上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Nano-scale materials in chemistry

Nano-scale materials in chemistry Nano materials:materials that have a dimension on the 10-100nm Scle.(任何至少有一个维度的尺寸小于100nm或由小于100nm的基本单元组成的材料) 2D Graphene C Nanotubes(CNTs) Fullerenes 石墨烯 C纳米管 富乐烯 http://www.google.com.tw/imgres?q=fullerenc&hl Cited from Nanoscale Materials in Chemistry;Edited by Kenneth J.Klabunde
Nano-scale materials in chemistry Nano materials: materials that have a dimension on the 10-100nm scale.(任何至少有一个维度的尺寸小于100nm或由小于100nm的基本单元组成的材料) http://www.google.com.tw/imgres?q=fullerene&hl Cited from Nanoscale Materials in Chemistry; Edited by Kenneth J. Klabunde Fullerenes 富乐烯 C Nanotubes (CNTs) C 纳米管 Graphene 石墨烯

Nano-Materials OD nanomaterials:Nano particles(原子团簇、纳米微粒等). 100 nm 200 nm 100 nm 黄页风 ww.huangye88.com Monodispersed Ag nano particles Commercial Ag nano particles
Nano-Materials 0D nanomaterials:Nano 0D nanomaterials:Nano nanomaterials:Nano particles particles (原子团簇、纳米微粒等). Monodispersed Ag nano particles Commercial Ag nano particles

Nanoscale materials (1)小尺寸效应:当纳米微粒尺寸与光波波长、传导电子的德布 罗意波长及超导态的相干长度、透射深度等物理特征尺寸相当或 更小时,它的周期性边界被破坏,从而使其声、光、电、磁,热 力学等性能呈现出“新奇”的现象。 Ep.I:The nano-scale copper particles are non conductive. Ep.2:Gold particles less than 20 nm in diameter melt at a far lower temperature than bulk gold.(Tmp.=1337.33K,1064.18)
(1)小尺寸效应:当纳米微粒尺寸与光波波长 :当纳米微粒尺寸与光波波长、传导电子的德布 、传导电子的德布 罗意波长及超导态的相干长度、透射深度等物理特征尺寸相当或 、透射深度等物理特征尺寸相当或 更小时,它的周期性边界被破坏 ,它的周期性边界被破坏,从而使其声、光、电、磁,热 力学等性能呈现出“新奇”的现象。 Ep.1: The nano-scale copper particles are non conductive. Nanoscale materials Ep.2:Gold particles less than 20 nm in diameter melt at a far lower temperature than bulk gold. (Tm.p.=1337.33 K ,1064.18 °)

Nanoscale materials in chemistry The Melting Points of Gold particles 1100 1000 一◆◆◆◆ 900- 800 Tmp=1064.18°C 700 202 1 0- 0 34567891011 Particle Radius [nm] FIGURE 2.6 Relation between the size of gold particles and their melting point. Cited from Nanoscale Materials in cCemistry;Edited by Kenneth J.Klabunc
Nanoscale materials in chemistry The Melting Points of Gold particles Tm.p. =1064.18 °C Cited from Nanoscale Materials in cCemistry; Edited by Kenneth J. Klabunde

The solubility of Gold nano-particles in water Ep.3 The nano-scale gold particles are soluble in water and deeply red colored. 2012P Figure 12.46 The solutions of colloidal gold nanoparticles made by Michael Faraday in the 1850s.(In the institute of Great Britain's Faraday Museum in London
The solubility of Gold nano-particles in water Ep.3 :The nano-scale gold particles are soluble in water and deeply red colored. Figure 12.46 The solutions of colloidal gold nanoparticles made by Michael Faraday in the 1850s. (In the institute of Great Britain’s Faraday Museum in London )

2012 Pearson Educalion.Inc Figure 12.45 Stained glass window from the Chartres Cathedral in France
Figure 12.45 Stained glass window from the Chartres Cathedral in France

Nanoscale materials (2)表面与界面效应:纳米晶体粒表面原子数与总原子数之比随粒径变小而 急剧增大后所引起的性质上的变化。 The percentage of TABLE 2.1 The relation between the total number of atoms in full surface atoms shell clusters and the percentage of surface atoms Full-shell Clusters Total Number Surface Atoms of Atoms (% 1 Shell 13 92 2 Shells 55 76 3 Shells 147 63 4 Shells 309 52 5Shells 561 45 7Shells 1415 35 Cited from Nanoscale Materials in Chemistry; Edited by Kenneth J.Klabunde
(2)表面与界面效应:纳米晶体粒表面原子数与总原子数之比随粒径变小而 急剧增大后所引起的性质上的变化。 Nanoscale materials The percentage of surface atoms Cited from Nanoscale Materials in Chemistry; Edited by Kenneth J. Klabunde

