电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)01 Introduction of Wireless Channel and Random Matrices(陈智)

Introduction of Wireless Channel and Random Matrices 5
Introduction of Wireless Channel and Random Matrices 5

1.1 Wireless Channels The performance of wireless communication is mainly governed by the wireless channel environment As opposed to the static and predictable characteristics of a wired channel,the wireless channel is rather random and unpredictable. A unique characteristic in a wireless channel is a phenomenon called fading',the variation of the signal amplitude over time and frequency. 6
6 The performance of wireless communication is mainly governed by the wireless channel environment. As opposed to the static and predictable characteristics of a wired channel, the wireless channel is rather random and unpredictable. A unique characteristic in a wireless channel is a phenomenon called ‘fading’ , the variation of the signal amplitude over time and frequency. 1.1 Wireless Channels
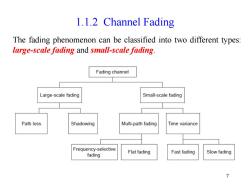
1.1.2 Channel Fading The fading phenomenon can be classified into two different types: large-scale fading and small-scale fading Fading channel Large-scale fading Small-scale fading Path loss Shadowing Multi-path fading Time variance Frequency-selective fading Flat fading Fast fading Slow fading 7
7 1.1.2 Channel Fading The fading phenomenon can be classified into two different types: large-scale fading and small-scale fading

1.1.2 Channel Fading:Large-scale Fading Definition:Large-scale fading is the result of signal loss due to propagation over large distances and diffraction around large objects in the propagation path. Large-scale fading is caused by path loss of signal .shadowing by large objects such as buildings 8
8 1.1.2 Channel Fading: Large-scale Fading Definition: Large-scale fading is the result of signal loss due to propagation over large distances and diffraction around large objects in the propagation path. Large-scale fading is caused by : •path loss of signal •shadowing by large objects such as buildings

1.1.2 Channel Fading:Small-scale Fading Definition:Small-scale fading is the rapid variation of signal level in the short term Small-scale fading is caused by .Multi-path propagation .High-speed move of mobile terminal .Move of surrounding objects 9
9 1.1.2 Channel Fading: Small-scale Fading Definition: Small-scale fading is the rapid variation of signal level in the short term Small-scale fading is caused by : •Multi-path propagation •High-speed move of mobile terminal •Move of surrounding objects
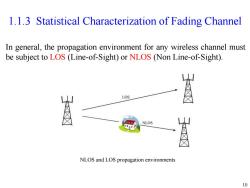
1.1.3 Statistical Characterization of Fading Channel In general,the propagation environment for any wireless channel must be subject to LOS (Line-of-Sight)or NLOS (Non Line-of-Sight). LOS NLOS NLOS and LOS propagation environments 10
10 1.1.3 Statistical Characterization of Fading Channel In general, the propagation environment for any wireless channel must be subject to LOS (Line-of-Sight) or NLOS (Non Line-of-Sight). NLOS and LOS propagation environments

1.1.3 Statistical Characterization of Fading Channel 1.NLOS propagation environments Any received signal in NLOS environment is the sum of the received signals from an infinite number of scatters. By central limit theorem,the received signal can be represented by a Gaussian random variable: W+jW2 where W and W2 are the independent and identically-distributed (i.i.d.)Gaussian random variables with a zero mean and variance 8? 11
11 1.1.3 Statistical Characterization of Fading Channel 1. NLOS propagation environments Any received signal in NLOS environment is the sum of the received signals from an infinite number of scatters. By central limit theorem, the received signal can be represented by a Gaussian random variable: where and are the independent and identically-distributed (i.i.d.) Gaussian random variables with a zero mean and variance . W +jW 1 2 W1 W2 2
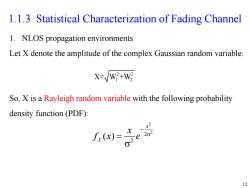
1.1.3 Statistical Characterization of Fading Channel 1.NLOS propagation environments Let X denote the amplitude of the complex Gaussian random variable: X-/W+W So,X is a Rayleigh random variable with the following probability density function(PDF): f.)=e 12
12 1. NLOS propagation environments Let X denote the amplitude of the complex Gaussian random variable: So, X is a Rayleigh random variable with the following probability density function (PDF): 1.1.3 Statistical Characterization of Fading Channel 2 2 X= W +W 1 2 2 2 2 2 ( ) x X x f x e
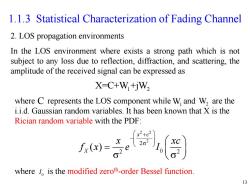
1.1.3 Statistical Characterization of Fading Channel 2.LOS propagation environments In the LOS environment where exists a strong path which is not subject to any loss due to reflection,diffraction,and scattering,the amplitude of the received signal can be expressed as X-C+W+jW, where C represents the LOS component while W and W,are the i.i.d.Gaussian random variables.It has been known that X is the Rician random variable with the PDF: where 1 is the modified zeroth-order Bessel function. 13
13 1.1.3 Statistical Characterization of Fading Channel 2. LOS propagation environments In the LOS environment where exists a strong path which is not subject to any loss due to reflection, diffraction, and scattering, the amplitude of the received signal can be expressed as 2 2 2 2 2 2 0 ( ) x c X x xc f x e I X=C+W +jW 1 2 where represents the LOS component while and are the i.i.d. Gaussian random variables. It has been known that X is the Rician random variable with the PDF: C W1 W2 where is the modified zeroth -order Bessel function. 0 I

