上海交通大学:《现代控制理论》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 6 Controllability and Observability

Chapter 6 2 Chapter 6 Controllability and Observability Objectives: Definition of controllability Definition of observability Detective methods for controllability I Theory Detective methods for observability ·Decomposition
Chapter 6 Controllability and Observability Objectives: • Definition of controllability • Definition of observability • Detective methods for controllability • Detective methods for observability • Decomposition Chapter 6 2

Chapter 6 3 6.1 controllability 。Definition: The state equation=x+Bu or the pair (A,B)is said to be controllable if for any initial state x(O)=xo and any final state x1,there exists an input that transfer xo to x1 in a finite time.Otherwise is said to be uncontrollable Theory
6.1 controllability • Definition: • The state equation or the pair (A,B) is said to be controllable if for any initial state x(0)=x0 and any final state x1 , there exists an input that transfer x0 to x1 in a finite time. Otherwise is said to be uncontrollable. 3 x Ax Bu Chapter 6
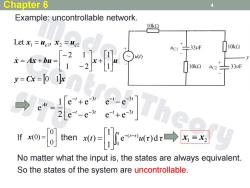
Chapter 6 4 Example:uncontrollable network. 10k2 Let x=uc,x2 =uc2 33μF 10k2 4C2 33uF y=Cx=0 1 f0n-日henx0-erdi→xE起 No matter what the input is,the states are always equivalent. So the states of the system are uncontrollable
Example: uncontrollable network. 4 y Cx x x Ax bu x u x uc , x uc 0 1 1 1 1 2 2 1 Let 1 1 2 2 t t t t t t t t t 3 3 3 3 e e e e e e e e 2 1 e A 0 0 If then x(0) x t u τ τ t t τ e ( )d 1 1 ( ) 0 ( ) x1 x2 No matter what the input is, the states are always equivalent. So the states of the system are uncontrollable. Chapter 6

Chapter 6 5 Theorem:The following statements are equivalent. 1.The n-dimensional pair(A,B)is controllable. 2. The following nxn matrix is non-singular for any t. W0-eBBte de-BBed 3. The following nxnp controllability matrix(Kalman matrix) has rank n(full row rank). C=BAB…A"B]
• Theorem: The following statements are equivalent. 1. The n-dimensional pair (A,B) is controllable. 2. The following nn matrix is non-singular for any t. 3. The following nnp controllability matrix (Kalman matrix) has rank n (full row rank). 5 W (t) e BB e dτ e BB e dτ A(t-τ ) T A (t τ) t Aτ T A τ t C T T 0 0 ] 1 C B AB A B n- [ Chapter 6

Chapter 6 A system is controllable if the following nxnp controllability matrix has rank n(full row rank). Oc=[B AB A'B·Am-B] rank Oc =n Proof:Caley-Hamilton theorem e*-d()I+a()4+>Fa.i()A->a() →x0)=-∑ABa,(ra(r)dr Ba neory i=0 a(r)u(r)dr- B2 =B(i=0,1,…,n-1) Br
A system is controllable if the following nnp controllability matrix has rank n (full row rank). Q [B AB A B A B] 2 n 1 C rank QC n Proof: Caley-Hamilton theorem 1 0 1 0 1 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) n i i i n- n τ e a τ I a τ A a τ A a τ A A x a τ τ τ t i n i i (0) ( ) ( )d 1 0 1 0 A B u i ir i i t i β β β a τ τ τ 2 1 0 ( ) ( )d 1 u (i 0,1, ,n 1) Chapter 6

Chapter 6 7 Bo Therefore x(0)=-[B AB A"B B The solution of B exists according to initial state x(0)only if following matrix has rank n. rank2c=rank[B7AB。AB A"-B]=n Theory
7 Therefore 1 1 0 1 (0) [ ] n n- β β β x B AB A B n rank Q rank[B AB A B A B] 2 n 1 C The solution of exists according to initial state x(0) only if following matrix has rank n. Chapter 6
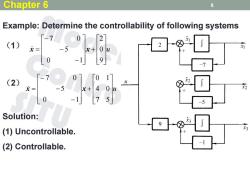
Chapter 6 8 Example:Determine the controllability of following systems 「-7 ●0 2 (1) = 0 2 9 -7 (2) Solution: 9 (1)Uncontrollable. (2)Controllable
8 Example: Determine the controllability of following systems u 9 0 2 0 1 5 7 0 x x u 7 5 4 0 0 1 0 1 5 7 0 x x (1) (2) Solution: (1) Uncontrollable. (2) Controllable. Chapter 6
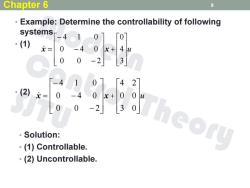
Chapter 6 9 Example:Determine the controllability of following systems -4.1 0 「0 (1) = 0 -4 0 X十 u 0 0 -2 3 -4 0 4 2 0 -4 0 x+ 0 -2 3 。Solution: Theory ·(1)Controllable. ·(2)Uncontrollable
• Example: Determine the controllability of following systems • (1) • (2) 9 u 3 4 0 0 0 2 0 4 0 4 1 0 x x u 3 0 0 0 4 2 0 0 2 0 4 0 4 1 0 x x • Solution: • (1) Controllable. • (2) Uncontrollable. Chapter 6

