上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)discussion-organic dyes-color

Team work report---"Chemistry at work---Organic Dye" a.What are HUMO and LUMO? b.What are the delocalized n electrons and delocalized n bonds? c.Why some substances,such as organic dyes,are colorful?briefly explain the reasons according to what you have learnt from"Organic dyes"(in the light of molecular orbital theory).What kinds of organic compounds are typical colorful materials? d.Answer the question of 9.93 9.104(f); (a)What is the hybridization at the N atom in each of the substances? (b)How many unhybridized atomic orbitals are there on the N and the C atoms in each ofthe substances? (c)Predict the N-N-C angles in each of the substances. (d)Azobenzene is said to have greater delocalization of its pi electrons than in hydrazobenzene.Discuss this statement. (e)All the atoms of azobenzene lie in one plane,whereas those of the azobenzene do not.Is this observation consistent with the statement in part(a)? (f)Azobenzene is an intensive orange color,whereas hydrazobenzene is nearly colorless.(How many conjugated pi electrons are delocalized in these two compounds?) (f)Benzene,naphthalene and anthracene are colorless,Tetracene is orange,how can this observation be explained? e.List the questions which you didn't understand after your learning and discussion
Team work report ---“Chemistry at work Chemistry at work---Organic Dye Organic Dye” a. What are HUMO and LUMO? b. What are the delocalized b. What are the delocalized π electrons and delocalized electrons and delocalized π bonds? c. Why some substances, such as organic dyes, are colorful? briefly explain the reasons according to what you have learnt from “Organic dyes” ( according to what you have learnt from “Organic dyes” (in the light of molecular orbital theory). What kinds of organic compounds are typical colorful materials? d. Answer the question of 9.93 & 9.104(f); (a)What is the hybridization at the N atom in each of the substances? (b)How many unhybridized atomic orbitals are there on the N and the C atoms in each of the substances? (c) Predict the N (c) Predict the N-N-C angles in each of the substances. C angles in each of the substances. (d) Azobenzene is said to have greater delocalization of its pi electrons than in hydrazobenzene hydrazobenzene. Discuss this statement. . Discuss this statement. (e) All the atoms of azobenzene lie in one plane, whereas those of the azobenzene do not. Is this observation consistent with the statement in part (a)? (f) Azobenzene is an intensive orange color, whereas (f) Azobenzene is an intensive orange color, whereas hydrazobenzene is nearly obenzene is nearly colorless. (How many conjugated pi electrons are delocalized in these two compounds?) (f) Benzene, naphthalene and (f) Benzene, naphthalene and anthracene anthracene are colorless, are colorless, Tetracene Tetracene is orange, how can is orange, how can this observation be explained? e. List the questions which you didn’t understand after your learning and discussion

Questions in your team work reports 1."Why Azobenzene is said to have greater delocalization of its electrons than hydrazobenzene?"We don't know why the n electrons of N should be delocalized?We think the bond between N-N is just a double bond rather than a delocalized a bond.(G.2) 2.What kind of n bonds are needed to delocalize the n electrons among all the main atoms in a molecule?Must all unhybridized orbitals be in the same direction?(G.7) 3.The following sentence is from the textbook Because B-carotene contains 11 conjugated double bonds,its n electrons are very extensively delocalized.We want to know whether the bonds in B-carotene are double bonds or not.If they are,why it still says n electrons are very extensively delocalized."We think double bonds'n electrons are localized.(G.2)
