北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 10 Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy to Deduce Structure

give al trum than d e bette rseparation between pe D) give different coupling constants than would be observed with weaker magnetic fields. E)Both A and C are true. Ans:E Page 1
Page 1 1. In nuclear magnetic resonance, stronger magnetic fields A) give a higher sensitivity spectrum than do lower magnetic fields. B) give different chemical shifts (in ppm) than would weaker magnets. C) give better separation between peaks in the spectrum (in Hz) than would weaker magnets. D) give different coupling constants than would be observed with weaker magnetic fields. E) Both A and C are true. Ans: E
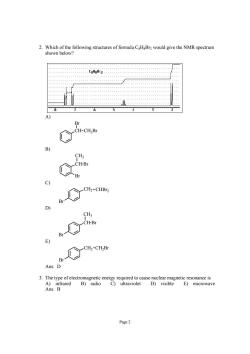
2.Which of the following structures of formula CsHsBra would give the NMR spectrum shown below _CH-CH-B B c) Ct-cus Br BeCt-cn.Bc Ans:D Ans:B E)microwave Page2
Page 2 2. Which of the following structures of formula C8H8Br2 would give the NMR spectrum shown below? A) CH CH2Br Br B) Br CH CH3 Br C) Br CH2 CHBr2 D) Br CH CH3 Br E) Br CH2 CH2Br Ans: D 3. The type of electromagnetic energy required to cause nuclear magnetic resonance is A) infrared B) radio C) ultraviolet D) visible E) microwave Ans: B

4.Which of the following structures would give the NMR spectrum shown? c5120 H:C-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2OH B OH H;C-CH2-CH-CH2-CH 9 OH HC-CH2-CH2-CH-CH 9 OH CH3-CH-CH-CH3 CH E) CH;-CH-CH2-CH2OH Ans:E 5.Which of the following is not true of C NMR? A)The sensitivity ofC NMR is much less than that of proton NMR. B)By simultaneously decoupling the proton region,Cpeaks appear as singlets. The chemical shifts cover a much larger range than doH chemical shifts. wmore peaks hanrerc E Ans:D spectrum will show one peak for each type of carbon in a molecule Page3
Page 3 4. Which of the following structures C5H12O would give the NMR spectrum shown? A) H3C CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2OH B) H3C CH2 CH CH2 CH3 OH C) H3C CH2 CH2 CH CH3 OH D) CH3 CH3 CH CH CH3 OH E) CH3 CH3 CH CH2 CH2OH Ans: E 5. Which of the following is not true of 13C NMR? A) The sensitivity of 13C NMR is much less than that of proton NMR. B) By simultaneously decoupling the proton region, 13C peaks appear as singlets. C) 13C chemical shifts cover a much larger range than do 1 H chemical shifts. D) The 13C NMR spectrum can show more peaks than there are carbons in the molecular formula. E) The 13C NMR spectrum will show one peak for each type of carbon in a molecule. Ans: D
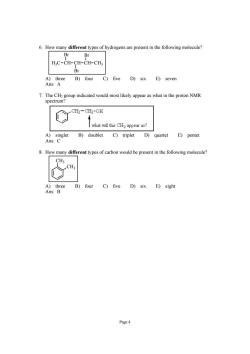
6.How many different types of hydrogens are present in the following molecule? BrBr H3C-CH-CH-CH-CH3 Br A)three B)four C)five D)six E)seven Ans:A 7.The CHa group indicated would most likely appear as what in the proton NMR spectrum? C CH2-CH2-OH what will this CH2 appear as? A)singlet B)doublet C)triplet D)quartet E)pentet Ans:C 8.How many different types of carbon would be present in the following molecule? CH; CH; A)three B)four C)five D)six E)eight Ans:B Page4
Page 4 6. How many different types of hydrogens are present in the following molecule? H3C CH CH CH Br Br CH3 Br A) three B) four C) five D) six E) seven Ans: A 7. The CH2 group indicated would most likely appear as what in the proton NMR spectrum? A) singlet B) doublet C) triplet D) quartet E) pentet Ans: C 8. How many different types of carbon would be present in the following molecule? CH3 CH3 A) three B) four C) five D) six E) eight Ans: B

specifying wh hchsomeawapwsetcafSaplS ent) u conclude that the bottle cor (para) 1 Ans:A 10.The most downfield proton NMR signal (ie..signal most to the left in the spectrum)in the following molecule would be ACH3Br H;C-C-CH2-C -CH34一 B B)B C)C D)D E) there is no way to tel Page5
Page 5 9. A bottle in a chemical stockroom was labeled simply “dichlorobenzene” without specifying which isomer was present. Capillary GC showed that it was a single pure compound, and the proton decoupled carbon NMR spectrum showed three peaks (not including solvent). You conclude that the bottle contained A) Cl Cl (ortho) B) Cl Cl (para) C) Cl Cl (meta) D) any of the dichlorobenzene isomers E) none of the dichlorobenzene isomers Ans: A 10. The most downfield proton NMR signal (i.e., signal most to the left in the spectrum) in the following molecule would be H3C C CH2 C CH3 Br Br CH3 Br D B C A A) A B) B C) C D) D E) there is no way to tell Ans: C

