北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acids
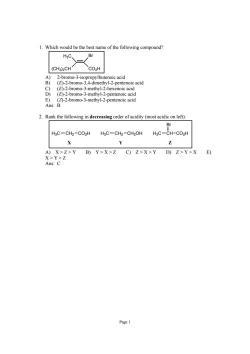
1.Which would be the best name of the following compound? Br (CHa)2CH `C02H tenoic acid -2-pentenoic acid me noic aci E) 2.Rank the following in decreasing order of acidity(most acidic on left): Br H3C-CH2-CO2H H3C-CH2-CH2OH HaC-CH-CO2H C)Z>X>Y D)Z>Y>X Ans:C Page1
Page 1 1. Which would be the best name of the following compound? CO2H H Br 3C (CH3)2CH A) 2-bromo-3-isopropylbutenoic acid B) (E)-2-bromo-3,4-dimethyl-2-pentenoic acid C) (E)-2-bromo-3-methyl-2-hexenoic acid D) (E)-2-bromo-3-methyl-2-pentenoic acid E) (Z)-2-bromo-3-methyl-2-pentenoic acid Ans: B 2. Rank the following in decreasing order of acidity (most acidic on left): H3C CH2 CO2H H3C CH CO2H Br H3C CH2 CH2OH X Y Z A) X > Z > Y B) Y > X > Z C) Z > X > Y D) Z > Y > X E) X > Y > Z Ans: C
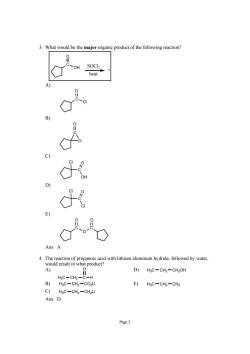
What would be the major organic product of the following reaction? Ans:A 4.The reaction of propanoic acid with lithium aluminum hydride,followed by water. would result in what product? A) Hc-CH-8-H D)H3C-CH2-CH2OH B)HaC-CH2-COzL E)HgC-CH2-CHg C)HgC-CH2-CH2Li Ans:D Page2
Page 2 3. What would be the major organic product of the following reaction? C O OH ? heat SOCl2 A) C O Cl B) C O O C) C O OH Cl D) C O Cl Cl E) C O O C O Ans: A 4. The reaction of propanoic acid with lithium aluminum hydride, followed by water, would result in what product? A) H3C CH2 C O H D) H3C CH2 CH2OH B) H3C CH2 CO2Li E) H3C CH2 CH3 C) H3C CH2 CH2Li Ans: D
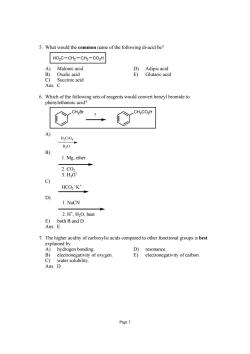
5.What would the common name of the following di-acid be? HOzC-CHz-CH2-CO2H A)Malonic acid Oxalic acid Baneaa Succinic acic 6.Which of the following sets of reagents would convert benzyl bromide to phenylethanoic acid? H.CO H,0 B) 1.Mg.ether 的 c) HCO2K* 1.NaCN 2.H',H2O,heat 7.The higher acidity of carboxylic acids compared to other functional groups is best explained by A)hydrogen bonding. D)resonance. B)electronegativity of oxygen. E)electronegativity of carbon. Page3
Page 3 5. What would the common name of the following di-acid be? HO2C CH2 CH2 CO2H A) Malonic acid D) Adipic acid B) Oxalic acid E) Glutaric acid C) Succinic acid Ans: C 6. Which of the following sets of reagents would convert benzyl bromide to phenylethanoic acid? CH2Br CH2CO2H ? A) H2CrO4 H2O B) 1. Mg, ether 2. CO2 3. H3O+ C) HCO2 - K+ D) 1. NaCN 2. H+ , H2O, heat E) both B and D Ans: E 7. The higher acidity of carboxylic acids compared to other functional groups is best explained by A) hydrogen bonding. D) resonance. B) electronegativity of oxygen. E) electronegativity of carbon. C) water solubility. Ans: D
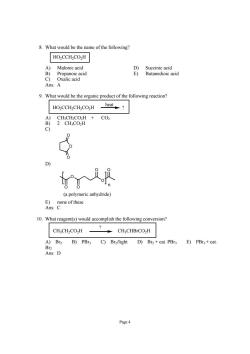
8.What would be the name of the following? HO2CCH2CO2H Malonic acid d Ans:A 9.What would be the organic product of the following reaction? HO2CCH2CH2CO2H _heat? A)CH;CH2CO2H CO2 B)2 CH;CO2H C) (a polymeric anhydride) 10.What reagent(s)would accomplish the following conversion? CH3CH2CO2H CH3CHBrCO2H A)Br2 B)PBr3 C)Bra/light D)Br+cat.PBra E)PBr3+cat Dr. Ans:D Page 4
Page 4 8. What would be the name of the following? HO2CCH2CO2H A) Malonic acid D) Succinic acid B) Propanoic acid E) Butanedioic acid C) Oxalic acid Ans: A 9. What would be the organic product of the following reaction? ? heat HO2CCH2CH2CO2H A) CH3CH2CO2H + CO2 B) 2 CH3CO2H C) O O O D) O O O O O O (a polymeric anhydride) n E) none of these Ans: C 10. What reagent(s) would accomplish the following conversion? CH3CH2CO2H CH3CHBrCO2H ? A) Br2 B) PBr3 C) Br2/light D) Br2 + cat. PBr3 E) PBr3 + cat. Br2 Ans: D
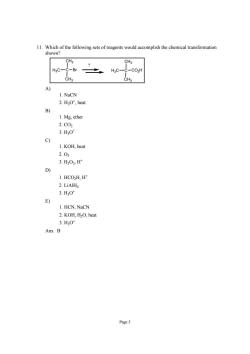
11.Which of the following sets of reagents would accomplish the chemical transformation shown? HgC-C-Br -C02h A 1.NaCN 2.HO',heat B) 1.Mg.ether 2.C02 3.H0 c) 1.KOH,heat 2.03 3.H202,H D) 1.HCO2H,H* 2.LiAlH 3.HO' E) 1.HCN,NaCN 2.KOH,H2O,heat 3.HO" Ans:B Page5
Page 5 11. Which of the following sets of reagents would accomplish the chemical transformation shown? CH3 C CH3 H3C Br CH3 C CH3 H3C CO2H ? A) 1. NaCN 2. H3O+, heat B) 1. Mg, ether 2. CO2 3. H3O+ C) 1. KOH, heat 2. O3 3. H2O2, H+ D) 1. HCO2H, H+ 2. LiAlH4 3. H3O+ E) 1. HCN, NaCN 2. KOH, H2O, heat 3. H3O+ Ans: B

