《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第四章 微生物的合成代谢(1/7)

第四章 微生物的合成代谢
第四章 微生物的合成代谢

Principles Governing Biosynthesis macromolecules are synthesized from limited number of simple structural units (monomers) -saves genetic storage capacity,biosynthetic raw material,and energy many enzymes used for both catabolic and anabolic processes saves materials and energy
Principles Governing Biosynthesis • macromolecules are synthesized from limited number of simple structural units (monomers ) – saves genetic storage capacity, biosynthetic raw material, and energy • many enzymes used for both catabolic and anabolic processes – saves materials and energy
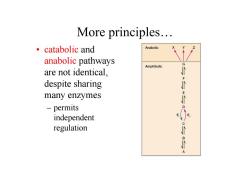
More principles. ·catabolic and Anabolic anabolic pathways Amphibolic are not identical. despite sharing many enzymes - permits 0 independent E regulation 日 A
More principles. • catabolic and anabolic pathways are not identical, despite sharing many enzymes – permits independent regulation

More principles. ● to synthesize molecules efficiently,anabolic pathways must operate irreversibly in the direction of biosynthesis done by coupling breakdown of ATP to certain reactions in biosynthetic pathways - drives the biosynthetic reaction to completion in eucaryotes,anabolic and catabolic reactions located in separate compartments allows pathways to operate simultaneously but independently
More principles. • to synthesize molecules efficiently, anabolic pathways must operate irreversibly in the direction of biosynthesis – done by coupling breakdown of ATP to certain reactions in biosynthetic pathways – drives the biosynthetic reaction to completion • in eucaryotes, anabolic and catabolic reactions located in separate compartments – allows pathways to operate simultaneously but independently

More principles. catabolic and anabolic pathways use different cofactors catabolism produces NADH -NADPH used as electron donor for anabolism large assemblies (e.g.,ribosomes)form spontaneously from macromolecules by self-assembly
More principles. • catabolic and anabolic pathways use different cofactors – catabolism produces NADH – NADPH used as electron donor for anabolism • large assemblies (e.g., ribosomes) form spontaneously from macromolecules by self-assembly

Precursor Metabolites generation of precursor metabolites is critical step in anabolism carbon skeletons are used as starting substrates for biosynthetic pathways -examples are intermediates of the central metabolic pathways most are used for the biosynthesis of amino acids
Precursor Metabolites • generation of precursor metabolites is critical step in anabolism • carbon skeletons are used as starting substrates for biosynthetic pathways – examples are intermediates of the central metabolic pathways – most are used for the biosynthesis of amino acids

The Organization of Anabolism Nucleosides Ribose-(P se-4-⊙ Glycerol-Triose-p Phenylalanine Tyrosine Tryptophar 3-phosphoglycerate Glycine Purines Histidine nolpyruvate Pyrimidines Threonine uccinyl-CoA Porphyrins 白to Arainine
7 The Organization of Anabolism

口本章的主要内容 ATP的利用和生物合成速率 C02的固定 一碳、二碳有机化合物的同化 糖类的合成 脂类的合成 含氮有机化合物的合成
本章的主要内容 ATP的利用和生物合成速率 含氮有机化合物的合成 CO2的固定 一碳、二碳有机化合物的同化 脂类的合成 糖类的合成

第四章微生物的合成代谢 口本章的主要内容 糖类的合成 √单糖的合成和相互转化 √寡糖及多聚糖的合成 √细胞壁的合成
糖类的合成 9单糖的合成和相互转化 9寡糖及多聚糖的合成 9细胞壁的合成 第四章 微生物的合成代谢 本章的主要内容

第四章微生物的合成代谢 口本章的主要内容 脂类的合成 √脂肪酸的合成 √磷脂的合成 √聚-B羟基丁酸的合成 萜类的合成
9脂肪酸的合成 9磷脂的合成 脂类的合成 9聚-β羟基丁酸的合成 9萜类的合成 第四章 微生物的合成代谢 本章的主要内容
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第四章 微生物的合成代谢(3/7).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第四章 微生物的合成代谢(6/7).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第四章 微生物的合成代谢(7/7).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第四章 微生物的合成代谢(5/7).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第四章 微生物的合成代谢(4/7).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程实验指导技术(共六个实验).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程授课教案(主讲教师:关国华、陈文峰).doc
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学大纲 Microbial Physiology.doc
- 《植物生物学野外实习》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)科技论文的写作.ppt
- 《植物生物学野外实习》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)植物标本的采集、制作和保存和鉴定.ppt
- 《生物多样性导论》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)19 遗传多样性(2/3).ppt
- 《生物多样性导论》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)20 遗传多样性(3/3).ppt
- 《生物多样性导论》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)18 遗传多样性(1/3).ppt
- 《生物多样性导论》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)15 农田生态系统中生物多样性应用.ppt
- 《生物多样性导论》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)17 遗传多样性.ppt
- 《生物多样性导论》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)14 农田生态系统中生物多样性应用.ppt
- 《生物多样性导论》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)12 植物获取营养的多样性.ppt
- 《生物多样性导论》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)13 农田生态系统中生物多样性应用.ppt
- 《生物多样性导论》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)11 珍稀动物.ppt
- 《生物多样性导论》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)09 物种多样性 species diversity.ppt
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第四章 微生物的合成代谢(2/7).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三章 产能代谢 Energy Yielding Metabolism(4/7).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三章 产能代谢 Energy Yielding Metabolism(5/7).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三章 产能代谢 Energy Yielding Metabolism(7/7).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三章 产能代谢 Energy Yielding Metabolism(6/7).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第二章 代谢概论 An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism.pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三章 产能代谢 Energy Yielding Metabolism(1/7).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三章 产能代谢 Energy Yielding Metabolism(2/7).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三章 产能代谢 Energy Yielding Metabolism(3/7).pdf
- 《微生物生理学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第一章 绪论 Microbial Physiology.pdf
- 《农业微生物学》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义)肽聚糖的合成及抗生素对肽聚糖合成的抑制.doc
- 《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义)第五章 微生物的营养和代谢 第一节 微生物的营养.doc
- 《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义)第六章 微生物的生长与环境条件(微生物的生长和测定方法).doc
- 《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义)第五章 微生物的营养和代谢 第二节 微生物的代谢.doc
- 《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义)第九章 基因突变与诱变育种.doc
- 《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义)第十章 微生物生态.doc
- 《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义)第八章 微生物遗传.doc
- 《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义)第十一章 微生物在农业及环保上的应用.doc
- 《农业微生物学》课程授课教案(讲义)第十章 微生物在自然界物质循环中的作用.doc
