西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三部分 数据链路层 第12章 多路访问 Multiple Access

Data Communications and Networking Forouzan Fourth Edition Chapter 12 Multiple Access 多路访问 12.1 CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display
12.1 Chapter 12 Multiple Access 多路访问 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display

Figure 12.1 Data link layer divided into two functionality-oriented sub 数据链路层分为两个功能子层: 数据链路控制子层和多路访问控制子层 Data link layer Data link control Multiple-access resolution 12.2
12.2 Figure 12.1 Data link layer divided into two functionality-oriented sublayers 数据链路层分为两个功能子层: 数据链路控制子层和多路访问控制子层

Figure 12.2 Taxonomy of multiple-access protocols discussed in this ch 多路访问控制协议的分类: 随机访问协议 受控访问控制协议 通道化协议 Multiple-access protocols Random access Controlled-access Channelization protocols protocols protocols ALOHA Reservation FDMA CSMA Polling TDMA CSMA/CD Token passing CDMA CSMA/CA 12.3
12.3 Figure 12.2 Taxonomy of multiple-access protocols discussed in this chapter 多路访问控制协议的分类: 随机访问协议 受控访问控制 协议 通道化协议

12-1 RANDOMACCESS 随机访问协议 In random access or contention methods,no station is superior to another station and none is assigned the control over another.No station permits,or does not permit,another station to send.At each instance,a station that has data to send uses a procedure defined by the protocol to make a decision on whether or not to send. 在随机访问或竞争访问方式中,没有一个站点是优于其它站点的, 也不能控制其它站点。没有站点有权力允许或不允许其它站点发 送或不发送数据。有数据要发送的站通过自身的协议决定发送还 是不发送数据。 Topics discussed in this section: ALOHA ALOHA协议 Carrier Sense Multiple Access 载波侦听多路访问协议CSMA Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection带有冲突检测能力CSMA Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance带冲突避免CSMA 12.4
12.4 12-1 RANDOM ACCESS 随机访问协议 In random access or contention methods, no station is superior to another station and none is assigned the control over another. No station permits, or does not permit, another station to send. At each instance, a station that has data to send uses a procedure defined by the protocol to make a decision on whether or not to send. 在随机访问或竞争访问方式中,没有一个站点是优于其它站点的, 也不能控制其它站点。没有站点有权力允许或不允许其它站点发 送或不发送数据。有数据要发送的站通过自身的协议决定发送还 是不发送数据。 ALOHA ALOHA协议 Carrier Sense Multiple Access 载波侦听多路访问协议 CSMA Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection 带有冲突检测能力CSMA Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance 带冲突避免CSMA Topics discussed in this section:
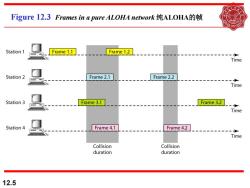
Figure12.3 Frames in a pure ALOHA network纯ALOHA的帧 Station 1 Frame 1.1 Frame 1.2 Time Station 2 Frame 2.1 Frame 2.2 Time Station 3 Frame 3.1 Frame 3.2 Time Station 4 Frame 4.1 Frame 4.2 Time Collision Collision duration duration 12.5
12.5 Figure 12.3 Frames in a pure ALOHA network 纯ALOHA的帧
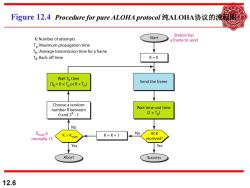
Figure12.4 Procedure for pure ALOHA protocol纯ALOHA协议的流 Station has K:Number of attempts Start a frame to send Tp:Maximum propagation time Tr:Average transmission time for a frame Tg:Back-off time K=0 Wait Tg time (TB=R×Tpor RXT) Send the frame Choose a random number R between Wait time-out time 0and 2K-1 (2×Tp) No Kmax is K=K+1 No ACK a normally 15 received? Yes Yes Abort Success 12.6
12.6 Figure 12.4 Procedure for pure ALOHA protocol 纯ALOHA协议的流程图