11.Avery old bottle labeled only"chlorinated benzene"was found in the stockroom. E) Ans:D resent in the proton NMR for ethylpropanoate? unt TMS as A)2 B)3C)4 D)5E)6 Ans:C Page6
Page 6 11. A very old bottle labeled only “chlorinated benzene” was found in the stockroom. Capillary GC showed (surprisingly) that the compound was pure, and a proton-decoupled 13C NMR spectrum showed only two peaks. Which of the following compounds was in the bottle? A) Cl B) Cl Cl C) Cl Cl D) Cl Cl E) Cl Cl Cl Ans: D 12. How many different signals will be present in the proton NMR for ethylpropanoate? (Do not count TMS as one of the signals!) A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 5 E) 6 Ans: C
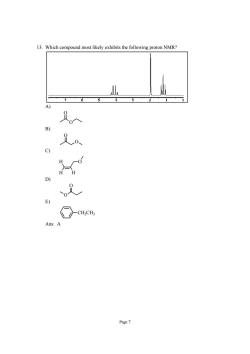
13.Which compound most likely exhibits the following proton NMR? c) D E) ns.A Page7
Page 7 13. Which compound most likely exhibits the following proton NMR? A) O O B) O O C) H H H O D) O O E) CH2CH3 Ans: A
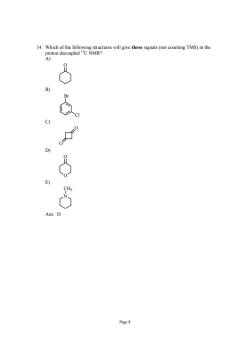
rs ill ive three sinls (not counting TMS)in the Page8
Page 8 14. Which of the following structures will give three signals (not counting TMS) in the proton decoupled 13C NMR? A) O B) Br Cl C) O O D) O O E) N CH3 Ans: D
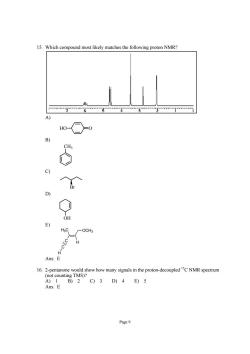
15.Which compound most likely matches the following proton NMR? H -OCH3 Ans:E 16乙2aameng,owhorygabnepoondaopeacNMRspecm Ans E C9)3D)4E)5 Page9
Page 9 15. Which compound most likely matches the following proton NMR? A) HO O B) CH3 C) Br D) OH E) C C H H H3C OCH3 Ans: E 16. 2-pentanone would show how many signals in the proton-decoupled 13C NMR spectrum (not counting TMS)? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 Ans: E

7”中g"2 gn皆CNMR mm2 Ans:A Page 10
Page 10 17. Acetone would show how many doublets in the proton-coupled 13C NMR spectrum? A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 3 E) 4 Ans: A
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 09 Further Reactions of Alcohols and the Chemistry of Ethers.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 08 Hydroxy Functional Group:Alcohols:Properties, Preparation, and Strategy of Synthesis.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 07 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes:Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 06 Properties and Reactions of Haloalkanes - Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 05 Stereoisomers.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 04 Cycloalkanes.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 03 Reactions of Alkanes:Bond-Dissociation Energies, Radical Halogenation, and Relative Reactivity.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 02 Structure and Reactivity:Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding in Organic Molecules.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(模拟试卷)有机B期末试题.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(模拟试卷)有机B期末试卷及其答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(模拟试卷)有机A期末试卷及其答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(模拟试卷)有机B期中试卷及其答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(模拟试卷)有机B期中试卷.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(模拟试卷)有机A期末试卷.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(模拟试卷)有机A期中试卷及其答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(模拟试卷)有机A期中试卷.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)[3,3]σ迁移反应过渡态立体化学过程的新观点.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)芳香过渡态理论及其在协同反应中的应用.pdf
- 《有机化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)芳香性概念的新发展.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 11 Alkenes; Infrared Spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 12 Reactions of Alkenes.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 13 Alkynes:The Carbon–Carbon Triple Bond.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 14 Delocalized Pi Systems:Investigation by Ultraviolet and Visible Spectroscopy.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 15 Benzene and Aromaticity:Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 16 Electrophilic Attack on Derivatives of Benzene:Substituents Control Regioselectivity.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones:The Carbonyl Group.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 18 Enols, Enolates, and the Aldol Condensation:a, b-Unsaturated Aldehydes and Ketones.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acids.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 21 Amines and Their Derivatives:Functional Groups Containing Nitrogen.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 22 Chemistry of Benzene Substituents:Alkylbenzenes, Phenols, and Benzenamines.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 23 Ester Enolates and the Claisen Condensation:Synthesis of b-Dicarbonyl Compounds; Acyl Anion Equivalents.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 24 Carbohydrates:Polyfunctional Compounds in Nature.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 25 Heterocycles:Heteroatoms in Cyclic Organic Compounds.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(章节测验,含答案)Chapter 26 Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids:Nitrogen-Containing Polymers in Nature.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 01 Structure and Bonding in Organic Molecules.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 02 Structure and Reactivity:Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 03 Reactions of Alkanes:Bond-Dissociation Energies, Radical Halogenation, and Relative Reactivity.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《有机化学》课程教学资源(习题与答案)Chapter 04 Cycloalkanes.pdf