1.2 Single Antenna Channels Let us consider the additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN)channel: Y=HX+Z where k∈{I,…,is the time index and ·(X,,Xw)is the input vector satisfying s EsP (Z...,ZN)is the noisy vector,independent of (.....N) .(Y,...,Y)is the output vector; .H,...,H are the fading coefficients. 14
14 1.2 Single Antenna Channels Let us consider the additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) channel: Y H X Z k k k k = + where is the time index and k 1, N , • (X1 ,…,X N ) is the input vector satisfying 2 1 1 P N k k X N • (Z1 ,…,Z N ) is the noisy vector, independent of (X1 ,…,X N ) • (Y1 ,…,Y N ) is the output vector; • H1 ,…,H N are the fading coefficients
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(文献书籍)Random Matrix Theory and Wireless Communications.pdf
- 《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(文献书籍)PRML中文版——模式识别与机器学习.pdf
- 《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(文献书籍)Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验十四 虚拟数字示波器实验.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验十三 基于FPGA的地址译码实验.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验十二 数字示波器信号调理通道实验.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验十一 数字示波器协议触发与解码应用测试.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验十 时域反射实验.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验九 参数测量实验.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验八 数字示波器中的信号插值.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验七 信号采集抽取功能设计实验.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验六 信号采集触发功能设计实验.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验五 数据采集动态性能评估方法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验四 基于FIFO采样与存储.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验三 信号产生实验.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验二 FPGA开发环境与基本设计流程.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)实验一 时域测试仪器原理及典型应用.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)概述.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《时域测试技术综合实验 Comprehensive Experiment of Time Domain Testing Technology》课程教学资源(教学大纲,邱渡裕).pdf
- 广东海洋大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第四章 有限长单位脉冲响应(FIR)滤波器的设计方法.pps
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)02 Types of Matrices and Local Non-Asymptotic Results.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)03 Transforms.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 Asymptotic Spectrum Theorems(1/4).pdf
- 《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(文献书籍)An Introduction to Random Matrices(Greg W. Anderson、Alice Guionnet).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 Asymptotic Spectrum Theorems(2/4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 Asymptotic Spectrum Theorems(3/4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04 Asymptotic Spectrum Theorems(4/4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)06 Non-asymptotic Analysis for Large Random Matrix.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)07 Analysis of neural networks - a random matrix approach.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)05 Free Probability.pdf
- 《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(学习资料)Random Matrix Theory and Wireless Communications.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)08 Linear Regression.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)09 Sparse Signal Recovery.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(学习资料)贝叶斯学习补充材料.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《贝叶斯学习与随机矩阵及在无线通信中的应用 BI-RM-AWC》课程教学资源(学习资料)随机矩阵补充材料 Analysis of neural networks - a random matrix approach.pdf
- 广东海洋大学:《数字信号处理 Digital Signal Processing》课程教学资源(电子教案).doc
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design(ASIC)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 1 Introduction(About IC technology).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design(ASIC)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 1 Introduction(About ASIC Design).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design(ASIC)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic1 Introduction(About Our Course).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design(ASIC)》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 2 FPGA Design with Verilog(FPGA Design Method、Design Examples).pdf
