长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 7 Load-Carrying Capacity of Normal Section of Members under Eccentric Loads

JPKIC 结构计原黑 Chapter 7 Load-Carrying Capacity of Normal Section of Members under Eccentric Loads
Chapter 7 Load-Carrying Capacity of Normal Section of Members under Eccentric Loads

JPKIC Focus of this chapter: 结构设计原理 The principle of structure design bias components are the mechanical characteristics of cross sections and two failure modes, Boundaries and determine the size of bias conditions; Familiar with eccentric compression ofthe second-ordereffect and calculation; Eccentric rectangular cross-section bearing capacity of compression members is calculated, Including the formula,the formula of the applicable conditions of reinforcement and non-symmetrical Design and reinforcement of the cross-section symmetrical cross section for review; OI-shaped,T shaped eccentric compression AND CIVIL ENGINEERING Calculation method; OCircularsectioneccentric compression member cross section design and review; OEccentric compression reinforcement of the structure and reasonable layout requirements
Focus of this chapter: ●bias components are the mechanical characteristics of cross sections and two failure modes, ●Boundaries and determine the size of bias conditions; Familiar with eccentric compression of the second-order effect and calculation; Eccentric rectangular cross-section bearing capacity of compression members is calculated, Including the formula, the formula of the applicable conditions of reinforcement and non-symmetrical ●Design and reinforcement of the cross-section symmetrical cross section for review; ●I-shaped, T shaped eccentric compression AND CIVIL ENGINEERING Calculation method; ●Circular section eccentric compression member cross section design and review; ●Eccentric compression reinforcement of the structure and reasonable layout requirements
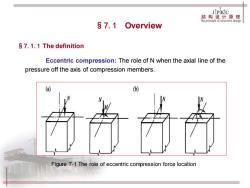
JPKIC 结构设计原理 Tfeprniipledistnctiredesign §7.1 Overview $7.1.1 The definition Eccentric compression:The role of N when the axial line of the pressure off the axis of compression members. (a) ) Figure 7-1 The role of eccentric compression force location
Eccentric compression: The role of N when the axial line of the pressure off the axis of compression members. Figure 7-1 The role of eccentric compression force location §7.1 Overview §7.1.1 The definition
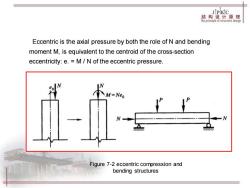
JPKic 箱构计原黑 Eccentric is the axial pressure by both the role of N and bending moment M,is equivalent to the centroid of the cross-section eccentricity:e.M/N of the eccentric pressure. M=Ne0 Figure 7-2 eccentric compression and bending structures
Eccentric is the axial pressure by both the role of N and bending moment M, is equivalent to the centroid of the cross-section eccentricity: e. = M / N of the eccentric pressure. Figure 7-2 eccentric compression and bending structures

JPKIC 结构设计原理 jhepnhepledstucturedesgn Eccentricity:The role of N point of the pressure from the member section centroid distance eo Bending structures:Axial pressure to bear on the same cross-section and moment components. Eccentric force component Large eccentric Eccentric: compression (flexure and compression) Small eccentric compression Two-way eccentric force component S 7.1.2 Engineering Eccentric compression:The reinforced concrete arch bridge,truss rod bent, rigid frame column,the column pier(Taiwan)Pier (Taiwan)column and so on
§7.1.2 Engineering Eccentric compression: The reinforced concrete arch bridge, truss rod bent, rigid frame column, the column pier (Taiwan) Pier (Taiwan) column and so on. Eccentric: (flexure and compression) Eccentric force component Two-way eccentric force component Large eccentric compression Small eccentric compression Bending structures: Axial pressure to bear on the same cross-section and moment components. Eccentricity: The role of N point of the pressure from the member section centroid distance e0

JIPlKIC 结构设计原理 The principle of structure design 7.1.3 Construction requirements (1)Rectangular cross-section for the most common form of Section height h is greater than 600mm,use more eccentric compression Shaped or box-shaped cross section. Circular section is mainly used for column Pier,Pile Foundation
(1) Rectangular cross-section for the most common form of Section height h is greater than 600mm, use more eccentric compression Shaped or box-shaped cross section. Circular section is mainly used for column Pier, Pile Foundation. §7.1.3 Construction requirements
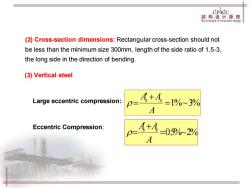
JPKIC 结构设计原理 jhepnihplestncturedesig (2)Cross-section dimensions:Rectangular cross-section should not be less than the minimum size 300mm,length of the side ratio of 1.5-3, the long side in the direction of bending. (3)Vertical steel Large eccentric compression: A+4=1%~3% A Eccentric Compression: A+A=0.5%~2% A
(2) Cross-section dimensions: Rectangular cross-section should not be less than the minimum size 300mm, length of the side ratio of 1.5-3, the long side in the direction of bending. (3) Vertical steel Large eccentric compression: Eccentric Compression: =1%~3% + = A As As =0.5%~2% + = A As As
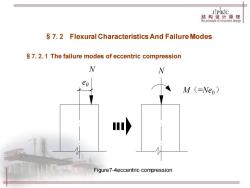
JPKIC 结构设计原理 The principle of structure design S 7.2 Flexural Characteristics And Failure Modes S 7.2.1 The failure modes of eccentric compression N M (=Neo) Figure7-4eccentric compression
Figure7-4eccentric compression N e0 N M(=Ne0) §7.2 Flexural Characteristics And Failure Modes §7.2.1 The failure modes of eccentric compression

