同济大学:《常微分方程》课程教学资源(讲义)高阶线性微分方程

2.Linear Differential Equations of Higher Order 4口卡0y4主,元,2只0
2. Linear Differential Equations of Higher Order Second-Order Linear Equations Recall a general second-order differential equation G(x, y, y 0 , y 00 ) = 0 It is linear provided that G is linear in the dependent variable y and y 0 , y 00 . A(x)y 00 +B(x)y 0 +C(x)y = F(x) Example e x y 00 + (cos x)y 0 + (1+x)y = tan −1 x y 00 = yy 0 y 00 +3(y 0 ) 2 +4y 3 = 0

2.Linear Differential Equations of Higher Order Second-Order Linear Equations Recall a general second-order differential equation G(x,y,y,y")=0 It is linear provided that G is linear in the dependent variable y and y,y". A(x)y"+B(x)y+C(x)y=F(x) Example e'y"+(cosx)y/+(1+x)y=tan-Ix y"=yy y"+36y)2+4y3=0
2. Linear Differential Equations of Higher Order Second-Order Linear Equations Recall a general second-order differential equation G(x, y, y 0 , y 00) = 0 It is linear provided that G is linear in the dependent variable y and y 0 , y 00 . A(x)y 00 +B(x)y 0 +C(x)y = F(x) Example e x y 00 + (cos x)y 0 + (1+x)y = tan−1 x y 00 = yy 0 y 00 +3(y 0 ) 2 +4y 3 = 0
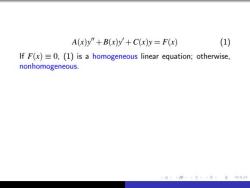
A(x)y"+B(x)y+C(x)y=F(x) (1) If F(x)=0,(1)is a homogeneous linear equation;otherwise, nonhomogeneous. 4日1①y至,无2000
A(x)y 00 +B(x)y 0 +C(x)y = F(x) (1) If F(x) ≡ 0, (1) is a homogeneous linear equation; otherwise, nonhomogeneous. Example x 2 y 00 +2xy 0 +3y−cos x = 0 (nonhomogenous) x 2 y 00 +2xy 0 +3y = 0 (homogeneous)

A(x)y"+B(x)y+C(x)y=F(x) (1) If F(x)=0,(1)is a homogeneous linear equation;otherwise, nonhomogeneous. Example x2y"+2xy+3y-cosx =0 4日10y至,无2000
A(x)y 00 +B(x)y 0 +C(x)y = F(x) (1) If F(x) ≡ 0, (1) is a homogeneous linear equation; otherwise, nonhomogeneous. Example x 2 y 00 +2xy 0 +3y−cos x = 0 (nonhomogenous) x 2 y 00 +2xy 0 +3y = 0 (homogeneous)

A(x)y"+B(x)y+C(x)y=F(x) (1) If F(x)=0,(1)is a homogeneous linear equation;otherwise, nonhomogeneous. Example x2y"+2xy +3y-cosx =0 (nonhomogenous) 4日10y至,无2000
A(x)y 00 +B(x)y 0 +C(x)y = F(x) (1) If F(x) ≡ 0, (1) is a homogeneous linear equation; otherwise, nonhomogeneous. Example x 2 y 00 +2xy 0 +3y−cos x = 0 (nonhomogenous) x 2 y 00 +2xy 0 +3y = 0 (homogeneous)

A(x)y"+B(x)y+C(x)y=F(x) (1) If F(x)=0,(1)is a homogeneous linear equation;otherwise, nonhomogeneous. Example x2y"+2xy+3y-cosx=0 (nonhomogenous) x2y"+2y+3y=0 4日10y至,无2000
A(x)y 00 +B(x)y 0 +C(x)y = F(x) (1) If F(x) ≡ 0, (1) is a homogeneous linear equation; otherwise, nonhomogeneous. Example x 2 y 00 +2xy 0 +3y−cos x = 0 (nonhomogenous) x 2 y 00 +2xy 0 +3y = 0 (homogeneous)

A(x)y"+B(x)y+C(x)y=F(x) (1) If F(x)=0,(1)is a homogeneous linear equation;otherwise, nonhomogeneous. Example x2y"+2xy+3y-cosx=0 (nonhomogenous) x2y"+2xy+3y=0 (homogeneous) 4日10y至,无2000
A(x)y 00 +B(x)y 0 +C(x)y = F(x) (1) If F(x) ≡ 0, (1) is a homogeneous linear equation; otherwise, nonhomogeneous. Example x 2 y 00 +2xy 0 +3y−cos x = 0 (nonhomogenous) x 2 y 00 +2xy 0 +3y = 0 (homogeneous)

A Typical Application In case the differential equation models a physical system, the nonhomogenous term F(x)frequently corresponds to some external influence on the system. 4口1日,1元2000
A Typical Application In case the differential equation models a physical system, the nonhomogenous term F(x) frequently corresponds to some external influence on the system. Suppose that a mass m is attached both to a spring that exerts on it a force FS and to a dashpot (shock absorber) that exerts a force FR on the mass. Assume that the restoring force FS of the spring is proportional to the displacement x (positive to the right, negative to the left) of the mass from equilibrium, and that the dashpot force FR is proportional to the velocity v = dx/dt of the mass. Then we have FS = −kx and FR = −cv (k, c > 0)