n(=oru omplish c ArCH2CH3 CH-CH-CO2H (Ar=aryl group) Ar 1.Br2,light 2.NaCN 3.H0,? B) 1.Br2,light 2.Mg,ether 3C0、 4.H0 c) 1.Br2,light 2.KOH 3.03 3.H202,f D) 1.Br2,light 2.CH;CO2K 3.H-O" R上Soth andB Page6
Page 6 12. Several 2-arylpropanoic acids are used as analgesics (painkillers). Three of these [Ibuprofen (= Advil), Naproxen (= Aleve) and Ketoprofen (= Orudis KT)] are currently available in over-the-counter form. Which of the following sets of reagents would accomplish conversion of an ethyl aromatic to a 2-arylpropanoic acid? CH3 CH CO2H Ar ArCH2CH3 ? (Ar = aryl group) A) 1. Br2, light 2. NaCN 3. H3O+ , ? B) 1. Br2, light 2. Mg, ether 3. CO2 4. H3O+ C) 1. Br2, light 2. KOH 3. O3 3. H2O2, H+ D) 1. Br2, light 2. CH3CO2 - K+ 3. H3O+ E) both A and B Ans: E
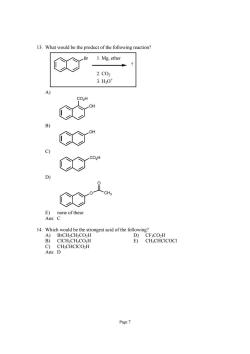
13.What would be the product of the following reaction? 1.Mg.ether 2.C02 3.H30 A) co" co" E)none of these Ans: B)CICH-CH.CO.,H E)CH:CHCICOCI C)CH;CHCICO2H Ans:D Page7
Page 7 13. What would be the product of the following reaction? Br ? 1. Mg, ether 2. CO2 3. H3O+ A) OH CO2H B) OH C) CO2H D) O O CH3 E) none of these Ans: C 14. Which would be the strongest acid of the following? A) BrCH2CH2CO2H D) CF3CO2H B) ClCH2CH2CO2H E) CH3CHClCOCl C) CH3CHClCO2H Ans: D

15.What bestacou for the high boiling points of i atoms The n bonding Cre mosothusr moty o cmound The presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding. E)Carboxylic acids do not have unusually high boiling points. Ans:D 16.What reagent is needed to complete the reaction shown? CH-CO.H HC CH-COct A)CH,CI B)PCl3 C)Cl2 D)LiAlHa E)none of these Ans:B Page8
Page 8 15. What best accounts for the unusually high boiling points of carboxylic acids relative to other organic compounds of similar molecular weight? A) The relatively large concentration of oxygen atoms. B) The presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonding. C) Carboxylic acids are mostly ionized and thus are mostly ionic compounds. D) The presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding. E) Carboxylic acids do not have unusually high boiling points. Ans: D 16. What reagent is needed to complete the reaction shown? H3C CH H3C CO2H H3C CH H3C COCl ? A) CH3Cl B) PCl3 C) Cl2 D) LiAlH4 E) none of these Ans: B
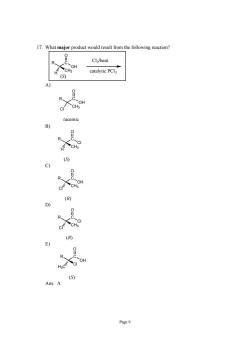
17.What major product would result from the following reaction? Cl/heat CH.OH catalytic PCl (S) CH racem Page9
Page 9 17. What major product would result from the following reaction? C OH O R CH3 H Cl2/heat catalytic PCl3 (S) A) C OH O R CH3 Cl racemic B) C Cl O R CH3 H (S) C) C OH O R CH3 Cl (R) D) C Cl O R CH3 Cl (R) E) C OH O R Cl H3C (S) Ans: A

18.What reagent(s)is(are)needed to complete the reaction shown? 1.C02 CH;CH2CO2H 2.H,0 CH;CH.B Ans:C 19.Which,if any,of the reactions below would produce 2-methylpropanoic acid? A) Mgr folowred byHgo B) +KCN followed by HOfand heat C) D All of these roduct Ans:D 20.Which,if any,functional group in the molecule below would undergo basic hydrolysis most easily? C A)A B)B C)C D)D E)None of these groups would react. Ans:C 21.What reagent(s)would accomplish the following? A)Cl2,light B)Cl2,H2O C)SOCL2 D)MgCl2 E)aqueous HCI Ans:C Page 10
Page 10 18. What reagent(s) is (are) needed to complete the reaction shown? CH3CH2CO2H 1. CO2 2. H3O+ ? A) CH3CH2Br D) CH3Li B) KMnO4/ - OH E) CH3COCl C) CH3CH2MgBr Ans: C 19. Which, if any, of the reactions below would produce 2-methylpropanoic acid? A) B) Br + KCN followed by H3O+ and heat C) CH2OH + H2CrO4 D) All of these reactions would produce the desired product. E) None of these reactions would produce the desired product. Ans: D 20. Which, if any, functional group in the molecule below would undergo basic hydrolysis most easily? O N C H3C O CN O H A B C D A) A B) B C) C D) D E) None of these groups would react. Ans: C 21. What reagent(s) would accomplish the following? R C O OH R C O Cl A) Cl2, light B) Cl2, H2O C) SOCL2 D) MgCl2 E) aqueous HCl Ans: C