JPKIC 结构设计原理 Tfepmieipleistrcturdesign 1.Tensile failure-big eccentric compressive damage Produce conditions:(e/h)large relative eccentricity, And the tension reinforcement configuration Debu too much. FAlLURE Some tension,some pressure,tensile reinforcement stress Yield strength is reached first,and then,concrete is pushed Chopped up to yield strength of compression reinforcement Bearing components Set depends upon the strength and tensile reinforcement quantity. Destruction of nature:plastic failure
1. Tensile failure - big eccentric compressive damage Destruction of nature: plastic failure. Produce conditions: (e/h)large relative eccentricity, And the tension reinforcement configuration Debu too much. Some tension, some pressure, tensile reinforcement stress Yield strength is reached first, and then, concrete is pushed Chopped up to yield strength of compression reinforcement. Bearing components Set depends upon the strength and tensile reinforcement quantity. FAILURE: N N

JPKic 结构设计原理 2.Compressive damage-damage to small eccentric compression The principle of structure design ●Produce conditions: (1)A very small eccentricity. (2)(h)smaller eccentricity,or eccentricity larger and more tensile reinforcement. (3)(e/centricity is small,but the pressure from the far side of the vertical bar a small number,while the N side of the bar near the longitudinal forces more time. FAILURE:Generally near the longitudinal force reached the limits of the first side of the concrete compressive strain and crushed the side of the steel reaches the yield strength of longitudinal force from either side of the steel in tension or compression,usually fail to yield strength.Capacity depends on the compression component of concrete compressive strength and steel strength. Destruction of nature:Brittle failure
⚫ Produce conditions: (1) A very small eccentricity. (2) smaller eccentricity, or eccentricity larger and more tensile reinforcement. (3) eccentricity is small, but the pressure from the far side of the vertical bar a small number, while the N side of the bar near the longitudinal forces more time. ⚫ FAILURE:Generally near the longitudinal force reached the limits of the first side of the concrete compressive strain and crushed the side of the steel reaches the yield strength of longitudinal force from either side of the steel in tension or compression, usually fail to yield strength. Capacity depends on the compression component of concrete compressive strength and steel strength. ⚫ Destruction of nature: Brittle failure. ( / ) 0 e h ( / ) 0 e h N N 2. Compressive damage - damage to small eccentric compression
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 6 Carrying Capacity of Members under Axial Loading 轴心受压构件承载力计算.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 4 Shear Strength of Inclined Section in Flexure(Shear strength of RC beams).ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 2 Probablisitic Limit States Design Method.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of RC Structures.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 0 General Introduction.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第9讲 受弯构件受力全过程和破坏特点.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第10讲 单筋矩形截面强度计算公式及其应用.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第8讲 受弯构件受力全过程和破坏特点.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第7讲 受弯构件截面形式和构造特点.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第6讲 作用、作用代表值和作用效应组合.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第5讲 概率极限状态设计法的基本原则.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第4讲 钢筋基本力学性能.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第3讲 混凝土基本力学性能.docx
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第2讲 钢筋混凝土结构基本概念.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第四讲 钢筋基本力学性能.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第十讲 受弯构件强度计算公式及其应用.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第六讲 作用、作用代表值和作用效应组合.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第八讲 受弯构件受力全过程和破坏特点.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第五讲 概率极限状态设计法的基本原则.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第二讲 钢筋混凝土结构基本概念.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 9 Crack width.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《水工钢筋混凝土结构》课程教学资源(教案大纲)水工钢筋混凝土结构教学大纲 Water Power Engineering Reinforced Concrete Structure (负责人:任宜春).pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《水工钢筋混凝土结构》课程教学资源(教案大纲)水工钢筋混凝土结构教案.pdf
- 《水工钢筋混凝土结构》课程教学资源(参考资料)中华人民共和国水利行业标准(SL191-2008)水工混凝土结构设计规范 Design code for hydraulic concrete structures.pdf
- 《水工钢筋混凝土结构》课程教学资源(参考资料)中华人民共和国电力行业标准(DL/T 5057-2009)水工混凝土结构设计规范 Design specification for hydraulic concrete structures.pdf
- 简支钢桁架非破损试验指导书.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第一章 制图基本知识.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第三章 点.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第二章 投影的基本知识.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第五章 平面.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第六章 直线与平面的相对位置、两平面相对位置.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第四章 直线.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(作业习题)道路工程制图习题集.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第12章 组合体视图(组合体的投影).ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第13章 工程形体的表达方法.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第16章 道路工程图.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第17章 桥梁、隧道、涵洞工程图.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第1章 国家制图标准与制图基本知识.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第3章 点、线、面的投影.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第9章 基本形体.ppt
