《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)04-Cancer immunotherapy

04-Cancer immunotherapy Cancer immunotherapy From Wikipedia,the free encyclopedia Cancer imm erapy (m-onor totrea cancer Immunoth passive or hybrid(active and passive).These approaches exploit the fact that cancer cells often have molecules on heir sur e that can be det Dy th often proteins or other macromolecules (e carbohydrates).Active immunotherapy directs the immune G system【o attack tu mor cells by targeting TAAs.Passive s en and cytokines. Among these rapies system that bind to a tar omemgmeotTeehodiesrtproeciipovCeSeoane n pathogens.Each antibody is specific to one or a few proteins.Those that bind to tumor antigens treat cancer rtace receptors are com non targets I antibo ody therapies and ir lude CD20,CD27 and CD279.Once Approved antibodies include alemtuzumab,iplimumab,nivolumab,ofatumumab and rituximab. Active cellular th ual of in mune cells from the blood or fro r.Thos immune cells can be genetically engineered to express a tumor-specific receptor,cultured and returned to the patient.Cell types t be use in this v cells,lymphokin e-activated killer cells -approved cell-based therapy is Dendren's Provenge for th Interleukin-and in a are cytokin regula e and coordinate the behaviour of the immune ed in the tre related Ka ci'c ma,follicular lymphoma,chronic myeloid leukaemia and malignant melanoma.Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma. Contents 3 Antibody therapy dy types 3.3 FDA-app .5 Combination immunotherapy .6 Combinatorial ablation and immunotherapy
04-Cancer immunotherapy

。7 Polysaccharide-K ·8 Research .8.3 Anti-GD2 antibodies History oy for th r has bee nt of infection in the desired location and cause regression of the tumour.In 13th century,St.Peregrine experienced spontaneous regression of tumor,after the tumor became infected.In the 18th and 19th centuries,deliberate were a stand wounds were left ope French physician Dusso y so o品洁n的 posing the tumor to infection includin there sea relationship between infection and cancer regression date back to at least the 1th Modern Immunotherapy began in 1796 when Edward Jenner produced the first vaccine involving immunisation with cowpox to prevent smallpox.Towards the end of the 19th century Emil von Behring and Shibasaburo Kitasato discovered that injecting animals with diphtheria toxin produced blood serum with antitoxins to i provoking ar acioraphgtobadeia.h1968apmoleinrehidohiseg was identified and calle in prod rapy for cancer was introduced by Ste 厂oc or regres ate (2. 33%)in 1205 patients with metastatic cancer who underwent In 1987,rese archers identified cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4,or CTLA-4.Allison found that CTLA-4 prevents cks tumo 00 CTLA WOU the immune rs in In 1999 b ch firm Med hts to the dy In 2010 Bristol-Myers Squibb,who acquired Medarex in 2009,reported that patients with metastatic melanoma lived ded life in advanced melanoma in a randomized trial.st tme any treatme an average of 10 months on the antibody,versus 6 month: In the early 1990s,a biologist discovered a molecule expressed in dying T cells,which he called programmed bler of T cells.An antibody that targeted PD-1 was remission in multiple subjects across multiple cancer types.In 2013

In 1997 rituximab,the first antibody homa Since this a alemtuzumab (2001). ofatumumab (2009)and ipilimumab (2011). n2002 电5eo部amdm9 ously adminis traction with appropriate stimulatory cytokines. with both nti-CTIA-4 and anti-PD-1 一oo西some时 later.Son atients kep onding after the antibody had been di prostate The first cell-ba rapy cancer vaccine,sipuleucel-T,was approved in 2010 for the After success harves cells ,expanding them in the lab and reinfusing them This technique is a personalized treatment that involves genetically modifying each patient'scetota cllsuc e remission nriuhu By mid 2016 the FDA had approved one PD-L1 inhibitor(atezolizumab)and two PD-1 inhibitors (nivolumab and pembrolizumab). Cellular immunotherapy Dendritic cell therapy Dendritic cell therapy provokes anti-tumor responses by causing dendritic cells to present tumor antigens to lymphocytes,which m,priming them to other cells that pres the antigen ce APCS) f the immune system id igens is by Blood cells are tem oved omthe body PpaCepOeare'ofemgemnconmbiaionwithajvantshighly immunogenic substances)to increase the immune and anti-tumor responses.Other adjuvants include prote ns or oth r chemicals tha (GM-CSP) such as granulocyte macrophage be ach virus that expres sses GM-CSE aoacolyb dendritic cells f outside the peptide/protein or a tumor cell lysate (asolution of broken down tumor cells).These cells(with optional adjuvants)are infused and provoke an immune response

