长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of RC Structures

JIPKIC 结构热计原黑 Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Reinforced Concrete Structure and Physical and Mechanical Properties of Materials
Chapter 1 Basic Concepts of Reinforced Concrete Structure and Physical and Mechanical Properties of Materials

JPKIC 结构计原黑 MAIN CONTENT Basic Concepts of Reinforced Concrete(RC) Strength and deformation of concrete under various stress conditions Type ,Grade and Mechanical Properties of Steel Reinforcement Bond between concrete and steel reinforcement
MAIN CONTENT ⚫ Basic Concepts of Reinforced Concrete(RC) ⚫ Strength and deformation of concrete under various stress conditions ⚫ Type ,Grade and Mechanical Properties of Steel Reinforcement ⚫ Bond between concrete and steel reinforcement

JIPKIC S1.1 The basic concepts of RC structures 箱构计原黑 1.Definition of RC Structure Reinforced concrete structures is a structure made of concrete configured by steel reinforcement and steel skeleton Production of reinforced concrete:the combination of steel and concrete work together.Concrete is in compression,and steel reinforcement is in tension,this fully play their advantages. Concrete:Non-homogeneous materials:high compressive strength,tensile strength is very low being (1/8~1/18)of compressive strength Steel reinforcement:high tensile and compressive strength. Often carry tension
§1.1 The basic concepts of RC structures • 1. Definition of RC Structure • Reinforced concrete structures is a structure made of concrete configured by steel reinforcement and steel skeleton. • Production of reinforced concrete: the combination of steel and concrete work together. Concrete is in compression, and steel reinforcement is in tension, this fully play their advantages. • Concrete: Non-homogeneous materials: high compressive strength, tensile strength is very low being (1 / 8 ~ 1 / 18) of compressive strength . • Steel reinforcement: high tensile and compressive strength. Often carry tension

P P P D 9 Simply supported Continuous beam beam stnuctuTGS RC plate P Column
RC plate P P P e P Column e Simply supported beam P P P P Continuous beam RC structures

JPKic 结构盘计原黑 Proems Why should steel rebar be set in common plate, beams,columns? Analysis of some common phenomena of crack of plate and beam structures
Why should steel rebar be set in common plate, beams, columns? Analysis of some common phenomena of crack of plate and beam structures
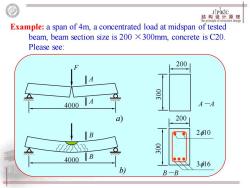
JPKIC 构盘计原 Example:a span of 4m,a concentrated load at midspan of tested beam,beam section size is 200 X300mm,concrete is C20. Please see: 200 4000 A A一A 200 210 4000 B 316 b) B—B
Example: a span of 4m, a concentrated load at midspan of tested beam, beam section size is 200 ×300mm, concrete is C20. Please see: 4000 A A F a) 200 300 A-A b) 4000 B B B-B 200 300 210 316

JIPKIC 结构热计原黑 Testing results: In fig.a),for plain concrete beam,the ultimate load P=8kN, controlled by the concrete tensile strength,failure modes: brittle failure In fig.b),the ultimate load of RC beam P=36kN,the steel rebar is in tension,and concrete is in compression to crush, failure mode:ductile failure (appropriate steel reinforcement) This can be concluded:the effectiveness of combination of steel and concrete: 1,greatly enhance the load-carrying capacity 2,improve the mechanical performance of structure
Testing results: • In fig. a),for plain concrete beam, the ultimate load P = 8kN, controlled by the concrete tensile strength, failure modes: brittle failure • In fig. b) , the ultimate load of RC beam P = 36kN, the steel rebar is in tension, and concrete is in compression to crush, failure mode: ductile failure (appropriate steel reinforcement) • This can be concluded: the effectiveness of combination of steel and concrete: 1, greatly enhance the load-carrying capacity 2, improve the mechanical performance of structure