Chapter 6 10 Theorem:If all the eigenvalues of a system are different,then the system can be transformed to the following form using similarity transformation.The system is controllable if there is no all zero row in B. 0 heory
10 Theorem: If all the eigenvalues of a system are different, then the system can be transformed to the following form using similarity transformation. The system is controllable if there is no all zero row in . x x Bu n λ λ λ 0 0 2 1 B Chapter 6
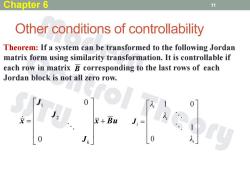
Chapter 6 11 Other conditions of controllability Theorem:If a system can be transformed to the following Jordan matrix form using similarity transformation.It is controllable if each row in matrix B corresponding to the last rows of each Jordan block is not all zero row. x+Bu J=
Other conditions of controllability 11 Theorem: If a system can be transformed to the following Jordan matrix form using similarity transformation. It is controllable if each row in matrix corresponding to the last rows of each Jordan block is not all zero row. B Chapter 6 x Bu J J J x 0 k 0 2 1 i i i i λ λ λ 0 1 1 0 J
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《现代控制理论》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 5 Stability Analysis.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《现代控制理论》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 4 State Space Solutions and Realizations.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《现代控制理论》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 3 Linear algebra.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《现代控制理论》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 2 Mathematic Description of Systems.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《现代控制理论》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 1 Introduction Morden Control Theory(主讲:鲍其莲).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《精密仪器设计》课程教学大纲(电气信息类测控技术与仪器专业).docx
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)电气化铁道供电系统的构成.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)高速电气化铁路接触网.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)铁道供电系统保护及远动控制.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)铁道供电系统的仿真研究及其智能测试.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)电气化铁道供电系统的供电方式(负责人:李彦哲).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)铁道供电系统的绝缘水平及防雷接地措施.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)电气化铁道供电系统的牵引变电所.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(实验指导)供电技术知识——中央信号回路.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(实验指导)供电技术知识——断路器的控制回路.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)绝缘油耐压实验.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)介质损耗角的测量.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)测量绝缘电阻和吸收比.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)电流互感器.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《电气化铁道供电系统与设计》课程教学资源(实验指导,打印版)电压互感器.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《现代控制理论》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 7 State Feedback and State Estimator.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《现代控制理论》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 8 Fundamentals of Optimal Control.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《信号与系统》课程教学资源(试卷习题)模拟试题1试题.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《信号与系统》课程教学资源(试卷习题)模拟试题1参考答案.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《信号与系统》课程教学资源(试卷习题)模拟试题2参考答案.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《信号与系统》课程教学资源(试卷习题)模拟试题2试题.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《信号与系统》课程教学资源(试卷习题)样题1试题.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《信号与系统》课程教学资源(试卷习题)样题1答案.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《信号与系统》课程教学资源(试卷习题)样题2试题.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《信号与系统》课程教学资源(试卷习题)样题2答案.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《信号与系统》课程教学资源(习题解答)第1章 信号与系统.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《信号与系统》课程教学资源(习题解答)第2章 连续系统的时域分析.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《信号与系统》课程教学资源(习题解答)第3章 离散系统的时域分析.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《信号与系统》课程教学资源(习题解答)第4章 连续系统的频域分析.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《信号与系统》课程教学资源(习题解答)第5章 连续系统的s域分析.pdf
- 安徽理工大学:《智能控制及仿真》课程教学大纲 Intelligent Control Theory and simulation(负责人:陈静).pdf
- 安徽理工大学:《智能控制及仿真》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第2章 专家控制.pdf
- 安徽理工大学:《智能控制及仿真》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第1章 绪论(负责人:陈静).pdf
- 安徽理工大学:《智能控制及仿真》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第3章 模糊控制的理论基础.pdf
- 安徽理工大学:《智能控制及仿真》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第4章 模糊控制.pdf