Dendritic cell therapies include the use of antibodies that bind to receptors on the surface of dendritic cells T6nmdm出e Sipuleucel-T nting cells from blood by leukapheresis and growing them with the fusion protein PA2024 高9 po Antibody therapy ibrboin oad playing a centr 八慧要 against specific antigens,such as those present on tumor surfaces. ”电 Antibody types Many forms of antibodies can be Conjugation Two typesare used in cancer treatments:4] Nakdnbdiesreibdehouadded elemeMost aibody therapesusehis Conjugated monoconaantibodies are joined to another moleue which is either cytotoxicor radioa tive. chemicals are tho e typically used as chemotherapy drugs,but other can be d-linked antbo immunotoxins antibodies are tagged with chemotherapeutic molecules or toxins,respectively.5 Human/non-human balance ,chimeric,humanized and human.Murine antibodies are from of th meric andin bodies rine aas the constant region.Humanized antibodies are almost completely human:only the complementarity determining o the varlable regions are derived fom mrine sources.Human antbodes have compleely human Cell death mechanisms Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity(ADCC) Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)reguires antibodies to bind to target cell surfaces. Antibodies are formed of a binding region(Fab)and the Fc region that can be detected by immune system cells pto und on many immun sys m c yme B to kill the or cell.E umab
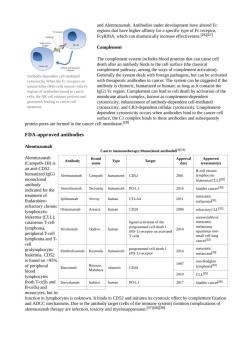
and alemtuzumab.antibodies under development have altered fc 将m代 Complement complement pathway,among the ways of complement activation). Antibody- ndent cell-mediated When the Ferecep Generally the systemr pathogens,but can be act the is chi ies in cance The system can be IgG1 Fc region.Com cells,the NK cel releses perforinand membrane attack complex,known as complement-dependent granzyme eadng tocancer cel r cytotox proeomplex binds to these antibodies and subseqny FDA-approved antibodies Alemtuzumab Cancer immunotherapy:Monoclonal antibodi Alemtuzu (Cam eth-1H)is Antibody Brand Type Approval m) an anti-CD52 humanized IgG1 CD52 2001 mo leukemia (CLL29) indicated for the Atezolizumab humanized PD-LI 2016 bladder cance treatment of fludarabine Ipilimumab Yervoy human CTLA4 2011 refractory chroni Ofatumumal human CD20 2009 refractory CLLB2] 1 eukemia(CLL】 cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Nivolumab Opdivo human 2014 mall cell lur Pembrolizumab 2014 leukemia.CD5. 95 197 non-Hodgkin Rituximab Mabthera chimeric CD20 lymphom 2010 CLLB51 lymphocytes T-cells and Durvalumab Imfinzi human PD-L1 2017 bladder cancer3同 ells)an oyeiskIbinds to CD52dtcyotoxiefect by come ixio aeoaa

