《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学课件(讲稿)龋病的治疗(非手术治疗)

Management (Therapy)of Dental Caries
Management (Therapy) of Management (Therapy) of Management (Therapy) of Management (Therapy) of Dental Caries Dental Caries Dental Caries Dental Caries
3 5 元兄

Caries is an infectious disease caused by bacteria originating from the resident oral microflora. Dental caries is a complex disease with numerous causes ofenvironmental and behavioural origin
� Caries is an infectious disease caused by bacteria originating from the resident oral microflora. � Dental caries is a complex disease with numerous causes of environmental and behavioural origin

SALIVA MICRO- ORGANISM5*★ SALIVA They Keyes diagram shows that cavities are the result of TOOTH CARIES TIME the interaction between a susceptible tooth,a dietary SALIVA F00D* SALIVA substrate (sugar),a chronic Fermentable Carbohydrate .Particularly Strepococcus mutans bacterial infection,and time. 时间、食物、细菌、牙齿 元元元
� They Keyes diagram shows that cavities are the result of the interaction between a susceptible tooth, a dietary substrate (sugar), a chronic bacterial infection, and time. 时间、食物、细菌、牙齿

There has been remarkable progress in the reduction oftooth decay in the developed countries over the past 30 years
� There has been remarkable progress in the reduction of tooth decay in the developed countries over the past 30 years

The Third National Oral Health Epidemiological Investigation in 2005 shows that caries levels at all ages are still a major problem in China,especially among teenagers
� The Third National Oral Health Epidemiological Investigation in 2005 shows that caries levels at all ages are still a major problem in China, especially among teenagers

Prevention and treatment ofdental caries have the same main objective,namely to prevent the disease from further progression leading to infection of teeth and other tissues which will create pain,suffering and reduced fumction
� Prevention and treatment of dental caries have the same main objective, namely to prevent the disease from further progression leading to infection of teeth and other tissues which will create pain, suffering and reduced function

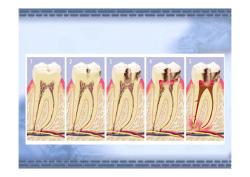
Dental caries is typically first observed clinically as a "white spot lesion.If the tooth surface remains intact and non-cavitated,then remineralization of the enamel is possible. 元元5
� Dental caries is typically first observed clinically as a “white spot lesion.” If the tooth surface remains intact and non-cavitated, then remineralization of the enamel is possible

Ifthe subsurface demineralization of enamel is extensive,it eventually causes the collapse of the overlying tooth surface,resulting in a“cavity
� If the subsurface demineralization of enamel is extensive, it eventually causes the collapse of the overlying tooth surface, resulting in a “cavity

The most important concept to remember is that caries is a dynamic disease process,and not a static problem. Secondly,before a cavity is formed in the tooth,the caries infection can actually be reversed!
� The most important concept to remember is that caries is a dynamic disease process, and not a static problem. � Secondly, before a cavity is formed in the tooth, the caries infection can actually be reversed!
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学课件(讲稿)龋病的治疗(窝洞充填术).pdf
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学课件(讲稿)着色牙和牙发育异常.pdf
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学课件(讲稿)牙本质过敏症.pdf
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学课件(讲稿)牙慢性损伤.pdf
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学课件(讲稿)Pulpal Disease and Periapical Disease.pdf
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学课件(讲稿)龋病的临床表现 Clinical Manifestation and Diagnosis of Dental Caries.pdf
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)实验十九、牙体牙髓病病例综合练习.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)实验十七、离体牙根管充填.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)实验十四、离体牙开髓术.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)实验十三、盖髓术,银汞合金充填术.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)实验八、离体磨牙Ⅰ类洞的制备.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)实验七、石膏牙Ⅴ类洞的制备.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)实验六、石膏牙Ⅲ类洞的制备.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)实验五、石膏牙Ⅱ类洞的制备.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)实验四、窝洞的结构分类,石膏牙Ⅰ类洞的制备.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)实验二、牙体牙髓病治疗常用器械及其使用.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)实验一、仿真人头模的使用,口腔医师的术式、支点.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)十一、根管治疗术.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)十、牙髓病及根尖周病治疗概述 活髓牙保存治疗.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学资源(教案)九、牙髓及根尖周病的检查和诊断方法、临床分类、临表表现及诊断.doc
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学课件(讲稿)感染牙髓的治疗方法 Therapies for infected pulp.pdf
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学课件(讲稿)根管治疗 Root canal therapy Root canal treatment.pdf
- 《牙体牙髓病学》课程教学课件(讲稿)活髓保存治疗 Therapies for preserving vitality of the pulp.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程教学大纲(供护理学本科专业使用).pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)呼吸系统疾病和重症监护.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)小儿惊厥.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)儿传教案.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)呼吸心跳骤停.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)小儿外科常见畸形.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)神经.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)儿科护理操作教案与讲稿.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)小儿外科常见畸形.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)小儿肠套叠.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)血液.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)新生儿及新生儿疾病护理.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)泌尿.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)液体疗法.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)第十章 循环系统.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)肺炎、呼吸衰竭.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《儿科护理学》课程授课教案(讲稿)腹泻病.doc
