同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)04 Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Cardiac Cells
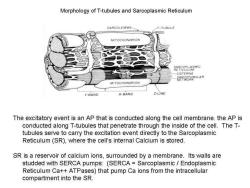
Morphology of T-tubules and Sarcoplasmic Reticulum SARCOLEMMA- T-TUBULE MITOCHONDRION RETTOLUMMIC CISTERNA NERCORBULAR MITOCHONDRION I-BAND A-BAND Z-LINE The excitatory event is an AP that is conducted along the cell membrane.the AP is conducted along T-tubules that penetrate through the inside of the cell.The T- tubules serve to carry the excitation event directly to the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum(SR),where the cell's internal Calcium is stored. SR is a reservoir of calcium ions,surrounded by a membrane.Its walls are studded with SERCA pumps:(SERCA Sarcoplasmic Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca++ATPases)that pump Ca ions from the intracellular compartment into the SR
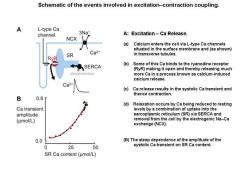
Schematic of the events involved in excitation-contraction coupling. A L-type Ca channel 3Na* A:Excitation-Ca Release. NCX (a)Calcium enters the cell via L-type Ca channels situated in the surface membrane and (as shown) Ca2 SR in transverse tubules. RyR SERCA (b)Some of this Ca binds to the ryanodine receptor (RyR)making it open and thereby releasing much phospholamban more Ca in a process known as calcium-induced calcium release. (c)Ca release results in the systolic Ca transient and thence contraction. B 0.8r (d)Relaxation occurs by Ca being reduced to resting Ca transient levels by a combination of uptake into the amplitude sarcoplasmic reticulum(SR)via SERCA and (umol/L) removal from the cell by the electrogenic Na-Ca exchange(NCX). 0.0 (B)The steep dependence of the amplitude of the 0 25 50 systolic Ca transient on SR Ca content. SR Ca content(umol/L)
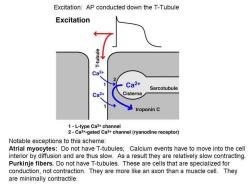
Excitation:AP conducted down the T-Tubule Excitation Ca2+ 2 Ca2+ Sarcotubule Ca2+ Cisterna troponin C 1-L-type Ca2+channel 2-Ca2+-gated Ca2+channel(ryanodine receptor) Notable exceptions to this scheme: Atrial myocytes:Do not have T-tubules;Calcium events have to move into the cell interior by diffusion and are thus slow.As a result they are relatively slow contracting. Purkinje fibers.Do not have T-tubules.These are cells that are specialized for conduction,not contraction.They are more like an axon than a muscle cell.They are minimally contractile
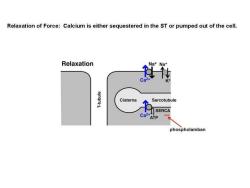
Relaxation of Force:Calcium is either sequestered in the ST or pumped out of the cell. Relaxation Na+Na+ Ca einqn1-L Cisterna Sarcotubule SERCA phospholamban

Sites of Control of Cardiac Force. 2 examples of how Contractility is changed by by phosphorylation events L-type Channels. (a)Action of norepinephrine...activation of B adrenergic receptor...increases cAMP...PKA produced...PKA phosphorylates L-Channels and increases their Calcium conductance...increasing Ca influx...increasing force (b)Action of acetylcholine...activation of muscarinic receptor...increases cGMP...results in phosphorylating a different site on L-Channel,which decreases Ca influx and thus decreases force. force is varied in cardiac muscle by altering the Calcium level in myocytes

More mechanisms causing contractility changes Phosphorylation of Troponin.Alter sensitivity of TN-C for Ca++. Phosphorylation of PhosphoLamban(PLN).Reduce activity of PLN,allow SERCA pumps to run faster thus promoting faster relaxation Phosphorylation of elements of the IP3 pathway
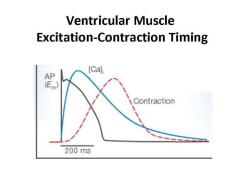
Ventricular Muscle Excitation-Contraction Timing [Ca] AP 】 Contraction 200ms
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷02.pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)生理学多选题(二).pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)生理学多选题(三).pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)生理学多选题(一).pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)03 Basics of the ElectroCardioGram(ECG).ppt
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)02 Cardiac Action Potential.ppt
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)01 Overview of Cardiovascular System(负责人:汪海宏).ppt
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷01.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验六 安全性评价.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验六 安全性评价.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验五 血清谷丙转氨酶活性的测定(King法).pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验五 实验动物染毒.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验四 急性经口毒性实验.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验四 经口急性毒性实验.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验三 生物材料的采集与制备.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验二 实验动物染毒(染毒方法介绍).pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验三 生物材料的采集.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)实验一 动物基本知识及基本操作、实验方法.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验二 实验动物染毒.pdf
- 新乡医学院:《毒理学》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验一 动物基本知识及基本操作、实验方法.pdf
- 同济大学:《生理学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)05 Cardiac Muscle Mechanics.ppt
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)01-Antibody.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)02-Monoclonal antibody.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)03-Monoclonal antibody therapy.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)04-Cancer immunotherapy.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)05-Immunoassay.pdf
- 《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(参考资料,电子版)06-Antibody microarray.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)01-抗体的结构与功能.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)02-多克隆抗体.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)03-单克隆抗体的制备.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)04-基因工程抗体之嵌合抗体.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《抗体及其应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,打印版)05-抗体的应用.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《人体解剖学》课程实验指导(打印版)局部解剖学实验指导.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《人体解剖学》课程实验指导(打印版)实验指导及强化训练习题集及答案(适用于医学本科临床、法医等专业).pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)生理学教学大纲 Physiology.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第一章 绪论(负责人:张秀娟).pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第二章 细胞的基本功能.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第三章 血液.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第四章 血液循环.pdf
- 广东医科大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(大纲教案)第五章 呼吸.pdf