Example 12.1 The stations on a wireless ALOHA network are a maximum of 600 km apart.If we assume that signals propagate at 3 X 108 m/s,we find Tp=(600 X 105)/(3 X 108)=2 ms.Now we can find the value of Te for different values of K. 一个纯ALOHA协议的站点之间最大距离为600公里,信号的传 播速度为30万公里/秒,那么Tp=(600×105)/(3×108)=2ms 。对于不同的K值,得到不同的T值。 For K 1,the range is 0,1.The station needs to generate a random number with a value of 0 or 1.This means that TB is either 0 ms (0 X 2)or 2 ms (1 X 2), based on the outcome of the random variable. 若K=1,则取值范围{0,1}。即站内的随机数位0或1。这意味着 TB是0ms(0X2)或是2ms(1X2)。 12.7
12.7 The stations on a wireless ALOHA network are a maximum of 600 km apart. If we assume that signals propagate at 3 × 108 m/s, we find Tp = (600 × 105 ) / (3 × 108 ) = 2 ms. Now we can find the value of TB for different values of K . 一个纯ALOHA协议的站点之间最大距离为600公里,信号的传 播速度为30万公里/秒,那么Tp = (600 × 105 ) / (3 × 108 ) = 2 ms 。对于不同的K值,得到不同的TB值。 a. For K = 1, the range is {0, 1}. The station needs to| generate a random number with a value of 0 or 1. This means that TB is either 0 ms (0 × 2) or 2 ms (1 × 2), based on the outcome of the random variable. 若K=1,则取值范围{0, 1}。即站内的随机数位0或1。这意味着 TB 是 0 ms (0 × 2)或是2 ms (1 × 2)。 Example 12.1

Example 12.1 (continued) UNIN b.For K -2,the range is 1,2,3.This means that TB can be 0,2,4,or 6 ms,based on the outcome of the random variable. 若K=2,则取值范围{0,1,2,3}。这意味着TB是0ms,2ms,4ms, 6ms。 c.For K -3,the range is 1,2,3,4,5,6,7.This means that Ts can be 0,2,4,··.,l4s,based on the outcome of the random variable. 若K=3,则取值范围{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7}。这意味着TB是0ms,2ms, 4ms,6ms,.,14ms。 d.We need to mention that if K 10,it is normally set to 10. 但是,若K值大于10时,随机数取值范围通常设定为10。 12.8
12.8 b. For K = 2, the range is {0, 1, 2, 3}. This means that TB can be 0, 2, 4, or 6 ms, based on the outcome of the random variable. 若K=2,则取值范围{0,1,2,3}。这意味着TB 是 0ms, 2ms, 4ms, 6ms。 c. For K = 3, the range is {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}. This means that TB can be 0, 2, 4, . . . , 14 ms, based on the outcome of the random variable. 若K=3,则取值范围{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7}。这意味着TB 是 0ms, 2ms, 4ms, 6ms,., 14ms。 d. We need to mention that if K > 10, it is normally set to 10. 但是,若K值大于10时,随机数取值范围通常设定为10。 Example 12.1 (continued)

Figure 12.5 Vulnerable time for pure ALOHA protocol 纯ALOHA可能的冲突时间是帧长度的两倍 B's end A's end collides with collides with A's beginning C's beginning 感 B 器 A 器 盈 器 t-Tfr t+Tir Time Vulnerable time =2 x Tfr 12.9
12.9 Figure 12.5 Vulnerable time for pure ALOHA protocol 纯ALOHA可能的冲突时间是帧长度的两倍

