电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)08 Linear Regression

Chapter 2 Linear Regression
Chapter 2 Linear Regression

Contents 。2.1 Introduction 2.2 Polynomial Curve Fitting:A Toy 。2.3Over-fitting 2.4 Cross-Validation ·2.5 Regularization 2.6 Linear Basis Function Models 2.7 Least Squares Revisited 2.8 Bayesian Linear Regression
Contents • 2.1 Introduction • 2.2 Polynomial Curve Fitting: A Toy • 2.3 Over-fitting • 2.4 Cross-Validation • 2.5 Regularization • 2.6 Linear Basis Function Models • 2.7 Least Squares Revisited • 2.8 Bayesian Linear Regression
2.1 Introduction Supervised learning:regression and classification.The goal of regression is to predict the value of one or more continuous target variable given the value of a p-dimensional vector of input variables. In linear regression,the model for such a relationship is a linear model. Alinear regression example:given a ata set linear regression model assumes that the relationship between the target variable yi and the p-dimensional vector of input variables xi is linear,i.e. yi=Bixu++Bpxip +s=xB+ i=1,.,n
2.1 Introduction • Supervised learning: regression and classification. The goal of regression is to predict the value of one or more continuous target variable given the value of a p-dimensional vector of input variables. • In linear regression, the model for such a relationship is a linear model. • A linear regression example: given a data set , a linear regression model assumes that the relationship between the target variable and the p-dimensional vector of input variables is linear, i.e

2.1.1 History for Regression The earliest form of regression was the method of least squares,which was published by Legendre in 1805,and by Gauss in 1809. ·The term"regression(倒退,退步)"was coined by Francis Galton in the 19th century to describe Gauss Francis Galton a biological phenomenon.The phenomenon was that the heights of descendants of tall ancestors tend to regress down towards a normal average. Galton's work was later extended by Udny Yule and Karl Pearson to a more general statistical context. Udny Yule Karl Pearson
2.1.1 History for Regression • The earliest form of regression was the method of least squares, which was published by Legendre in 1805, and by Gauss in 1809. • The term "regression (倒退,退步)" was coined by Francis Galton in the 19th century to describe a biological phenomenon. The phenomenon was that the heights of descendants of tall ancestors tend to regress down towards a normal average. • Galton’s work was later extended by Udny Yule and Karl Pearson to a more general statistical context. Gauss Francis Galton Udny Yule Karl Pearson

2.1.2 Development for Regression Regression methods continue to be an active research area. New methods have been developed for √robust regression regression involving correlated responses such as time series and growth curves regression in which the predictor (independent variable)or response variables are curves, images,graphs,or other complex data objects regression methods accommodating various types of missing data,nonparametric regression Bayesian methods for regression regression in which the predictor variables are measured with error regression with more predictor variables than observations causal inference with regression
2.1.2 Development for Regression • Regression methods continue to be an active research area . • New methods have been developed for robust regression regression involving correlated responses such as time series and growth curves regression in which the predictor (independent variable) or response variables are curves, images, graphs, or other complex data objects regression methods accommodating various types of missing data, nonparametric regression Bayesian methods for regression regression in which the predictor variables are measured with error regression with more predictor variables than observations causal inference with regression
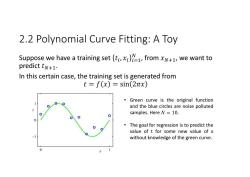
2.2 Polynomial Curve Fitting:A Toy Suppose we have a training set ti,,from xN+1,we want to predict tN+1. In this certain case,the training set is generated from t=f(x)=sin(2πx) 。 Green curve is the original function and the blue circles are noise polluted samples.Here N =10. The goal for regression is to predict the value of t for some new value of x without knowledge of the green curve
2.2 Polynomial Curve Fitting: A Toy Suppose we have a training set , from , we want to predict . In this certain case, the training set is generated from • Green curve is the original function and the blue circles are noise polluted samples. Here . • The goal for regression is to predict the value of t for some new value of x without knowledge of the green curve

2.2 Polynomial Curve Fitting:A Toy The prediction objective is intrinsically difficult in that we have to generalize from a finite and noise-corrupted data set. We have many approaches to deal with this regression,here for our teaching purpose,we adopt this linear polynomial model. ·Suppose,f(x,W)=w0+ω1x+ω2x2+..+WMxM where M is the order of the polynomial
2.2 Polynomial Curve Fitting: A Toy • The prediction objective is intrinsically difficult in that we have to generalize from a finite and noise-corrupted data set. • We have many approaches to deal with this regression, here for our teaching purpose, we adopt this linear polynomial model. • Suppose, where M is the order of the polynomial