A Typical Application In case the differential equation models a physical system, the nonhomogenous term F(x)frequently corresponds to some external influence on the system. Suppose that a mass m is attached both to a spring that exerts on it a force Fs and to a dashpot(shock absorber)that exerts a force FR on the mass. 1口1日,元卡20只0
A Typical Application In case the differential equation models a physical system, the nonhomogenous term F(x) frequently corresponds to some external influence on the system. Suppose that a mass m is attached both to a spring that exerts on it a force FS and to a dashpot (shock absorber) that exerts a force FR on the mass. Assume that the restoring force FS of the spring is proportional to the displacement x (positive to the right, negative to the left) of the mass from equilibrium, and that the dashpot force FR is proportional to the velocity v = dx/dt of the mass. Then we have FS = −kx and FR = −cv (k, c > 0)

A Typical Application In case the differential equation models a physical system, the nonhomogenous term F(x)frequently corresponds to some external influence on the system. Suppose that a mass m is attached both to a spring that exerts on it a force Fs and to a dashpot (shock absorber)that exerts a force FR on the mass.Assume that the restoring force Fs of the spring is proportional to the displacement x(positive to the right,negative to the left)of the mass from equilibrium, 4口①,t元2月00
A Typical Application In case the differential equation models a physical system, the nonhomogenous term F(x) frequently corresponds to some external influence on the system. Suppose that a mass m is attached both to a spring that exerts on it a force FS and to a dashpot (shock absorber) that exerts a force FR on the mass. Assume that the restoring force FS of the spring is proportional to the displacement x (positive to the right, negative to the left) of the mass from equilibrium, and that the dashpot force FR is proportional to the velocity v = dx/dt of the mass. Then we have FS = −kx and FR = −cv (k, c > 0)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《常微分方程》课程教学资源(讲义)微分方程基本概念及几类可求解析解的方程.pdf
- 同济大学:《常微分方程》课程教学资源(讲义)First-order differential equations.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《博弈论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Lecture 5 Dynamic game with Incomplete Information.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《博弈论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Lecture 4 Static game of incomplete information.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《博弈论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Lecture 3 Dynamic games of complete information.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《博弈论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Lecture 2 Mixed strategy game(任课教师:栾浩).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《博弈论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Lecture 1 GAME THEORY - Static complete information pure strategy game.ppt
- 《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(参考教材)概率论教材 Probability and Statistics《A FIRST COURSE IN PROBABILITY》英文电子版(Eighth Edition,Sheldon Ross).pdf
- 同济大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 9 Sampling Distributions.pdf
- 同济大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 10 Point Estimation.pdf
- 同济大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 8 Limit Theorems.pdf
- 同济大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 6 Jointly Distributed Random Variables.pdf
- 同济大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 5 Continuous Random Variables.pdf
- 同济大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 4 Mathematics.pdf
- 同济大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 3 Conditional Probability and Independence.pdf
- 同济大学:《概率论与数理统计》课程教学资源(讲稿)Chapter 2 Axioms of Probability(负责人:花虹).pdf
- 同济大学:《复变函数和积分变换》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)习题选讲4(积分的计算、共形映照).pptx
- 同济大学:《复变函数和积分变换》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)习题选讲3(级数及其应用、奇点与留数).pptx
- 同济大学:《复变函数和积分变换》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)习题选讲2(复变函数的两种形式、计算解析函数的级数).pptx
- 同济大学:《复变函数和积分变换》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)习题选讲1(复数的四则运算、复数的幂与根).pptx
- 同济大学:《常微分方程》课程教学资源(讲义)线性微分方程组 Linear Systems of Differential Equations(负责人:尚培培).pdf
- 同济大学:《常微分方程》课程教学资源(讲义)非线性微分方程及现象 Nonlinear Systems and Phenomena.pdf
- 同济大学:《运筹学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)运筹学试卷1.doc
- 同济大学:《运筹学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)运筹学试卷2.doc
- 同济大学:《运筹学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)引言 Operations Research(负责人:陈雄达).pdf
- 同济大学:《运筹学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)线性规划基本性质.ppt
- 同济大学:《运筹学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)一维搜索.ppt
- 同济大学:《运筹学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)单纯形方法.ppt
- 同济大学:《运筹学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)对偶理论及灵敏度分析.ppt
- 同济大学:《运筹学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)整数(线性)规划.ppt
- 同济大学:《运筹学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)使用导数的最优化方法(无约束优化方法).ppt
- 同济大学:《运筹学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)最优性条件.ppt
- 同济大学:《运筹学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)惩罚函数法.ppt
- 《线性代数》课程教学资源(文献资料)THE $25,000,000,000 EIGENVECTOR THE LINEAR ALGEBRA BEHIND GOOGLE.pdf
- 《线性代数》课程教学资源(文献资料)数据降维方法综述(清华大学:马小龙).pdf
- 《线性代数》课程教学资源(文献资料)主元分析(PCA)理论分析及应用.pdf
- 同济大学:《线性代数》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2006-2007学年第二学期B卷(含答案).pdf
- 同济大学:《线性代数》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2008-2009学年第一学期(B卷).pdf
- 同济大学:《线性代数》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)线性代数习题课(负责人:张莉).pdf
- 同济大学:《线性代数》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Linear Algebra—Determinants.pdf
