《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 33 Molecular Basis of Inherited Disease

ABIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYRequirementMasterthecontentMolecular cloningFamiliarwith the content1.Genetic disease2. Molecular hybridization3.Polymerasechainreaction4.Restriction fragment length polymorphism(RFLP)Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Requirement Master the content Familiar with the content 1.Genetic disease 2. Molecular hybridization 3. Polymerase chain reaction 4.Restriction fragment length polymorphism(RFLP) Molecular cloning

BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYChapter 28MolecularBasis ofInherited DiseaseDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Chapter 28 Molecular Basis of Inherited Disease

BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYOutline*Overview*Genetic disease*Molecular cloning* Polymerase chain reaction*Molecularhybridization* Restriction fragment length polymorphism(RFLP)Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Outline *Overview *Genetic disease *Molecular cloning * Polymerase chain reaction * Molecular hybridization * Restriction fragment length polymorphism(RFLP)

BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY1.overview>Genetic diseases are disorders in which theclinical symptoms are linked to alterations in DNA The human genome contains DNA withapproximately 3 billion(109) base pairs that encode30,000 to 40,000 genes located on 23 pairs ofchromosomes.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ➢Genetic diseases are disorders in which the clinical symptoms are linked to alterations in DNA ➢ The human genome contains DNA with approximately 3 billion(109) base pairs that encode 30,000 to 40,000 genes located on 23 pairs of chromosomes. 1. overview
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY1.overview>It is now to determine the nucleotide sequence oflong stretches of DNA, and it is expected that theentire seguence of the human genome called thehuman genome project.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ➢It is now to determine the nucleotide sequence of long stretches of DNA, and it is expected that the entire sequence of the human genome called the human genome project. 1. overview
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY2.GeneticDiseases:Genetic Diseases:The molecular defects of inherited diseases range fromthe conceptually simple- a point mutation in DNAcausing the incorporation of an incorrect amino acid intoa protein- to errors in chromosome movement andtranscription that are complex and poorly understoodDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 2. Genetic Diseases: The molecular defects of inherited diseases range from the conceptually simple- a point mutation in DNA causing the incorporation of an incorrect amino acid into a protein- to errors in chromosome movement and transcription that are complex and poorly understood. Genetic Diseases:
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY2.Genetic Diseases:Genetic diseases are currently divided into five majorcategories:A. Single gene defectsB.Multifactorial disordersC. Chromosome disordersD.Somatic cell gene defectsE.Mitochondrial mutationsDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 2. Genetic Diseases: Genetic diseases are currently divided into five major categories: A. Single gene defects B. Multifactorial disorders C. Chromosome disorders D. Somatic cell gene defects E. Mitochondrial mutations
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY2.GeneticDiseases:SinglegenedefectsSingle gene, or monogenic, disorders result from amutation at a single siteona chromosome and areinherited in a simple mendelian pattern.Recessive and dominantHeterozygoter is generally normal and homozygotereceiving two defective genes shows clinical symptomsDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 2. Genetic Diseases: Single gene, or monogenic, disorders result from a mutation at a single site on a chromosome and are inherited in a simple mendelian pattern. Recessive and dominant Heterozygoter is generally normal and homozygote receiving two defective genes shows clinical symptoms Single gene defects
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY2.GeneticDiseases:Multifactorial disordersMost genetic diseases do not show a mendelian mode ofinheritancebecausethey aredetermined bymanygenesandareofteninfluenced by environmentalfactorsDiabetes mellitusHypertensionManicdepressionDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 2. Genetic Diseases: Most genetic diseases do not show a mendelian mode of inheritance because they are determined by many genes and are often influenced by environmental factors. Diabetes mellitus Hypertension Manic depression Multifactorial disorders
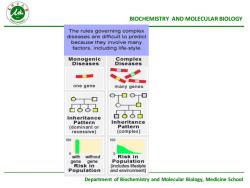
ABIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYTherules governing complexdiseases aredifficultto predictbecause theyinvolve manyfactors,includinglife-styleMonogenicComplexDiseasesDiseasesone genemanygenes广8InheritanceInheritancePatternPattern(dominantor(complex)recessive)100100withwithoutRisk inPopulationgenegeneRiskinlincludeslifestylePopulationandenvironment)Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 09 Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 10 Gluconeogenesis.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 28 Vitamins.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry,5th EDITION,David L. Nelson、Michael M. Cox.pdf
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)临床医本考试大纲.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)临床医本实验大纲 Biochemistry Experiment.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)实验教程.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)蛋白质的结构与功能.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)DNA的生物合成.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)糖代谢.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)细胞信息转导.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)CURRICULUM FOR UNDER-GRADUATE MEDICAL EDUCATION IN BANGLADESH 2002.pdf
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry,26th edition,Robert K. Murray Daryl K. Granner Peter A. Mayes Victor W. Rodwell.pdf
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Syllabus MBBS at the AIIMS(印度).pdf
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-护理本科-B卷-题目.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012级本科-B卷-题目.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-护理本科-B卷-答案.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012级本科-B卷-答案.doc
- 《生物化学》课程授课教案(石河子大学:黄瑾).pdf
- 《生物化学》课程教学大纲 Biochemistry(五年制医学专业本科生使用).pdf
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 22 Amino acids - metabolism of carbon skeletons.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 06 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Phosphorylation.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 21 Amino acids - disposal of nitrogen.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 07 Introduction of Carbohydrates.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 15 glycosaminoglycans.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 14 Metabolism of monosaccharides and disaccharides.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 01 Amino Acids(structure of amino acid、acid/base properties of amino acid).ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 01 Amino Acids(overview).ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 31 Structure and Function of RNA.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 20 The metabolism of cholesterol.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 29 Metabolism of Nucleotides.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 18 phospholipid metabolism.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 19 glycolipid metabolism.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 32 Biosynthesis of Protein.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)18 维生素 Vitamins.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)16 血液的生物化学 Hemal Biochemistry.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)17 肝的生物化学 Biochemistry in Liver.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 30 DNA Structure and Replication.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)13 基因表达调控 Regulation of Gene Expression.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)15 信号转导(细胞信息传递 Cell Communication and Signal Transduction).ppt