JPKIC 结构计原黑 2.Reasons for steel and concrete working together (1)a good bond strength between them (2)The temperature linear expansion coefficient are close steel a=1.2×10-5 concrete ac=1.0 ~1.5 x 10-5 (3)Steel rebar embedded in concrete,which can prevent steel from rust
2、Reasons for steel and concrete working together (1) a good bond strength between them (2) The temperature linear expansion coefficient are close (3) Steel rebar embedded in concrete, which can prevent steel from rust. steel st = 1.2 10–5 concrete ct = 1.0 ~ 1.5 10–5

JPKIC 结构设计原理 The principle of structure design 3.The main advantages and disadvantages of RC structures ·Advantages: 1)rich materials resource,saving steel 2)Durability 3)good fire resistance 4)mold well,easy realization of structural type; 5)A good structural integrity due to cast-in-site
3、 The main advantages and disadvantages of RC structures • Advantages: 1) rich materials resource, saving steel 2) Durability 3) good fire resistance 4) mold well, easy realization of structural type; 5) A good structural integrity due to cast-in-site

JPKIC Disadvantages: 结构势计原黑 (1 high self-weight solution Light aggregate material (2)Crack resistance is,work with cracks solution Prestressed concrete (3)Construction is impacted by climate conditions,the a long construction period (4)More mold tools and wood waste (5 )Difficult strengthening and reconstruction,poor heat and noise-resistance performance
⚫ Disadvantages: (2)Crack resistance is, work with cracks (3)Construction is impacted by climate conditions, the a long construction period (4 ) More mold tools and wood waste (5)Difficult strengthening and reconstruction, poor heat and noise- resistance performance. (1)high self-weight Light aggregate material Prestressed concrete solution solution
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 0 General Introduction.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第9讲 受弯构件受力全过程和破坏特点.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第10讲 单筋矩形截面强度计算公式及其应用.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第8讲 受弯构件受力全过程和破坏特点.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第7讲 受弯构件截面形式和构造特点.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第6讲 作用、作用代表值和作用效应组合.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第5讲 概率极限状态设计法的基本原则.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第4讲 钢筋基本力学性能.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第3讲 混凝土基本力学性能.docx
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(作业习题)第2讲 钢筋混凝土结构基本概念.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第四讲 钢筋基本力学性能.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第十讲 受弯构件强度计算公式及其应用.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第六讲 作用、作用代表值和作用效应组合.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第八讲 受弯构件受力全过程和破坏特点.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第五讲 概率极限状态设计法的基本原则.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第二讲 钢筋混凝土结构基本概念.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第九讲 受弯构件正截面承载力计算的基本原则.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第三讲 混凝土基本力学性能.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第七讲 受弯构件截面形式和构造要求.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(技能点)第一讲 总论.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 2 Probablisitic Limit States Design Method.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 4 Shear Strength of Inclined Section in Flexure(Shear strength of RC beams).ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 6 Carrying Capacity of Members under Axial Loading 轴心受压构件承载力计算.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 7 Load-Carrying Capacity of Normal Section of Members under Eccentric Loads.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《结构设计原理》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 9 Crack width.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《水工钢筋混凝土结构》课程教学资源(教案大纲)水工钢筋混凝土结构教学大纲 Water Power Engineering Reinforced Concrete Structure (负责人:任宜春).pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《水工钢筋混凝土结构》课程教学资源(教案大纲)水工钢筋混凝土结构教案.pdf
- 《水工钢筋混凝土结构》课程教学资源(参考资料)中华人民共和国水利行业标准(SL191-2008)水工混凝土结构设计规范 Design code for hydraulic concrete structures.pdf
- 《水工钢筋混凝土结构》课程教学资源(参考资料)中华人民共和国电力行业标准(DL/T 5057-2009)水工混凝土结构设计规范 Design specification for hydraulic concrete structures.pdf
- 简支钢桁架非破损试验指导书.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第一章 制图基本知识.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第三章 点.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第二章 投影的基本知识.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第五章 平面.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第六章 直线与平面的相对位置、两平面相对位置.pdf
- 《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(参考教材)第四章 直线.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(作业习题)道路工程制图习题集.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第12章 组合体视图(组合体的投影).ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第13章 工程形体的表达方法.ppt
- 长沙理工大学:《土木工程识图》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第16章 道路工程图.ppt
