同济大学:《中国知识产权保护》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)03 中国法律制度概述 Chinese Legal System

Contents 1.Chinese Legal Tradition 2.The Modernization of the Chinese Law 3.The legal system of modern China: Court System,Judge System,Trial System and others
Contents Contents 1. Chinese Legal Tradition 1. Chinese Legal Tradition 2. The Modernization of the Chinese 2. The Modernization of the Chinese Law 3.The legal system of modern China: The legal system of modern China: Court System, Judge System, Trial Court System, Judge System, Trial System and others System and others

Part I 1.Chinese Legal Tradition Chinese law has the oldest legal tradition in the world.For most of the history of China,it has been based on the Confucian philosophy of social control through moral education,as well as the Legalist emphasis on codified law and criminal sanction
Part I 1. Chinese Legal Tradition 1. Chinese Legal Tradition Chinese Chinese law has the oldest has the oldest legal tradition in the world. For most of tradition in the world. For most of the history history of China, it has been , it has been based on the based on the Confucian Confucian philosophy philosophy of social control of social control through moral education, as well through moral education, as well as the Legalist Legalist emphasis on emphasis on codified law codified law and criminal sanction criminal sanction

1.Chinese Legal Tradition ■ Shang Yang商鞅,390-338B.C.) a famous legalist during the time Warring States Period 475-221 B.C. ■ criminal code-Great Qing Legal Code (221-206B.C.)
1. Chinese Legal Tradition 1. Chinese Legal Tradition Shang Yang Shang Yang商鞅, 390 —338 B.C. 338 B.C. ) , a famous legalist during the time , a famous legalist during the time Warring States Period 475 Warring States Period 475 -221 B.C. criminal code criminal code -Great Qing Legal Code Great Qing Legal Code (221 -206 B.C. 206 B.C. )

1.1 The idea of law The word for law in classical Chinese was Fa ()The Chinese character for Fa denotes a meaning of "fair","straight"and "just“(recht). ■fa(法)had an association with yi(義:"social rightness") ■ The word 'law'in Western languages has four different interpretations in Chinese as in f(理:"order'"),f(礼:"rites","rules of human made law)and
1.1 The idea of law 1.1 The idea of law The word for law in The word for law in classical Chinese classical Chinese was Fa ( 法). The Chinese character Chinese character for Fa denotes a denotes a meaning of "fair", "straight" and meaning of "fair", "straight" and "just “ (recht). (recht). fa ( 法) had an association with ) had an association with yi ( 義: "social : "social rightness") rightness") The word 'law' in Western languages has The word 'law' in Western languages has four different interpretations in Chinese as in four different interpretations in Chinese as in li ( 理: "order"), : "order"), li ( 礼: "rites", "rules of : "rites", "rules of propriety"), propriety"), fa ( 法: "human made laws") and : "human made laws") and zhi ( 制: "control") : "control")

The idea of law ■ A term which preceded fa (was xng(刑),which originally probably referred to decapitation.Xing later evolved to be a general term for laws that related to criminal punishment
The idea of law The idea of law A term which preceded A term which preceded fa(法) was xing ( 刑), which originally probably ), which originally probably referred to referred to decapitation decapitation. Xing later evolved to be a general term for laws evolved to be a general term for laws that related to criminal punishment. that related to criminal punishment

Character of chinese Law:
Character of chinese Law: Character of chinese Law:

1.2 Confucianism and Legalism儒家和法家 The traditional Chinese law developed from Confucianism and Legalism,two rival schools of thought during the Spring and Autumn(770-476 B.C. and Warring States periods(475-221 B.C.). Konfuzius Konfuzianismus Konfuzius Institut
1.2 Confucianism and 1.2 Confucianism and Legalism Legalism 儒家和法家 The traditional Chinese law developed The traditional Chinese law developed from Confucianism Confucianism and Legalism Legalism, two rival schools schools of thought during the of thought during the Spring and Autumn Spring and Autumn (770 -476 B.C. ) 476 B.C. ) and Warring States Warring States periods( periods(475 -221 B.C. ). Konfuzius / Konfuzianismus / Konfuzius / Konfuzianismus / Konfuzius Konfuzius Institut Institut

