上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.1-9.3)

Chap.9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.I Molecular Geometry 9.2 YSEPR model 9.3 Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity 9.4 Covalent Bonding and Orbital Overlap 9.5 Hybridization Hybrid Orbitals 9.6 Multiple bond 9.7 Molecular Orbitals
Chap. 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Geometry 9.2 VSEPR model 9.3 Molecular Shape and Molecular Polarity 9.4 Covalent Bonding and Orbital Overlap 9.5 Hybridization & Hybrid 9.5 Hybridization & Hybrid Orbitals Orbitals 9.6 Multiple bond 9.7 Molecular 9.7 Molecular Orbitals Orbitals

Do SO2 CO2 and NO2 have the similar 3D structures? How about their Polarity?
Do SO2, CO2 and NO2 have the similar 3D structures? How about their Polarity?

Molecular Geometry (Shapes) Lewis structures give atomic connectivity 妇 The shape of a molecule is determined by its H&C&H bond angles OX H Bond distance, 1.78A Bond angle, 109.5
Molecular Geometry (Shapes) Lewis structures give atomic connectivity The shape of a molecule is determined by its bond angles H H H C Hx x x x
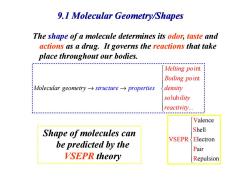
9.1 Molecular Geometry/Shapes The shape of a molecule determines its odor,taste and actions as a drug.It governs the reactions that take place throughout our bodies. Melting point Boiling point Molecular geometry->structure->properties density · solubility reactivity... Valence Shape of molecules can Shell VSEPR Electron be predicted by the Pair VSEPR theory Repulsion
9.1 Molecular Geometry/Shapes The shape of a molecule determines its odor, taste and actions as a drug. It governs the reactions that take place throughout our bodies. int int Melting po B Molecular geo oiling po metry structure properties density → → Shape of molecules can be predicted by the VSEPR theory lub ... Molecular geo density so ility structure reactivit metr prope y y → → rties alence hell lectron air epulsion V S VSEPR E P R

9.2 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR)theory imt0predicttheshapesofaoleocule2 a)The valence electrons repel each other Bonding electrons Valence electrons of Central Atom- Non-bonding electrons b)The molecule adopts whichever 3D geometry minimized this repulsion. Valence electrons staying as far apart as possible!
9.2 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory a) The valence electrons repel each other - Bonding electro Valence ele ns Non bon ctrons din of Ce g elec nt tr r o al Atom ns b) The molecule adopts whichever 3D geometry minimized this repulsion. Valence electrons staying as far apart as possible!
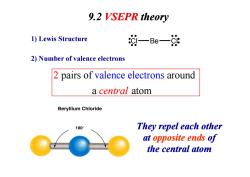
9.2 VSEPR theory 1)Lewis Structure 汝一Be一处 2)Number of valence electrons 2 pairs of valence electrons around a central atom Beryllium Chloride 180° They repel each other at opposite ends of the central atom
9.2 VSEPR theory pairs of around val a 2 ence ele a ctron t s central om 1) Lewis Structure Cl Be Cl 2) Number of valence electrons a central atom They repel each other at opposite ends of the central atom
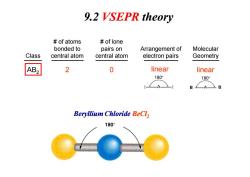
9.2 VSEPR theory of atoms of lone bonded to pairs on Arrangement of Molecular Class central atom central atom electron pairs Geometry AB2 2 0 linear linear 180° 180° :A Beryllium Chloride BeCl 180°
AB2 2 0 Class # of atoms bonded to central atom # of lone pairs on central atom Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry linear linear B B 9.2 VSEPR theory B B Beryllium Chloride BeCl2
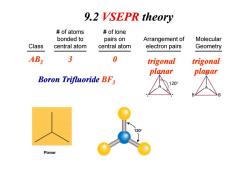
9.2 VSEPR theory of atoms of lone bonded to pairs on Arrangement of Molecular Class central atom central atom electron pairs Geometry AB3 3 0 trigonal trigonal planar planar Boron Trifluoride BF3 120° \ Planar
Class # of atoms bonded to central atom # of lone pairs on central atom Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry AB3 3 0 trigonal planar trigonal planar Boron Trifluoride BF3 9.2 VSEPR theory
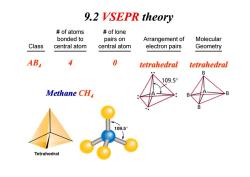
9.2 VSEPR theory of atoms of lone bonded to pairs on Arrangement of Molecular Class central atom central atom electron pairs Geometry AB 4 0 tetrahedral tetrahedral B 109.5° Methane CHa B B 109.5° Tetrahedral
Class # of atoms bonded to central atom # of lone pairs on central atom Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry AB4 4 0 tetrahedral tetrahedral Methane CH 9.2 VSEPR theory Methane CH4
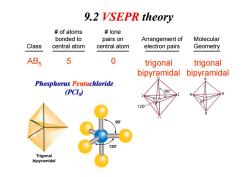
9.2 VSEPR theory of atoms lone bonded to pairs on Arrangement of Molecular Class central atom central atom electron pairs Geometry AB5 5 0 trigonal trigonal bipyramidal bipyramidal Phosphorus Pentachloride (PCL) 90 B 90° 120° Trigonal bipyramidal
Class # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry AB5 5 0 trigonal bipyramidal trigonal bipyramidal Phosphorus Pentachloride (PCl ) 9.2 VSEPR theory (PCl5)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms(6.4-6.9).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap.20 Voltaic Cells(Galvanic Cells).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Nano-scale materials in chemistry.pdf
- 《高分子化学》课程教学资源(参考材料)Lecture Notes in Chemistry Volume 82《Principles of Polymer Design and Synthesis》.pdf
- 《高分子化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Paul C. Hiemenz&Timothy P. Lodge《Polymer Chemistry》第二版(Second Edition).pdf
- 《高分子化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)CHRISTOPHER S.BRAZEL、STEPHEN L.ROSEN《FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES OF POLYMERIC MATERIALS》(Third Edition).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高分子化学 Polymer Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)自由基聚合(连锁聚合).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高分子化学 Polymer Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)缩聚和逐步聚合.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高分子化学 Polymer Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)缩聚和逐步聚合的实施方法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高分子化学 Polymer Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)体型缩聚与缩聚共聚.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高分子化学 Polymer Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)绪论(郭晓霞).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第四章 太阳能与光伏发电.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第二章 化学电池原理与应用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第三章 氢能与高分子电解质膜燃料电池(Hydrogen Energy and Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第一章 能源与高分子概论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第四章 太阳能与光伏发电.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第五章 风力发电与储能电池.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第二章 化学电池原理与应用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.4-9.7).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Nanoscale materials in chemistry.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)polymers and plastics.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics(2/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics(3/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics(1/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap.20 Voltaic Cells(Galvanic Cells).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms(6.1-6.4).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms(6.5-6.9).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap. 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.1-9.3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap. 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.4-9.6).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap. 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.7).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap. 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)discussion-organic dyes-color.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Introduction of Chem(刘萍).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 Naming Inorganic Compounds.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chromatography-A colarful world.pdf
- 苏州大学化学化工学院:《无机化学》课程教学资源(授课教案,药学、生物制药、中药专业).pdf
