢筋混凝土结构》课程教学资源(参考资料)中华人民共和国电力行业标准(DL/T 5057-2009)水工混凝土结构设计规范 Design specification for hydraulic concrete structures.pdf
- 简支钢桁架非破损试验指导书.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第一章 制图基本知识.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第三章 点.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第二章 投影的基本知识.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第五章 平面.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第六章 直线与平面的相对位置、两平面相对位置.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第四章 直线.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(作业习题)道路工程制图习题集.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第12章 组合体视图(组合体的投影).ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第13章 工程形体的表达方法.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第16章 道路工程图.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第17章 桥梁、隧道、涵洞工程图.ppt