Confucianism and Legalism North Pacific KAZAKHSTAN Ocean MONGOLIA TAJIKISTAN hangh Philippine Chengdu Sea Lhasa Guangzhou 030000m Hong Kong S'AR Arabian BANG A月.So Sea BURMA PHILIPPINES
Confucianism and Legalism Confucianism and Legalism
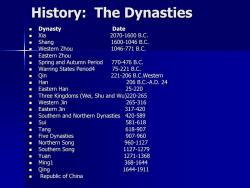
History:The Dynasties Dynasty Date ■ Xia 2070-1600B.C Shang 1600-1046B.C Western Zhou 1046-771B.C. ■ Eastern Zhou Spring and Autumn Period 770-476B.C. Warring States Period4 75-221B.C ■ Qin 221-206 B.C.Western ◆ Han 206B.C.-A.D.24 ■ Eastern Han 25-220 Three Kingdoms (Wei,Shu and Wu)220-265 Western Jin 265-316 ■ Eastern Jin 317-420 Southern and Northern Dynasties 420-589 Sui 581-618 Tang 618-907 ■ Five Dynasties 907-960 ■ Northern Song 960-1127 ■ Southern Song 1127-1279 ■ Yuan 1271-1368 ■ Ming1 368-1644 ■ Qing 1644-1911 ■ Republic of China
History: History: The Dynasties The Dynasties Dynasty Dynasty Date Date Xia Xia 2070 2070-1600 B.C. 1600 B.C. Shang Shang 1600 1600-1046 B.C. 1046 B.C. Western Zhou Western Zhou 1046 1046-771 B.C. 771 B.C. Eastern Zhou Eastern Zhou Spring and Autumn Period 770 Spring and Autumn Period 770-476 B.C. 476 B.C. Warring States Period4 75 Warring States Period4 75-221 B.C. 221 B.C. Qin Qin 221 221-206 B.C.Western B.C.Western Han Han 206 B.C. 206 B.C.-A.D. 24 A.D. 24 Eastern Han Eastern Han 25 25-220 Three Kingdoms (Wei, Three Kingdoms (Wei, Shu and Wu)220 and Wu)220-265 Western Jin Western Jin 265 265-316 Eastern Jin Eastern Jin 317-420 Southern and Northern Dynasties 420 Southern and Northern Dynasties 420-589 Sui Sui 581 581-618 Tang Tang 618 618-907 Five Dynasties Five Dynasties 907 907-960 Northern Song Northern Song 960 960-1127 Southern Song Southern Song 1127 1127-1279 Yuan Yuan 1271 1271-1368 Ming1 Ming1 368 368-1644 Qing Qing 1644 1644-1911 Republic of China Republic of China