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 18 Enols, Enolates, and the Aldol Condensation:a, b-Unsaturated Aldehydes and Ketones.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones:The Carbonyl Group.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 16 Electrophilic Attack on Derivatives of Benzene:Substituents Control Regioselectivity.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 15 Benzene and Aromaticity:Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 14 Delocalized Pi Systems:Investigation by Ultraviolet and Visible Spectroscopy.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 13 Alkynes:The Carbon–Carbon Triple Bond.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 12 Reactions of Alkenes.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 11 Alkenes; Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 10 Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy to Deduce Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 09 Further Reactions of Alcohols and the Chemistry of Ethers.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 08 Hydroxy Functional Group:Alcohols:Properties, Preparation, and Strategy of Synthesis.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 07 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes:Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 06 Properties and Reactions of Haloalkanes - Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 05 Stereoisomers.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 04 Cycloalkanes.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 03 Reactions of Alkanes:Bond-Dissociation Energies, Radical Halogenation, and Relative Reactivity.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 02 Structure and Reactivity:Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding in Organic Molecules.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(模拟试卷)有机B期末试题.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(模拟试卷)有机B期末试卷及其答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 21 Amines and Their Derivatives:Functional Groups Containing Nitrogen.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 22 Chemistry of Benzene Substituents:Alkylbenzenes, Phenols, and Benzenamines.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 23 Ester Enolates and the Claisen Condensation:Synthesis of b-Dicarbonyl Compounds; Acyl Anion Equivalents.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 24 Carbohydrates:Polyfunctional Compounds in Nature.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 25 Heterocycles:Heteroatoms in Cyclic Organic Compounds.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 26 Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids:Nitrogen-Containing Polymers in Nature.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding in Organic Molecules.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 02 Structure and Reactivity:Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 03 Reactions of Alkanes:Bond-Dissociation Energies, Radical Halogenation, and Relative Reactivity.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 04 Cycloalkanes.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 05 Stereoisomers.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 06 Properties and Reactions of Haloalkanes - Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 07 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes:Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 08 Hydroxy Functional Group:Alcohols:Properties, Preparation, and Strategy of Synthesis.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 09 Further Reactions of Alcohols and the Chemistry of Ethers.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 10 Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy to Deduce Structure.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 11 Alkenes; Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 12 Reactions of Alkenes.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 13 Alkynes:The Carbon–Carbon Triple Bond.pdf