2.2 Polynomial Curve Fitting:A Toy The values of the coefficients will be determined by fitting the polynomial to the training data. To do this,we can minimize an error function which measures the misfit between f(x,w)and the training set w.r.t w. A natural choice of error function is E0w)=2∑fw)-tn m=
2.2 Polynomial Curve Fitting: A Toy • The values of the coefficients will be determined by fitting the polynomial to the training data. • To do this, we can minimize an error function which measures the misfit between and the training set w.r.t . • A natural choice of error function is

2.2 Polynomial Curve Fitting:A Toy ·E(w)=2∑m1f(x,wW)-tn2=2∑m=1{x7w-tn2 where xn [1 xnx...xM] Further simplifications yield E(w)=2∑wrxw-2tw+ n=1 Setting the derivative of E(w)equal to 0,we have: ∑xnw=∑tnxn n=1 n=1 By solving this equation,we get the optimum w in least square sense
2.2 Polynomial Curve Fitting: A Toy • = where • Further simplifications yield • Setting the derivative of equal to 0, we have: • By solving this equation, we get the optimum w in least square sense
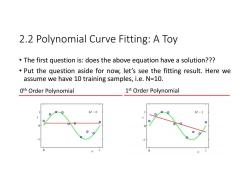
2.2 Polynomial Curve Fitting:A Toy The first question is:does the above equation have a solution??? Put the question aside for now,let's see the fitting result.Here we assume we have 10 training samples,i.e.N=10. Oth Order Polynomial 1st Order Polynomial M=0 M=1 0 0
2.2 Polynomial Curve Fitting: A Toy • The first question is: does the above equation have a solution??? • Put the question aside for now, let’s see the fitting result. Here we assume we have 10 training samples, i.e. N=10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(学习资料)Random Matrix Theory and Wireless Communications.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)05 Free Probability.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)07 Analysis of neural networks - a random matrix approach.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)06 Non-asymptotic Analysis for Large Random Matrix.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 Asymptotic Spectrum Theorems(4/4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 Asymptotic Spectrum Theorems(3/4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 Asymptotic Spectrum Theorems(2/4).pdf
- 《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(文献书籍)An Introduction to Random Matrices(Greg W. Anderson、Alice Guionnet).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 Asymptotic Spectrum Theorems(1/4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)03 Transforms.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)02 Types of Matrices and Local Non-Asymptotic Results.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)01 Introduction of Wireless Channel and Random Matrices(陈智).pdf
- 《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(文献书籍)Random Matrix Theory and Wireless Communications.pdf
- 《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(文献书籍)PRML中文版——模式识别与机器学习.pdf
- 《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(文献书籍)Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验十四 虚拟数字示波器实验.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验十三 基于FPGA的地址译码实验.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验十二 数字示波器信号调理通道实验.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验十一 数字示波器协议触发与解码应用测试.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验十 时域反射实验.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)09 Sparse Signal Recovery.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(学习资料)贝叶斯学习补充材料.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(学习资料)随机矩阵补充材料 Analysis of neural networks - a random matrix approach.pdf
- 广东海洋大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(电子教案).doc
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design(ASIC)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 1 Introduction(About IC technology).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design(ASIC)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 1 Introduction(About ASIC Design).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design(ASIC)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic1 Introduction(About Our Course).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design(ASIC)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 2 FPGA Design with Verilog(FPGA Design Method、Design Examples).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design(ASIC)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 2 FPGA Design with Verilog(Supplementary).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design(ASIC)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 3 Verification and Test.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design(ASIC)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 4 VLSI for DSP.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高等数字集成电路设计 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Design》课程教学资源(教学大纲,负责人:贺雅娟).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《高等数字集成电路设计 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 1 Introduction & The Fabrics.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《模拟集成电路分析与设计 Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(教学大纲,负责人:罗萍).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《模拟集成电路分析与设计 Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 01 Introduction、Models and comparison of integrated-circuit active devices.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《模拟集成电路分析与设计 Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuit》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 02 Amplifiers, source followers and cascodes.pdf
- 川北医学院:《模拟电子技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第四章 集成运算放大器 integrated operational amplifier.pdf
- 川北医学院:《模拟电子技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第四章 双极结型三极管及放大电路基础.pdf
- 《信号与系统》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 线性时不变系统的时域分析.pdf
- 川北医学院:《模拟电子技术》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第五章 场效应管放大电路.pdf
