同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)01 Overview of Cardiovascular System(负责人:汪海宏)
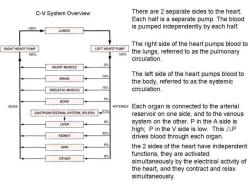
C-V System Overview There are 2 separate sides to the heart. Each half is a separate pump.The blood 100% is pumped independently by each half. LUNGS The right side of the heart pumps blood to RIGHT HEART PUMP LEFT HEART PUMP 100% 100% the lungs,referred to as the pulmonary circulation. HEART MUSCLE 3% 14% The left side of the heart pumps blood to BRAIN the body,referred to as the systemic SKELETAL MUSCLE 15% circulation. BONE 5% VEINS ARTERIES Each organ is connected to the arterial GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM,SPLEEN21% reservoir on one side,and to the venous 6% LIVER system on the other.P in the A side is high;P in the V side is low.This AP KIDNEY 22% drives blood through each organ. 6% SKIN the 2 sides of the heart have independent functions,they are activated OTHER 8% simultaneously by the electrical activity of the heart,and they contract and relax simultaneously

Within each organ: Networks of capillaries function to bring blood close to cells. All cells are surrounded by a highly branching,interweaving network of capillary vessels This network provides every cell in the body with short-range access to the blood supply.Thus it is possible for metabolites move from blood to interstitial fluid,and from interstitial fluid to cells,by diffusion.. In order to support cellular metabolism within organs,cells need to exchange gases,fuel,and waste products.O2 and fuel have to be delivered,and CO2 and other waste products need to be removed from cells.This is accomplished by Cast of capillary network diffusion between cells and the interstitial fluid that surrounds them
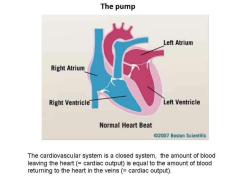
The pump Left Atrium Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Ventricle Normal Heart Beat @2007 Boston Scientific The cardiovascular system is a closed system,the amount of blood leaving the heart(=cardiac output)is equal to the amount of blood returning to the heart in the veins(=cardiac output)
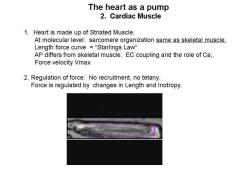
The heart as a pump 2.Cardiac Muscle 1.Heart is made up of Striated Muscle At molecular level:sarcomere organization same as skeletal muscle. Length force curve=“Starlings Law” AP differs from skeletal muscle:EC coupling and the role of Ca;. Force velocity Vmax 2.Regulation of force:No recruitment,no tetany. Force is regulated by changes in Length and Inotropy
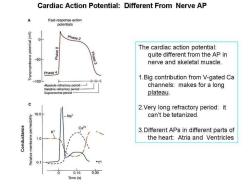
Cardiac Action Potential:Different From Nerve AP A Fast-response action potentials (Aw) Phase 2 The cardiac action potential: Phase 3 quite different from the AP in -50 nerve and skeletal muscle. Phase 4 1.Big contribution from V-gated Ca -100 Absolute refractory period- channels:makes for a long Relative refractory period Supranormal period- plateau. 2.Very long refractory period:it 10.0 can't be tetanized. 3.Different APs in different parts of 0 the heart:Atria and Ventricles 0.1 0.15 0.30 Time(s)
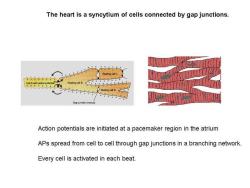
The heart is a syncytium of cells connected by gap junctions. Gap junction (nexu Action potentials are initiated at a pacemaker region in the atrium APs spread from cell to cell through gap junctions in a branching network. Every cell is activated in each beat
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷01.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验六 安全性评价.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验六 安全性评价.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验五 血清谷丙转氨酶活性的测定(King法).pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验五 实验动物染毒.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验四 急性经口毒性实验.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验四 经口急性毒性实验.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验三 生物材料的采集与制备.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验二 实验动物染毒(染毒方法介绍).pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验三 生物材料的采集.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验一 动物基本知识及基本操作、实验方法.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验二 实验动物染毒.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验一 动物基本知识及基本操作、实验方法.pdf
- 《病原生物学与免疫学》课程教学资源(教材讲义)病原生物学与免疫学参考教材PDF电子版(高职,共二十六章).pdf
- 安庆医药高等专科学校:《病原生物与免疫学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)绪论——免疫与医学免疫学概述.ppt
- 安庆医药高等专科学校:《病原生物与免疫学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)高中病免知识.ppt
- 安庆医药高等专科学校:《病原生物与免疫学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)病原生物学概述.ppt
- 安庆医药高等专科学校:《病原生物与免疫学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二十五章 医学原虫(叶足虫-溶组织内阿米巴).ppt
- 安庆医药高等专科学校:《病原生物与免疫学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)支原体.ppt
- 安庆医药高等专科学校:《病原生物与免疫学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二十章 人类免疫缺陷病毒(HIV)和其他virus.ppt
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)02 Cardiac Action Potential.ppt
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)03 Basics of the ElectroCardioGram(ECG).ppt
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)生理学多选题(一).pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)生理学多选题(三).pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)生理学多选题(二).pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷02.pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)04 Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Cardiac Cells.ppt
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)05 Cardiac Muscle Mechanics.ppt
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)01-Antibody.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)02-Monoclonal antibody.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)03-Monoclonal antibody therapy.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)04-Cancer immunotherapy.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)05-Immunoassay.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)06-Antibody microarray.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)01-抗体的结构与功能.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)02-多克隆抗体.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)03-单克隆抗体的制备.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)04-基因工程抗体之嵌合抗体.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)05-抗体的应用.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《人体解剖学》课程实验指导(打印版)局部解剖学实验指导.pdf