春秋Spring and Autumn(770-476 B.C.) ◆ During "Spring und Autumn"period,there were 5 superpowers,namely Qi,Song,Jing,Qin und Chu. Later followed by Warring States ■ 春秋时期,简称春秋,前770年一前476年,东周的一 个时期,春秋时代周王的势力减弱,群雄纷争,齐桓 公、晋文公、宋襄公、 素穆公、楚庄王相笨称霸虞 称“春秋五霸”。(一说是齐桓公、晋文公、楚庄王、 王阖闾、越王勾践)。春秋时期之后是战国时期。 春秋时期的得名,是因孔子修订《春秋》而得名。这 部书记载了从鲁隐公元年(前722年)到鲁哀公十四 年(前481年)的历史。现代的学者为了方便起见, 一般从周平王元年(前770年)东周立国起,到周敬 王四十三年(前477年)为止,称为“春秋时期
春秋Spring and Spring and Autumn (770 -476 B.C. ) 476 B.C. ) During “Spring und Autumn Spring und Autumn ” period, there were 5 period, there were 5 superpowers, namely superpowers, namely Qi, Song, Jing, Qin und Chu. , Song, Jing, Qin und Chu. Later followed by Warring States Later followed by Warring States 春秋时期,简称春秋,前 春秋时期,简称春秋,前770 年 — 前476年,东周的一 个时期,春秋时代周王的势力减弱,群雄纷争,齐桓 个时期,春秋时代周王的势力减弱,群雄纷争,齐桓 公、晋文公、宋襄公、秦穆公、楚庄王相继称霸,史 公、晋文公、宋襄公、秦穆公、楚庄王相继称霸,史 称 “春秋五霸 ” 。 (一说是齐桓公、晋文公、楚庄王、吴 一说是齐桓公、晋文公、楚庄王、吴 王阖闾、越王勾践 王阖闾、越王勾践 )。春秋时期之后是战国时期。 。春秋时期之后是战国时期。 春秋时期的得名,是因孔子修订 春秋时期的得名,是因孔子修订 《春秋 》而得名。这 部书记载了从鲁隐公元年(前 部书记载了从鲁隐公元年(前722年)到鲁哀公十四 年)到鲁哀公十四 年(前481年)的历史。现代的学者为了方便起见, 年)的历史。现代的学者为了方便起见, 一般从周平王元年(前 一般从周平王元年(前770年)东周立国起,到周敬 年)东周立国起,到周敬 王四十三年(前 王四十三年(前477年)为止,称为 年)为止,称为 “春秋时期 ”
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《中国知识产权保护》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)02 知识产权历史沿革和执法 Legal System of IP Protection in China and Enforcement Mechanism.pdf
- 同济大学:《中国知识产权保护》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)01 中国知识产权保护导论 Intellectual Protection in China(Introduction to IP and Chinese legal system).ppt
- 同济大学:《中国知识产权保护》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷(2012-2013).doc
- 同济大学:《中国知识产权保护》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷(2009-2010).doc
- 《知识产权法》课程教学资源(参考文献)知识产权手册 WIPO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HANDBOOK(Second Edition).pdf
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四模块 工资法律制度.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六模块 工作时间与休息时间法律制度.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八模块 社会保险法律制度.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五模块 劳动安全与卫生法律制度(违反劳动法责任).ppt
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五模块 劳动安全与卫生法律制度(劳动安全卫生法律制度).pptx
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七模块 劳动争议处理、保护、监察制度与违反劳动法的责任.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三模块 劳动合同 序号5-劳动争议的处理程序.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三模块 劳动合同 序号4-无效劳动合同与劳动争议处理制度.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三模块 劳动合同 序号3劳动合同的解除.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三模块 劳动合同 序号2劳动合同的签订履行变更终止.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三模块 劳动合同 序号1劳动合同概述与内容.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二模块 劳动法律关系.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一模块 劳动法概述.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(教案)第八模块 社会保障法编.docx
- 私立华联学院:《劳动与社会保障法律制度》课程教学资源(教案)第六模块 工作时间与休息时间法律制度.docx
- 同济大学:《中国知识产权保护》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)04 商业秘密保护 Protection of trade secret in China(负责人:张韬略).ppt
- 同济大学:《中国知识产权保护》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)05 专利保护 Patent Protection in China.ppt
- 同济大学:《中国知识产权保护》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)06 版权保护 Copyright Protection in China.ppt
- 同济大学:《中国知识产权保护》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)07 商标保护 Trademark Protection in China(1/2).ppt
- 同济大学:《中国知识产权保护》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)08 商标保护 Trademark Protection in China(2/2).pptx
- 吉林大学:《婚姻家庭法》课程教学资源(试卷习题)考试题(一)参考答案.doc
- 吉林大学:《婚姻家庭法》课程教学资源(试卷习题)考试题(二)参考答案.doc
- 吉林大学:《婚姻家庭法》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)绪论(主讲人:曹险峰).ppt
- 吉林大学:《婚姻家庭法》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)第一章 婚姻法概述.ppt
- 吉林大学:《婚姻家庭法》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)第二章 婚姻法之基本原则.ppt
- 吉林大学:《婚姻家庭法》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)第三章 亲属关系原理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《婚姻家庭法》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)第四章 结婚制度.ppt
- 吉林大学:《婚姻家庭法》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)第五章 家庭关系.ppt
- 吉林大学:《婚姻家庭法》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)第六章 离婚制度.ppt
- 吉林大学:《婚姻家庭法》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)第七章 救助措施与法律责任.ppt
- 吉林大学:《国际经济法学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)客观试题归类精解.doc
- 吉林大学:《国际经济法学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第五编 国际货物贸易政府管制法.ppt
- 吉林大学:《国际经济法学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第四编 国际货物买卖相关法.ppt
- 吉林大学:《行政法与行政诉讼法》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)第三章 行政主体.ppt
- 吉林大学:《行政法与行政诉讼法》课程电子教案(PPT课件讲稿)第五章 行政行为概述.ppt
