重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)气胸 PNEUMOTHORAX

PNEUMOTHORAX DR.LIU ZHONG DEPARTMENT OF CHEST MEDICINE THE FIRST ASSOCIATED HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
PNEUMOTHORAX DR. LIU ZHONG DEPARTMENT OF CHEST MEDICINE THE FIRST ASSOCIATED HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES

Definition The accumulation of air in the pleural space with secondary lung collapse. Spontaneous pneumothorax,which occurs without trauma or obvious cause 。Traumatic pneumothorax (iatrogenic), which occurs as a result of direct trauma to the chest
Definition The accumulation of air in the pleural space with secondary lung collapse. • Spontaneous pneumothorax, which occurs without trauma or obvious cause • Traumatic pneumothorax (iatrogenic), which occurs as a result of direct trauma to the chest

Spontaneous pneumothorax Spontaneous pneumothorax is by far the commonest form in clinical practice and is always secondary to pulmonary or pleural abnormality. This may be congenital or due to acute or chronic acquired disease. Classification 1.Primary spontaneous (idiopathic)pneumothorax which occurs in healthy persons 2.Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax which occurs in persons with diseases that affect the lung
Spontaneous pneumothorax Spontaneous pneumothorax is by far the commonest form in clinical practice and is always secondary to pulmonary or pleural abnormality. This may be congenital or due to acute or chronic acquired disease. Classification 1. Primary spontaneous (idiopathic) pneumothorax which occurs in healthy persons 2. Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax which occurs in persons with diseases that affect the lung

Aetiology 1.Primary spontaneous pneumothorax (idiopathic) Defined as a pneumothorax occurring in patients without obvious pulmonary disease clinically or on chest X-ray, although chest CT usually reveals subapical blebs and bullae. 2.Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax Defined as a pneumothorax occurring in patients with underlying lung disease
Aetiology 1. Primary spontaneous pneumothorax (idiopathic) Defined as a pneumothorax occurring in patients without obvious pulmonary disease clinically or on chest X-ray, although chest CT usually reveals subapical blebs and bullae. 2. Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax Defined as a pneumothorax occurring in patients with underlying lung disease

Clinical types 1.Closed pneumothorax There is no movement of air takes place because the hole through which air entered has been sealed off
Clinical types 1. Closed pneumothorax There is no movement of air takes place because the hole through which air entered has been sealed off
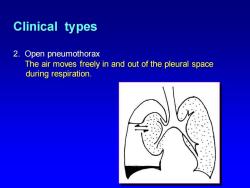
Clinical types 2.Open pneumothorax The air moves freely in and out of the pleural space during respiration
Clinical types 2. Open pneumothorax The air moves freely in and out of the pleural space during respiration

Clinical types 3.Tension pneumothorax (valvular pneumothorax) A one-way valve is created where air enters pleural space in inspiration but cannot exit in expiration
Clinical types 3. Tension pneumothorax (valvular pneumothorax) A one-way valve is created where air enters pleural space in inspiration but cannot exit in expiration

Clinical features 1.Symtoms ★ Strenuous activity,unilateral chest pain and dyspnoea. *The clinical manifestations of pneumothorax depend on its size,type,and the healthy condition of patient's lung
Clinical features 1. Symtoms ★ Strenuous activity, unilateral chest pain and dyspnoea. ★ The clinical manifestations of pneumothorax depend on its size, type, and the healthy condition of patient’s lung

Clinical features 2.Physical signs Signs of air accumulation in the thorax decreased expansion of the involved hemithorax decreased fremitus tympanitic percussion decreased breath sounds on the involved side
Clinical features 2. Physical signs Signs of air accumulation in the thorax • decreased expansion of the involved hemithorax • decreased fremitus • tympanitic percussion • decreased breath sounds on the involved side
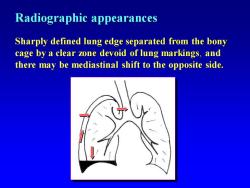
Radiographic appearances Sharply defined lung edge separated from the bony cage by a clear zone devoid of lung markings,and there may be mediastinal shift to the opposite side
Radiographic appearances Sharply defined lung edge separated from the bony cage by a clear zone devoid of lung markings, and there may be mediastinal shift to the opposite side
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)慢性支气管炎 Chronic Bronchitis.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(实验指导)内科诊疗操作常规.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)高血压.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)贫血概述.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)胃食管反流病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)胃炎.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)肠结核.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)肝癌.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)肝性脑病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)缺铁性贫血.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)结核性腹膜炎.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)溶血性贫血.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)淋巴瘤.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)消化性溃疡.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)有机磷.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)慢性肾小球肾炎.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)慢性肾功能衰竭.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)急性胰腺炎.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)心肌病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)心律失常.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)胸腔积液 Pleural effusion.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)冠心病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)肺炎(Pneumonia).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)原发性支气管肺癌 Primary Bronchogenic Carcinoma.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)肾上腺皮质功能减退症 Chronic adrenocortical hypofunction.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)皮质醇增多症 hypercortisolism.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)甲状腺功能亢进症(hyperthyroidism).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)慢性肾小球肾炎(chronic glomerulonephritis).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)糖尿病(diabetes mellitus,DM).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)心肌病 Cardiomyopathies.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)CIRRHOSIS of LIVER.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)消化性溃疡 Peptic ulcer.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)肠结核 Intestinal tuberculosis.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)心包炎(Pericarditis).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)出血性疾病总论.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)原发性肝癌 Primary Carcinoma of Liver.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)心律失常(Arythmia).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)贫血总论(缺铁、再生障碍性贫血).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)淋巴瘤(附属一院:胡妮妮).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《内科学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)溶血性贫血概述.ppt