Nanoscale materials in chemistry Particle radii Number of atoms Percentage of surface atoms 10nm 4000 40% 1nm 30 99% 100 20 0 10 2030 4050 粒度nm Ex.Gold particles between 2 to 3 nm in diameter becomes chemically active
Nanoscale materials in chemistry Particle radii Number of atoms Percentage of surface atoms 10nm 4000 40% 1nm 30 99% Ex. Gold particles between 2 to 3 nm in diameter becomes chemically active
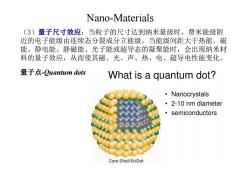
Nano-Materials (3)量子尺寸效应:当粒子的尺寸达到纳米量级时,费米能级附 近的电子能级由连续态分裂成分立能级。当能级间距大于热能、磁 能、静电能、静磁能、光子能或超导态的凝聚能时,会出现纳米材 料的量子效应,从而使其磁、光、声、热、电、超导电性能变化。 量子点-Quantum dots What is a quantum dot? ·Nanocrystals ·2-10 nm diameter ·semiconductors Core-Shell EviDot
Nano-Materials (3)量子尺寸效应:当粒子的尺寸达到纳米量级时,费米能级附 近的电子能级由连续态分裂成分立能级。当能级间距大于热能、磁 能、静电能、静磁能、光子能或超导态的凝聚能时,会出现纳米材 料的量子效应,从而使其磁、光、声、热、电、超导电性能变化。 量子点-Quantum dots

Nano-Materials (3)量子尺寸效应:当粒子的尺寸达到纳米量级时,费米能级附 近的电子能级由连续态分裂成分立能级。当能级间距大于热能、磁 能、静电能、静磁能、光子能或超导态的凝聚能时,会出现纳米材 料的量子效应,从而使其磁、光、声、热、电、超导电性能变化。 量子点(Quantum dots):the band gaps of a quantum dot will change greatly when its diameter is adjusted between 1-10 nm CB As particle gets smaller, the band gap gets bigger. VB Semiconductor
Nano-Materials (3)量子尺寸效应:当粒子的尺寸达到纳米量级时,费米能级附 近的电子能级由连续态分裂成分立能级。当能级间距大于热能、磁 能、静电能、静磁能、光子能或超导态的凝聚能时,会出现纳米材 料的量子效应,从而使其磁、光、声、热、电、超导电性能变化。 量子点(Quantum dots): the band gaps of a quantum dot will change greatly when its diameter is adjusted between 1- 10 nm As particle gets smaller, the band gap gets bigger
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《高分子化学》课程教学资源(参考材料)Lecture Notes in Chemistry Volume 82《Principles of Polymer Design and Synthesis》.pdf
- 《高分子化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Paul C. Hiemenz&Timothy P. Lodge《Polymer Chemistry》第二版(Second Edition).pdf
- 《高分子化学》课程教学资源(参考书籍)CHRISTOPHER S.BRAZEL、STEPHEN L.ROSEN《FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES OF POLYMERIC MATERIALS》(Third Edition).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高分子化学 Polymer Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)自由基聚合(连锁聚合).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高分子化学 Polymer Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)缩聚和逐步聚合.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高分子化学 Polymer Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)缩聚和逐步聚合的实施方法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高分子化学 Polymer Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)体型缩聚与缩聚共聚.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《高分子化学 Polymer Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)绪论(郭晓霞).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第四章 太阳能与光伏发电.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第二章 化学电池原理与应用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第三章 氢能与高分子电解质膜燃料电池(Hydrogen Energy and Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第一章 能源与高分子概论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第四章 太阳能与光伏发电.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第五章 风力发电与储能电池.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第二章 化学电池原理与应用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第三章 氢能与高分子电解质燃料电池(Hydrogen Energy and Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《清洁能源技术原理与应用》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第一章 能源与高分子概论(主讲:房建华).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学(通识)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)绪论.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学(通识)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第一篇 能源篇(2/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学(通识)》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第一篇 能源篇(1/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap.20 Voltaic Cells(Galvanic Cells).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms(6.4-6.9).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.1-9.3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.4-9.7).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Nanoscale materials in chemistry.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)polymers and plastics.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics(2/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics(3/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics(1/3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap.20 Voltaic Cells(Galvanic Cells).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms(6.1-6.4).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms(6.5-6.9).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap. 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.1-9.3).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap. 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.4-9.6).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap. 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories(9.7).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《大学化学 Chemistry》教学资源(课件讲稿)Chap. 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories.pdf
