电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 视觉的神经机制与计算模型(3.8-3.9)

目录 /956 一、 视觉系统的形态学 二、经典感受野与非经典感受野 三、视网膜的组成与信息处理 四、外膝体的组成与信息处理 ·五、视皮层细胞的反应特性和视觉功能 ■六、 视觉系统中的串行与平行处理机制 七、选择性注意机制与模型 ■八、立体视觉模型 ·九、神经信息整合作用
目 录 一、视觉系统的形态学 二、经典感受野与非经典感受野 三、视网膜的组成与信息处理 四、外膝体的组成与信息处理 五、视皮层细胞的反应特性和视觉功能 六、视觉系统中的串行与平行处理机制 七、选择性注意机制与模型 八、立体视觉模型 九、神经信息整合作用

Background /956 We perceive the world as three-dimensional. The inputs to our visual system,however,are only a pair of two-dimensional projections on the two retinal surfaces. EBUR EBURY Image in left eye Image in right eye depth
We perceive the world as three-dimensional. The inputs to our visual system, however, are only a pair of two-dimensional projections on the two retinal surfaces. Image in left eye Image in right eye depth Background

鸟类、家禽:双眼朝向两边,双眼(共同)视觉功能一般 /966 Pigeon ☐Binocular vision 捕食者与 被捕食者
鸟类、家禽: 双眼朝向两边,双眼(共同)视觉功能一般 捕食者与 被捕食者

昆虫主要依靠复眼提供距离、速度、方向信息 /966 IC
昆虫主要依靠复眼提供距离、速度、方向信息
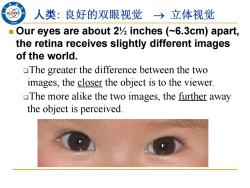
人类:良好的双眼视觉→立体视觉 Our eyes are about 2%inches (~6.3cm)apart, the retina receives slightly different images of the world. The greater the difference between the two images,the closer the object is to the viewer. The more alike the two images,the further away the object is perceived
Our eyes are about 2½ inches (~6.3cm) apart, the retina receives slightly different images of the world. The greater the difference between the two images, the closer the object is to the viewer. The more alike the two images, the further away the object is perceived. 人类: 良好的双眼视觉 立体视觉

Stereovision Depth Perception /956 The ability to see objects in three dimensions although the images that strike the retina are two-dimensional,allows us to judge distance How do we see a 3-D world using only the 2-D retinal images? -We are able to see in 3-D because the visual system can utilize depth cues that appear in the retinal images
Stereovision / Depth Perception The ability to see objects in three dimensions although the images that strike the retina are two-dimensional, allows us to judge distance How do we see a 3-D world using only the 2-D retinal images? We are able to see in 3-D because the visual system can utilize depth cues that appear in the retinal images

Depth Cues Many depth cues have been discovered. Many of them,such as perspective,shading, texture,motion,and occlusion,are present in the retina of a single eye,and are thus called monocular depth cues(单眼线索). Other cues are binocular as they result from comparing the two retinal projections binocular depth cues(双眼线索)
Many depth cues have been discovered. Many of them, such as perspective, shading, texture, motion, and occlusion, are present in the retina of a single eye, and are thus called monocular depth cues (单眼线索). Other cues are binocular as they result from comparing the two retinal projections --- binocular depth cues (双眼线索). Depth Cues

Monocular Depth Cues /966 Depth cues that require the use of only one eye. Monocular depth cues include: o relative size CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required tor reproduction or display. Linear Perspective:Depth Cues ▣relative motion interposition 口 relative height 0 texture gradient relative clarity linear perspective
Monocular Depth Cues Depth cues that require the use of only one eye. Monocular depth cues include: relative size relative motion interposition relative height texture gradient relative clarity linear perspective

Depth Illusions /986 Our perception of depth may be tricked. Julian Beever's Sidewalk Chalk Art http://users.skynet.be/J.Beever/pave.htm
Depth Illusions Our perception of depth may be tricked. Julian Beever’s Sidewalk Chalk Art http://users.skynet.be/J.Beever/pave.htm

Binocular Depth Cues /96 Horizontal disparity(conventional stereopsis) Vertical disparity (induced effect) Monocular regions (da Vinci stereopsis) Interocular time delay (Pulfrich effects) The strongest binocular depth cue is the horizontal component of binocular disparity
Horizontal disparity (conventional stereopsis) Vertical disparity (induced effect) Monocular regions (da Vinci stereopsis) Interocular time delay (Pulfrich effects) The strongest binocular depth cue is the horizontal component of binocular disparity. Binocular Depth Cues
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 视觉的神经机制与计算模型(3.7)选择性注意机制与模型.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 视觉的神经机制与计算模型(3.6)视觉系统中的串行与平行处理机制.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 视觉的神经机制与计算模型(3.4-3.5).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 视觉的神经机制与计算模型(3.1-3.3).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 神经信息传导的生理基础.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 生物神经系统的结构基础.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)绪论(李永杰、夏阳).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 8.2 Time-Frequency Analysis - Wavelet Analysis 小波分析.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 8.1 Time-frequency analysis - Short Time Fourier Transformation(STFT).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(参考文献)Time-Frequency Analysis(Kernel nonnegative matrix factorization for spectral EEG feature extraction).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 7 Multivariate Signal Processing and Biomedical Applications.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 6 Establishing Causality Bewteen Biomedical Signals.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 5.2 Biomedical Applications of Kalman Filter.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 5.1 卡尔曼滤波器 Kalman Filter.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 4.2 biomedical Applications of AR Model.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 4.1 Parametric Model Method.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 3 Adaptive Wiener Filter and Biomedical Applications.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 2 Classical Power Spectral Estimation Methods and Biomedical Applications.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 1 Introduction(饶妮妮).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(案例教学)心电信号处理.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 眼动 Eye movements(4.1-4.4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 眼动 Eye movements(4.5)眼动跟踪技术的应用领域.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 脑电 EEG/ERP(5.1-5.2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 脑电 EEG/ERP(5.3-5.4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 脑机接口 Brain-Computer Interfaces - BCI(6.1-6.3).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 脑机接口 Brain-Computer Interfaces - BCI(6.4)Challenges & Future.pdf
- 《金陵科技学院学报》:中国安息香属植物的形态特征及自然地理分布.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:生物技术专业教学计划(植物).pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:生物技术专业人才培养方案 Biotechnology.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《遗传学》课程教学资源(电子教案,任课教师:王丽).pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《遗传学》课程教学资源(教学大纲)Genetics.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 绪言(主讲:王丽)Genetics.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 孟德尔遗传.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 遗传的细胞学基础.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 染色体变异.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 连锁遗传和性连锁.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 遗传与发育.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 群体遗传与进化.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八章 数量遗传.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《遗传学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 细胞质遗传.pdf
