电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 4.2 biomedical Applications of AR Model

Lecture 4-2 Biomedical Applications of AR Model Prof.N Rao
Lecture 4-2 Biomedical Applications of AR Model Prof. N Rao

The Auto-Regressive (AR)technique for Spectral Analysis A numerical example: (n)=√2cos(2π(0.1)n)+V2cos(2π(0.13)n)+o(n) where n=0,1,...,(N-1)and w(n)is white Gaussian noise with variance 10-. Taking N=19
The Auto-Regressive (AR) technique for Spectral Analysis A numerical example: where n = 0,1,…, (N-1) and ω ( n) is white Gaussian noise with variance = 10-6 . Taking N = 19. x ( n ) = 2 cos( 2 π ( 0.1 ) n ) + 2 cos( 2 π ( 0.13 ) n ) + ω( n )

The Auto-Regressive (AR)technique for Spectral Analysis using aR method 15 20 10 1 -100 0.50.40.3 0.2 00.10.20.30.40.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0.1 0.2 0.30.40.6 01 Frequenoy Frequency The periodogram The AR spectrum
The Auto-Regressive (AR) technique for Spectral Analysis using AR method The periodogram The AR spectrum

It can clearly be seen from Figure 1 that the AR technique exhibits superior resolution.It has distinguished the two sinusoids even though they are very closely spaced in frequency. The periodogram cannot resolve the signals because their spacing is 0.03 cycles/sample which would require a data record of at least N=1/0.03 34 points. In addition,note the smoothness of the AR spectrum which exhibits fewer random fluctuations due to noise and statistical estimation errors as well as an absence of sidelobes.Having justified the advantages of the AR model,we now describe it and its use
• It can clearly be seen from Figure 1 that the AR technique exhibits superior resolution. It has distinguished the two sinusoids even though they are very closely spaced in frequency. • The periodogram cannot resolve the signals because their spacing is 0.03 cycles/sample which would require a data record of at least N = 1/0.03 = 34 points. • In addition, note the smoothness of the AR spectrum which exhibits fewer random fluctuations due to noise and statistical estimation errors as well as an absence of sidelobes. Having justified the advantages of the AR model, we now describe it and its use

Homework4:取19点和多于34点,用周期图方法和 AR模型方法观察下列信号的功率谱,并作对比分析。 x(n)=V2cos(2π(0.1)n)+√2cos(2π(0.13)n)+on)
x(n) = 2 cos(2π (0.1)n) + 2 cos(2π (0.13)n) + ω(n) Homework 4: 取19点和多于34点,用周期图方法和 AR模型方法观察下列信号的功率谱,并作对比分析

The Auto-Regressive (AR)technique for Coding Region Prediction 1 H(z)= 1+a2 02 P(k)= E where o2 is the variance of w(n)and w=ei(z/N)
The Auto-Regressive (AR) technique for Coding Region Prediction • where σ 2 is the variance of w(n) and w N = e -j(2π/N) ∑= − + = p r r k a z H z 1 1 1 ( ) 2 1 2 1 ˆ ( ) kr N p r r x a W p k − = + ∑ = σ
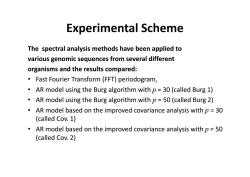
Experimental Scheme The spectral analysis methods have been applied to various genomic sequences from several different organisms and the results compared: Fast Fourier Transform(FFT)periodogram, AR model using the Burg algorithm with p=30(called Burg 1) AR model using the Burg algorithm with p=50(called Burg 2) AR model based on the improved covariance analysis with p=30 (called Cov.1) AR model based on the improved covariance analysis with p=50 (called Cov.2)
Experimental Scheme The spectral analysis methods have been applied to various genomic sequences from several different organisms and the results compared: • Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) periodogram, • AR model using the Burg algorithm with p = 30 (called Burg 1) • AR model using the Burg algorithm with p = 50 (called Burg 2) • AR model based on the improved covariance analysis with p = 30 (called Cov. 1) • AR model based on the improved covariance analysis with p = 50 (called Cov. 2)
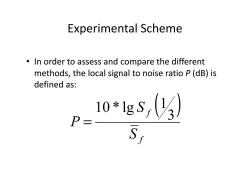
Experimental Scheme In order to assess and compare the different methods,the local signal to noise ratio P(dB)is defined as: 10*1gs,(3) P= S1
Experimental Scheme • In order to assess and compare the different methods, the local signal to noise ratio P (dB) is defined as: ( ) f f S S P 3 1 10 * lg =