1. “Why Azobenzene is said to have greater delocalization of its π electrons than hydrazobenzene?” We don’t know why the π electrons of N should be delocalized? We think the bond between N-N is just a double bond rather than a delocalized π bond. (G. 2) 2. What kind of π bonds are needed to delocalize the π electrons among all the main atoms in a molecule? Must all unhybridized Questions in your team work reports : orbitals be in the same direction? (G. 7) 3. The following sentence is from the textbook :Because β-carotene contains 11 conjugated double bonds, its π electrons are very extensively delocalized. We want to know whether the bonds in β-carotene are double bonds or not. If they are, why it still says “π electrons are very extensively delocalized.” We think double bonds’ π electrons are localized. (G. 2)
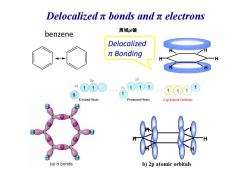
Delocalizedπbonds andπelectrons 离域pi键 benzene Delocalized πBonding 2p 2p 2s 111 Ground State Promoted State 3 sphybrid Orbitals (a)o bonds b)2p atomic orbitals
benzene H H H H H H Delocalized π Bonding 离域pi键 Delocalized π bonds and π electrons
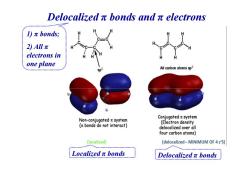
Delocalizedπbonds andπelectrons )元bonds;. 2)Allπ electrons in one plane Sp3 All carbon atoms sp2 Non-conjugated x system Conjugatedπsystem (Electron density bonds do not interact) delocalized over all four carbon atoms) (localized) (delocalized-MINIMUM OF 4 c'S) Localizedπbonds Delocalizedπbonds
Delocalized π bonds and π electrons 1) π bonds; 2) All π electrons in one plane Localized π bonds Delocalized π bonds
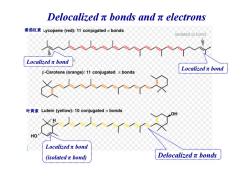
Delocalizedπbonds andπelectrons 番茄红素Lycopene(red:11 conjugated x bonds isolated pi bond Localizedπbond a年8s年0s048年8ss8年年s888esa Localizedπbond B-Carotene (orange):11 conjugated x bonds 叶黄素Lutein(yellow):10 conjugated x bonds OH Localizedπbond isolatedπbond edπbon Delocalizedπbonds
Delocalized π bonds and π electrons 番茄红素 Localized π bond Localized π bond Localized π bond (isolated π bond) Delocalized π bonds 叶黄素
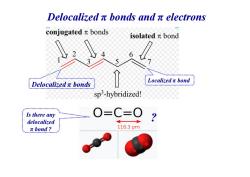
Delocalizedπbonds andπelectrons conjugatedπbonds isolatedπbond 6 Localizedπbond Delocalizedπbonds sp3-hybridized! 用目国图图名a Is there any O=C=0 delocalized πbond? 116.3pm
Delocalized π bonds and π electrons Delocalized π bonds Localized π bond Is there any delocalized π bond ? ?
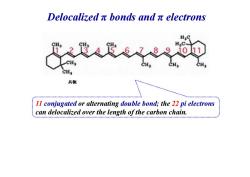
Delocalizedπbonds andπelectrons H 共轭 11 conjugated or alternating double bond;the 22 pi electrons can delocalized over the length of the carbon chain
Delocalized π bonds and π electrons 共轭 11 conjugated or alternating double bond; the 22 pi electrons can delocalized over the length of the carbon chain
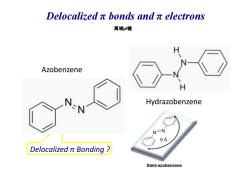
Delocalizedπbonds andπelectrons 离域pi键 Azobenzene H Hydrazobenzene N=N 9A Delocalized t Bonding trans-azobenzene
Azobenzene 离域pi键 Delocalized π bonds and π electrons Delocalized π Bonding ? Hydrazobenzene

Questions in your team work reports 4.Why does delocalization make the HOMO-LUMO gap smaller? (G.7,4,9,12,13,15,17) 5.If a molecule has several atoms with different maximum absorbable wavelength,do we say it has many maximum absorbable wavelength,or we just consider the largest one (G.7) 6.Does the electron inside a molecule only absorb the light which can be used to cover the HOMO-LUMO gap?(G.11) 7. Can the electrons in an organic molecule be excited only by the light of certain wavelength or all the wavelengths in the visible range?(G.7) 8. Will the number of excited electrons do any different to the color? (G.7) 9.What's the exact correlation between a molecule's color and the light it absorbs,resulting from its HOMO-LUMO gap?(G.11) 10.Can the relationship between HOMO-LUMO gap and absorbed light be quantized?(G.8)