atezolizumab Durvalumab Durvalumab amfinzi)is a human immunoglobulin gi kappa)monoclonal antibody that blocks the interaction of programmed cell death ligand 1(PD-L1)with the PD-1 and CD80(B7.1)molecules.Durvalumab is approved for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who: .have disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy. Ipilimumab Ipilimumab(Yervoy)is a human IgG1 antibody that binds the surface protein CTLA4.In normal physiology T receptor CD28 bnding to CaoorC prevenin RdDa6pmotei therefore negatively regulates the activation of T-c Active cytotoxic T-cells are required for the immune system to attack melanoma cells.Normally inhibited e an en ectoytoroxicTcs to increase te anti-um Regulatory T Nivolumab Ofatumumab Ofatumumab is Unlike rituximab,which binds to a large loop of the CD20 protein,ofatumumab binds to a separate,small loop This may explain their different characteristics.Compared to ritu pcndeatcotoictvyatalomcrdoewlGsmnmunogentaWohatumumabricscomolene Pembrolizumab Pembrolizumab is ap ved for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer whose tumors have high PD-L1 expression as determined by an FDA-approved test. Rituximab CD20 is relatively unknown,CD20 may be a calcium channel involved in B-cell activation.The antibody's mode of action is prmarily through t induction OT ADC B-cells to ch Cytokine therapy

Cytokines ar proteins produced by many types of cells present within a tumor.they can modulate immune responses.The tumor often employs them to allow it to grow and reduce the immune response.These immune modulating effects allow them to be used as drugs to provoke an immune response.Two commonly used cytokines are interferons and interleukins. Interferon Interferons are produced by the immune system.They are usually involved in anti-viral response,but also have in three groups:type I(IFNa and IFNB),type II (IFNY)and type oma,cl ote anti-tumor immur yp :ha e been sho melanoma cancers.The most promising result was achieved in patients with stage 2 and 3 of ovarian carcinoma.The in vitro study of IFN-gamma in cancer cells is more extensive and results i ndicate ant IFN-gamma Interleukin Interleukins have an array of immune system effects.Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant cells,but its exact mechanism of action is unknown Combination immunotherapy CombnnaioscPDI and CTLA4inibitors can enhance anti-tmor response leading to durable response Combinatorial ablation and immunotherapy Combnnghrayofmhhances themming reponsendhas synergistic effects for curative metastatic cancer treatmen Polysaccharide-K Ministry of Heath,Labourand Welareappvhof polysaccharide-Kracted o ietary supplement in the US and Research Adoptive T-cell therapy Adoptive t-cell th fusion of T-cells(ado ransfer) thogens specifically the activate when the T-cell's surface receptors encounter cells that display parts of foreign proteins on their surface antigens.These can be either infected cells,or antigen presenting cells(APCs).They are found in normal tissue and in tumor tissue,where they are known as tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs).They are activated by the

presence of apcs such as dendritic cells that present tum or anti Although these cells can attack the tumor.the environment within the umomsuppressive,preventing immune-mediated Multiple ways of producing and obtaining tumour targeted T-cells have been developed.T-cells specific to a tumor antigen can be removed Subsequen an take pla e resu infused ah aon cellsttumorngouarh has made races in on and isolation of tumou dopdl erpy Asof1.multipeACT clinical trials were underway. andgrown prior the 空二二om Anti-CD47 antibodies Anti-cD47 antibodies.which block the p ein cD47 from telling the cancer host's immun m not to attack it,have been shown to eliminate or inhibit the growth of multiple cancers and tumors in laboratory tests on cells and mice.CD47 is present on many cancer cells and on many healthy cells.After the cancer cells have 尚 rophages,the host immune system's CD8+T Cells becom mobilized against the 7 is to use Pol silencing tool formed by DNA hairins.as shown in M e Anti-GD2 antibodies Carbohydrate antigens on the surface of cells can be used as targets for immunotherapy. D2 I a ganglioside found on the rtace of many mall cell hrain rhabdomvosarcoma ewing's sarcoma liposarcoma fibrosarcoma leiomyosarcoma and other soft tissue sarcomas.It is not usually The GD2 ganglioside expressed on the surface of normal tissu .mtin3tago0argtfor Immune checkpoints Immune checkpoints affect immune system functioning.Immune checkpoints can be stimulatory or inhibitory. bscan use these checkpoints to protect themselves from immune system attacks.Checkpoint therapy can block inhibitory One e receptor inter PD-1 nd 1 (PD-LI.CD274)PD-L inds to PDI Tcaweaom2 inhibit T cells that might othe atta k.Antibodies that bind to either PD-1 or PD-L1 and therefore block the interaction may allow the T-ce ells to attack the tumo CTLA-4 blockade