Example 12.2 UNI A pure ALOHA network transmits 200-bit frames on a shared channel of 200 kbps.What is the requirement to make this frame collision-free? 一个纯ALOHA帧长200比特,带宽200kbps,这个帧在传输过程中无冲 突的条件是什么? Solution Average frame transmission time Tfr is 200 bits/200 kbps or I ms. The vulnerable time is 2 X I ms 2 ms.This means no station should send later than I ms before this station starts transmission and no station should start sending during the one 1-ms period that this station is sending. 帧的传输时间为Tr=200bits/200kbps=1ms.则可能的冲突时间 为2ms。意味着前1ms和后1ms都没有其它站发送数据帧。 12.10
12.10 A pure ALOHA network transmits 200-bit frames on a shared channel of 200 kbps. What is the requirement to make this frame collision-free? 一个纯ALOHA帧长200比特,带宽200kbps, 这个帧在传输过程中无冲 突的条件是什么? Example 12.2 Solution Average frame transmission time Tfr is 200 bits/200 kbps or 1 ms. The vulnerable time is 2 × 1 ms = 2 ms. This means no station should send later than 1 ms before this station starts transmission and no station should start sending during the one 1-ms period that this station is sending. 帧的传输时间为Tfr = 200 bits/200 kbps = 1 ms. 则可能的冲突时间 为2ms。意味着前1ms和后1ms都没有其它站发送数据帧
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三部分 数据链路层 第11章 数据链路控制 Data Link Control.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三部分 数据链路层 第10章 检错与纠错 Error Detection and Correction.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第二部分 第9章 使用电话网和有线电视网进行数据传输.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第二部分 第8章 交换.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第二部分 第7章 传输介质.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第二部分 第6章 带宽利用 Bandwidth Utilization:Multiplexing and Spreading.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第二部分 第5章 模拟传输 Analog Transmission.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第二部分 第4章 数字传输 Digital Transmission.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第二部分 物理层和介质 第3章 物理层——数据和信号.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第一部分 概述 第2章 网络模型.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第一部分 概述 第1章 绪论(主讲:权义宁).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字信号处理》课程教学课件(讲稿)09 多采样率数字信号处理.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字信号处理》课程教学课件(讲稿)08 时域离散系统的实现.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字信号处理》课程教学课件(讲稿)07 FIR数字滤波器(FIRDF)设计.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字信号处理》课程教学课件(讲稿)06 IIR数字滤波器(IIRDF)设计.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字信号处理》课程教学课件(讲稿)05 数字滤波器的基本概念及一些特殊滤波器.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字信号处理》课程教学课件(讲稿)04 模拟信号数字处理.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字信号处理》课程教学课件(讲稿)03 离散傅里叶变换DFT及其快速算法FFT.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字信号处理》课程教学课件(讲稿)02 时域离散信号和系统的频域分析(2/2).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《数字信号处理》课程教学课件(讲稿)02 时域离散信号和系统的频域分析(1/2).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三部分 数据链路层 第13章 有线局域网——以太网.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三部分 数据链路层 第14章 无线局域网.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三部分 数据链路层 第15章 连接局域网、主干网和虚拟局域网 Connecting LANs, Backbone Networks, and Virtual LANs.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三部分 数据链路层 第16章 无线WAN——移动电话和卫星网络 Cellular Telephone and Satellite Networks.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三部分 数据链路层 第17章 广域网SONET、SDH.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三部分 数据链路层 第18章 虚电路网络——帧中继和ATM.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第四部分 网络层 第19章 逻辑寻址.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第四部分 网络层 第20章 IP协议.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第四部分 网络层 第21章 地址映射、差错报告和多播.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第四部分 网络层 第22章 传递、转发和路由选择.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第五部分 传输层 第23章 UDP、TCP和SCTP.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第五部分 传输层 第24章 拥塞控制和服务质量.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第六部分 传输层 第25章 域名系统 Domain Name System.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第六部分 传输层 第26章 远程登录、电子邮件和文件传输 Remote Logging, Electronic Mail, and File Transfer.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《计算机通信与网络》课程教学课件(讲稿)第六部分 传输层 第27章 万维网与超文本传输协议 WWW and HTTP.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)知识点串讲(主讲教师:杨龙).pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)绪论、第一章 电路的基本定律(1/2).pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)总复习课件(共六章,主讲:杨龙).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 电路的基本定律(2/2)、第二章 电阻电路分析(1/5).pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《电路分析基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 电阻电路分析(3/5).pptx