Experimental Results ·Large DNA sequences (more than 10000 base pairs) Method I FFT Burgl B12 Co.1 Cov.2 F 5.0048 6.80869.54296.79919.5431
Experimental Results • Large DNA sequences (more than 10000 base pairs )

Experimental Results ·Medium DNA sequences (between 3000 and 10000 base pairs) Method FFT Burgl Bug2 Cov.1 Cov.2 P 281487.834010.81077.758310.6904
Experimental Results • Medium DNA sequences (between 3000 and 10000 base pairs)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 4.1 Parametric Model Method.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 3 Adaptive Wiener Filter and Biomedical Applications.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 2 Classical Power Spectral Estimation Methods and Biomedical Applications.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 1 Introduction(饶妮妮).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(案例教学)心电信号处理.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(案例教学)脑电信号处理(格兰杰因果关系及其在脑电中的应用).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(案例教学)基因组信号处理.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(案例教学)蛋白质信号处理 Deep-Kcr - accurate detection of lysine crotonylation sites using deep learning method.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(教学大纲,饶妮妮).pdf
- 西藏农牧学院:《动物生物化学 Animal biochemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案,杨晓梅).pdf
- 西藏农牧学院:《动物生物化学 Animal biochemistry》课程教学资源(教学大纲,本科).pdf
- 西藏农牧学院:《动物生物化学 Animal biochemistry》课程教学资源(教学大纲,大专).pdf
- 惠州学院:《基础生物学》课程教学资源(实验讲义)河蚌(或田螺)的解剖.pdf
- 惠州学院:《基础生物学》课程教学资源(实验讲义)蛔虫和环毛蚓的比较.pdf
- 河南大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第二十二章 癌基因与抑癌基因(Oncogene and anti-oncogene).pdf
- 河南大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第二十一章 细胞通讯与细胞信号转导的分子机理 Cell Communication and Cell Signal Transduction.pdf
- 河南大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第二十章 DNA重组与基因工程 DNARecombination and Genetic engineering.pdf
- 河南大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十九章 基因表达调控(Gene Expression and Its Regulation).pdf
- 河南大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十八章 蛋白质的生物合成(The Biosynthesis of protein).pdf
- 河南大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)第十七章 RNA的生物合成(TheBiosynthesis of RNA).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 5.1 卡尔曼滤波器 Kalman Filter.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 5.2 Biomedical Applications of Kalman Filter.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 6 Establishing Causality Bewteen Biomedical Signals.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 7 Multivariate Signal Processing and Biomedical Applications.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(参考文献)Time-Frequency Analysis(Kernel nonnegative matrix factorization for spectral EEG feature extraction).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 8.1 Time-frequency analysis - Short Time Fourier Transformation(STFT).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《生物医学信号处理 Biomedical Signal Processing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 8.2 Time-Frequency Analysis - Wavelet Analysis 小波分析.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)绪论(李永杰、夏阳).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 生物神经系统的结构基础.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 神经信息传导的生理基础.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 视觉的神经机制与计算模型(3.1-3.3).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 视觉的神经机制与计算模型(3.4-3.5).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 视觉的神经机制与计算模型(3.6)视觉系统中的串行与平行处理机制.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 视觉的神经机制与计算模型(3.7)选择性注意机制与模型.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 视觉的神经机制与计算模型(3.8-3.9).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 眼动 Eye movements(4.1-4.4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 眼动 Eye movements(4.5)眼动跟踪技术的应用领域.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 脑电 EEG/ERP(5.1-5.2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 脑电 EEG/ERP(5.3-5.4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《神经信息学基础 The Basis of Neuroinformatics》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 脑机接口 Brain-Computer Interfaces - BCI(6.1-6.3).pdf