4. Why does delocalization make the HOMO-LUMO gap smaller? (G. 7, 4, 9, 12, 13, 15, 17) 5. If a molecule has several atoms with different maximum absorbable wavelength, do we say it has many maximum absorbable wavelength, or we just consider the largest one ? (G. 7) 6. Does the electron inside a molecule only absorb the light which can be used to cover the HOMO-LUMO gap? (G. 11) 7. Can the electrons in an organic molecule be excited only by the Questions in your team work reports : light of certain wavelength or all the wavelengths in the visible range? (G. 7) 8. Will the number of excited electrons do any different to the color? (G. 7) 9. What’s the exact correlation between a molecule’s color and the light it absorbs, resulting from its HOMO-LUMO gap? (G. 11) 10. Can the relationship between HOMO-LUMO gap and absorbed light be quantized? (G. 8)
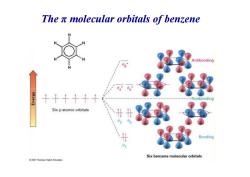
The n molecular orbitals of benzene Antibonding 6 十+千十十十 --Nonbonding Six p atomic orbitals 2 Bonding Six benzene molecular orbitals 2007 Thomson Higher Educabion
The π molecular orbitals of benzene
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap. 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap. 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.7).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap. 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.4-9.6).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap. 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.1-9.3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms(6.5-6.9).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms(6.1-6.4).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap.20 Voltaic Cells(Galvanic Cells).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics(1/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics(3/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics(2/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)polymers and plastics.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Nanoscale materials in chemistry.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.4-9.7).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.1-9.3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms(6.4-6.9).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap.20 Voltaic Cells(Galvanic Cells).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Introduction of Chem(刘萍).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 Naming Inorganic Compounds.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chromatography-A colarful world.pdf
- 苏州大学化学化工学院:《无机化学》课程教学资源(授课教案,药学、生物制药、中药专业).pdf
- 苏州大学医学部药学院:《生物化学(五)Biochemistry V》课程教学资源(教学大纲).docx
- 苏州大学医学部药学院:《生物化学(五)实验 Experiment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology》课程教学资源(教学大纲).docx
- 苏州大学化学化工学院:《无机化学 Inorganic chemistry》课程教学资源(教学大纲).docx
- 苏州大学化学化工学院:《无机化学实验 Inorganic Chemistry Experiments》课程教学资源(教学大纲,药学类专业).docx
- 长春理工大学化学与环境工程学院:教学大纲合集(学科基础课程、专业教育课程、大光电课程、基础实践课程、专业实践课程、综合实践课程).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:波色系统(PPT讲稿)超流性.ppt
- 东莞理工学院:《循环经济与可持续发展》课程教学资源(教学大纲)程可可-化卓.docx
- 东莞理工学院:《循环经济与可持续发展》课程教学资源(教学大纲)程可可-应化.docx
- 东莞理工学院:2022-2023 第一学期《功能高分子材料》课程教学资源(教学大纲)赵莉丽-19应用化学,化卓班.docx
- 东莞理工学院:2022-2023学年第一学期《锂离子电池工程思维与方法》课程教学资源(教学大纲)赵丽源(1).docx
- 东莞理工学院:2022-2023学年第一学期《无机化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)李超-2022级应化1、2班-教学大纲.docx
- 东莞理工学院:2022-2023学年第一学期《无机化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)王永东-2022级应化卓越1、2班-教学大纲.docx
- 东莞理工学院:2022-2023学年第一学期《物理化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)2020级应用化学1、2班-宋金刚 苗荣荣-教学大纲-20220826.docx
- 东莞理工学院:2022-2023学年第一学期《物理化学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)2021级食品科学与工程1班-宋金刚-教学大纲-20220826.docx
- 东莞理工学院:2022-2023学年第一学期《物理化学实验》课程教学资源(教学大纲)2021级食品科学与工程1班-宋金刚、黄斯珉-教学大纲-20220826.docx
- 东莞理工学院:2022-2023学年第一学期一流专业《精细化学品工艺学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)课程教学大纲—赵丽源(1).docx
