厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第13章 Adaptation of pelagic life

ADAPTATION OF PELAGIC LIFE Lin Yuan-Shao (林元烧), tel: 218 9433, email: yslin@xmu.edu.cn Cao Wen-Qing (曹文清), tel: 218 9433, email: wqcao@xmu.edu.cn Guo Dong-Hui (郭东晖), tel: 218 8471, email:dhguo@jingxian.xmu.edu.cn Wu Li-Sheng (吴荔生), tel: 218 8455, email: lisheng@jingxian.xmu.edu.cn Fang Lv-Ping (方旅平), tel: 218 9433, email: lpfang@xmu.edu.cn Chapter 13
ADAPTATION OF PELAGIC LIFE Lin Yuan-Shao (林元烧), tel: 218 9433, email: yslin@xmu.edu.cn Cao Wen-Qing (曹文清), tel: 218 9433, email: wqcao@xmu.edu.cn Guo Dong-Hui (郭东晖), tel: 218 8471, email:dhguo@jingxian.xmu.edu.cn Wu Li-Sheng (吴荔生), tel: 218 8455, email: lisheng@jingxian.xmu.edu.cn Fang Lv-Ping (方旅平), tel: 218 9433, email: lpfang@xmu.edu.cn Chapter 13

Adaptation of pelagic life ◼ Significance of staying afloat ◼ Keep buoyancy mechanism ◼ Movement
Adaptation of pelagic life ◼ Significance of staying afloat ◼ Keep buoyancy mechanism ◼ Movement

§13.1 Significance of staying afloat ◼ Phytoplankton: to get enough light for photosynthesis. ◼ Once sinking or being carried out of the photic zone by water movement, in generally, they will stop metabolism and die, unless they can somehow get back into the sunlit layer. ◼ zooplankton: they need sunlight for their bio rhythm and their food is in the shallowwater
§13.1 Significance of staying afloat ◼ Phytoplankton: to get enough light for photosynthesis. ◼ Once sinking or being carried out of the photic zone by water movement, in generally, they will stop metabolism and die, unless they can somehow get back into the sunlit layer. ◼ zooplankton: they need sunlight for their bio rhythm and their food is in the shallowwater

Staying afloat ◼ To live in the water layers, organisms must stay in the epipelagic. All epipelagic organisms face a fundamental problem——cells and tissue are denser than water
Staying afloat ◼ To live in the water layers, organisms must stay in the epipelagic. All epipelagic organisms face a fundamental problem——cells and tissue are denser than water

Keep buoyancy mechanism Organisms must avoid sinking to stay in the epipelagic. This is achieved by ◼ Increased resistance ◼ Increased buoyancy ◼ The floaters ◼ Reduced body density
Keep buoyancy mechanism Organisms must avoid sinking to stay in the epipelagic. This is achieved by ◼ Increased resistance ◼ Increased buoyancy ◼ The floaters ◼ Reduced body density

Increased resistance ❑ Surface-to-Volume Ratio
Increased resistance ❑ Surface-to-Volume Ratio
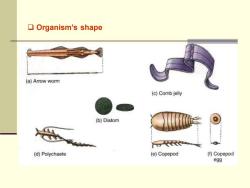
❑ Organism’s shape
❑ Organism’s shape
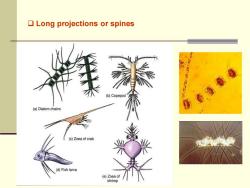
❑ Long projections or spines
❑ Long projections or spines

§13.2 Increased buoyancy ◼ The second way that epipelagic organisms can stay near the surface is to have special adaptations that make them more buoyant. Unlike adaptations that help the organism resist sinking, buoyancy reduces the tendency to sink
§13.2 Increased buoyancy ◼ The second way that epipelagic organisms can stay near the surface is to have special adaptations that make them more buoyant. Unlike adaptations that help the organism resist sinking, buoyancy reduces the tendency to sink
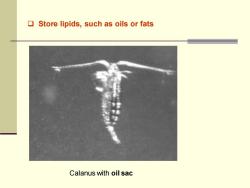
❑ Store lipids, such as oils or fats Calanus with oil sac
❑ Store lipids, such as oils or fats Calanus with oil sac
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第12章 浮游幼体.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第11章 其他浮游生物.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第10章 被囊动物.pdf
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 传染与免疫.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 微生物的生态.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 微生物的遗传变异与育种.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 微生物的生长与控制.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 微生物的代谢.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 微生物的营养和培养基.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 病毒(Viruses)和亚病毒(virusoid).ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学实验指导书(共十一个实验).doc
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 真核微生物的形态和构造.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学实验室主要设备.doc
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 原核微生物的形态和构造.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学实验常用基本操作技术.doc
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)微生物学实验(讲稿,主讲:王振河).ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 微生物的分类和鉴定.ppt
- 华东理工大学:《酶工程》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)第三章 固定化酶.ppt
- 渤海大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 微生物与食品变质.ppt
- 渤海大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 微生物的遗传.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第14章 seasonal distribution.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第15章 geographic distribution.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第16章 vertical distribution.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第17章 Diurnal vertical migration(DVM).ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第18章 Plankton and Fishery.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第01章 硅藻门.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第02章 甲藻门.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第03章 其他海洋浮游植物.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第04章 原生动物.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第05章 腔肠动物.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第06章 栉水母.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第1节 绪论.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第2节 枝角类.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第3节 桡足类 1/2.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第3节 桡足类 2/2.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第4节 磷虾类.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第5节 糠虾类.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第6节 端足类.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第7节 樱虾类.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第08章 浮游软体动物.pdf