e cc。 CA therapy on lung cancer or pancreatic cancer,specifically in combinaton ith other nnhe comnioof CTLA-blockadewh PD-1or PD-LI inhibrors is esd on different types of cancer However,patients treated with check-point blockade(specifically CTLA-4 blocking antibodies),or a combnation of check-point blocking antibodies,are at high risk of sufferngfom mreated adverse the el-tbodmmisre had the r cancer blood 9 At the same time the levels of circulating antibodies lower.suggestng that local administration of the i-A-therapyrversev PD-1inhibitors rresu G PDIanibody Nivolumab were publishedin1ppro er head and neck the firs g cance ed i v [81] Pembrolizumab isanother PD1 approved to treat melanoma and lung cance Antibody BGB-A317 isa PD-1 inhibitor(designed to not bind Fc gamma receptor D)in early clinical trials PD-L1 inhibitors In May 2016PD-L1 inhibitor was approved for treating bladder cancer 内d网o Other Polysaccharides Certain compounds found in mus immune system and Tcells and immune system cytokines and have been investigated in clinical trials as immunologic adjuvants. (often mistakenly called ago cus blazei)lentinula edodes (shiitake mush Grifola frondose Hericmrncure fungi that produce betagucans and have been testor Neoantigens

The presence of CD8+Tcells in cancer lesions,as identified using RN natural kille 《 tively 90 load in many human tumors.In non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with lambrolizumab,mutational load shows a strong correlation with e.In melanoma patier reated with.long redicted MHC bnding with a long-term clinical benefit were enriched for a series of However,human other studies do not show the bias toward tetrapeptide signatures. See also gen recepto .Coley's Toxins ·Combinatori aondmnotheray References TRalingprooinve oo 2017 doi101016.co-20160021plo 89016%2F1.Ct0.2016.01.021) .()of tumour and the role of microbial 7220).PMID26813865(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26813865) articles/PMC3312698 43-9.PMC312698ig6 pubmed2470231802m10g0976eR28aPM1D224702330t -9668.82318 (https::/doi.org/10.4103% 4.Ding AH (November 1985)."[Observation of the conversion rate of breech presentation by laser .gov/pmc/artic PMC3833486). 2248 PMID 24278806(https: ww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24278806).doi:10.7453/gahmj.2012.1.1.016(h 5.ptoi.0g107453%2 Fgahmj.2012.11.016 3916.PMID11726133 tps:/doi.0rg/10.1007%2Fs002620100216) hidon Cann nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11812185).doi:10.1054/mehy.2001.1469(https:/doi.org/10.1054%2Fmehy.2001.1 469)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)03-Monoclonal antibody therapy.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)02-Monoclonal antibody.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)01-Antibody.pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)05 Cardiac Muscle Mechanics.ppt
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)04 Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Cardiac Cells.ppt
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷02.pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)生理学多选题(二).pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)生理学多选题(三).pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)生理学多选题(一).pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)03 Basics of the ElectroCardioGram(ECG).ppt
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)02 Cardiac Action Potential.ppt
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)01 Overview of Cardiovascular System(负责人:汪海宏).ppt
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷01.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验六 安全性评价.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验六 安全性评价.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验五 血清谷丙转氨酶活性的测定(King法).pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验五 实验动物染毒.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验四 急性经口毒性实验.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验四 经口急性毒性实验.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验三 生物材料的采集与制备.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)05-Immunoassay.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)06-Antibody microarray.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)01-抗体的结构与功能.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)02-多克隆抗体.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)03-单克隆抗体的制备.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)04-基因工程抗体之嵌合抗体.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)05-抗体的应用.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《人体解剖学》课程实验指导(打印版)局部解剖学实验指导.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《人体解剖学》课程实验指导(打印版)实验指导及强化训练习题集及答案(适用于医学本科临床、法医等专业).pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)生理学教学大纲 Physiology.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第一章 绪论(负责人:张秀娟).pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第二章 细胞的基本功能.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第三章 血液.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第四章 血液循环.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第五章 呼吸.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第六章 消化和吸收.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第八章 尿的生成和排出.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第九章 神经系统的功能.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第十章 内分泌.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第十一章 生殖.pdf
