《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 15 glycosaminoglycans

BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYChapter 15glycosaminoglycansDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Chapter 15 glycosaminoglycans
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYGlycosaminoglycans(GAGs)(GAGs) are large complexes of negatively chargedheteropolysaccharide chainsgenerally associatedwith a small amount of proteinGel-like matrix that forms the basis of the body'sground substance.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (GAGs) are large complexes of negatively charged heteropolysaccharide chains generally associated with a small amount of protein Gel-like matrix that forms the basis of the body’s ground substance. Glycosaminoglycans(GAGs)

BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYStructureofglycosaminoglycansGlycosaminoglycans are long, in most casesunbranched, heteropolysaccharide chains generallycomposed of a repeating disaccharide unitlacidicsugar amino sugarnDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Glycosaminoglycans are long, in most cases unbranched, heteropolysaccharide chains generally composed of a repeating disaccharide unit[acidic sugar amino sugar]n Structure of glycosaminoglycans

BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYBecause of their large number of negativecharges, these heteropolysaccharide chains tendto be extended in solution and repel each other,and are surrounded by a shell of water molecules.The six major types of the glycosaminoglycansare classified according to their monomericcompositions, type of glycosidic linkages, anddegree and location of their sulfate units.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Because of their large number of negative charges, these heteropolysaccharide chains tend to be extended in solution and repel each other, and are surrounded by a shell of water molecules. The six major types of the glycosaminoglycans are classified according to their monomeric compositions, type of glycosidic linkages, and degree and location of their sulfate units

BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYAll of the glycosaminoglycans except hyaluronicacid are found covalently attached to protein,forming proteoglycan monomers.A proteoglycanmonomer found in cartilage consists of a coreprotein to which the linear carbohydrate chainsare covalently attached.These chains, which may each be composed ofmore than 1o0 monosaccharides, extend out fromthe core protein and remain separated from eachother because of charge repulsion.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY All of the glycosaminoglycans except hyaluronic acid are found covalently attached to protein, forming proteoglycan monomers.A proteoglycan monomer found in cartilage consists of a core protein to which the linear carbohydrate chains are covalently attached. These chains, which may each be composed of more than 100 monosaccharides, extend out from the core protein and remain separated from each other because of charge repulsion
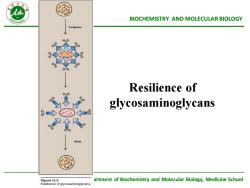
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYResilience ofglycosaminoglycansartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine SchoolPgure14.3Reeilianceofgycosaminoglyoans
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Resilience of glycosaminoglycans

BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYSynthesis ofglcosaminoglycansyDepartment of Biochemistryand Molecular Biology,MedicineSchool
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Synthesis of glcosaminoglycansy

BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYThe polysaccharide chains are elongated by the sequentialaddition of alternating acidic and amino sugars, donatedby their UDP-derivatives. The reactions are catalyzed by afamily of specific transferases.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY The polysaccharide chains are elongated by the sequential addition of alternating acidic and amino sugars, donated by their UDP-derivatives. The reactions are catalyzed by a family of specific transferases

BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYThe synthesis of the glycosaminoglycans is analogousto that of glycogen except that the glycosaminoglycansare produced for export from the cell.The synthesis occurs, therefore, in the endoplasmicreticulum and Golgi.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY The synthesis of the glycosaminoglycans is analogous to that of glycogen except that the glycosaminoglycans are produced for export from the cell. The synthesis occurs, therefore, in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi

山BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYA. Synthesis of amino sugarsB. Synthesis of acidic sugarsC. Synthesis of the core proteinD. Synthesis of the carbohydrate chainE. Addition of sulfate groupsDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY A. Synthesis of amino sugars B. Synthesis of acidic sugars C. Synthesis of the core protein D. Synthesis of the carbohydrate chain E. Addition of sulfate groups
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 07 Introduction of Carbohydrates.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 21 Amino acids - disposal of nitrogen.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 06 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Phosphorylation.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 22 Amino acids - metabolism of carbon skeletons.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 33 Molecular Basis of Inherited Disease.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 09 Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 10 Gluconeogenesis.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 28 Vitamins.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry,5th EDITION,David L. Nelson、Michael M. Cox.pdf
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)临床医本考试大纲.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)临床医本实验大纲 Biochemistry Experiment.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)实验教程.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)蛋白质的结构与功能.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)DNA的生物合成.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)糖代谢.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)细胞信息转导.doc
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)CURRICULUM FOR UNDER-GRADUATE MEDICAL EDUCATION IN BANGLADESH 2002.pdf
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry,26th edition,Robert K. Murray Daryl K. Granner Peter A. Mayes Victor W. Rodwell.pdf
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)Syllabus MBBS at the AIIMS(印度).pdf
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2012-护理本科-B卷-题目.doc
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 14 Metabolism of monosaccharides and disaccharides.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 01 Amino Acids(structure of amino acid、acid/base properties of amino acid).ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 01 Amino Acids(overview).ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 31 Structure and Function of RNA.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 20 The metabolism of cholesterol.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 29 Metabolism of Nucleotides.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 18 phospholipid metabolism.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 19 glycolipid metabolism.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 32 Biosynthesis of Protein.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)18 维生素 Vitamins.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)16 血液的生物化学 Hemal Biochemistry.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)17 肝的生物化学 Biochemistry in Liver.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程PPT教学课件(留学生)Chapter 30 DNA Structure and Replication.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)13 基因表达调控 Regulation of Gene Expression.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)15 信号转导(细胞信息传递 Cell Communication and Signal Transduction).ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)14 基因重组与基因工程 Genetic Recombination and Genetic Engineering.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)09 物质代谢的联系与调节 Metabolic Interrelationships and Regulation.ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)12 蛋白质的生物合成 Biosynthesis of Protein(翻译).ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)11 RNA的生物合成 RNA Biosynthesis(转录 transcription).ppt
- 《生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)10 DNA的生物合成(复制).ppt
