厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第16章 vertical distribution

Vertical distribution Lin Yuan-Shao, Cao Wen-Qing and Guo Dong-Hui 2004. 6. 3 Chapter 16
Vertical distribution Lin Yuan-Shao, Cao Wen-Qing and Guo Dong-Hui 2004. 6. 3 Chapter 16

This chapter includes there parts of section: §16.1 Vertical distribution in phytoplankton §16.2 Vertical distribution in zooplankton
This chapter includes there parts of section: §16.1 Vertical distribution in phytoplankton §16.2 Vertical distribution in zooplankton

Vertical distribution in phytoplankton Studies on the different layers of water shows much variation in the distribution of the phytoplankton and it becomes scarce in deep layers. Some examples on vertical distribution in phytoplankton are given bellow. §16.1
Vertical distribution in phytoplankton Studies on the different layers of water shows much variation in the distribution of the phytoplankton and it becomes scarce in deep layers. Some examples on vertical distribution in phytoplankton are given bellow. §16.1
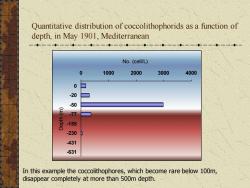
Quantitative distribution of coccolithophorids as a function of depth, in May 1901, Mediterranean No. (cell/L) 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 0 -20 -50 -77 -155 -230 -431 -631 Depth (m) In this example the coccolithophores, which become rare below 100m, disappear completely at more than 500m depth
Quantitative distribution of coccolithophorids as a function of depth, in May 1901, Mediterranean No. (cell/L) 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 0 -20 -50 -77 -155 -230 -431 -631 Depth (m) In this example the coccolithophores, which become rare below 100m, disappear completely at more than 500m depth
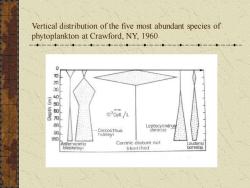
Vertical distribution of the five most abundant species of phytoplankton at Crawford, NY, 1960
Vertical distribution of the five most abundant species of phytoplankton at Crawford, NY, 1960

Vertical distribution of chlorophyll a (shaded) and density (dashed) of phaeophytin in Japan ,132oE)
Vertical distribution of chlorophyll a (shaded) and density (dashed) of phaeophytin in Japan ,132oE)
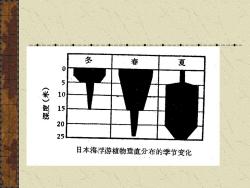
多 春 夏 0 50505 日本海浮游植物垂直分布的季节变化
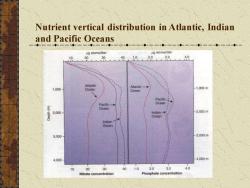
Nutrient vertical distribution in Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans
Nutrient vertical distribution in Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans

From the examples above, we can see: phytoplankton must have adequate light for photosynthesis and can develop only in the upper layers (photic zone). Phytoplankton is not most abundant in the superficial water, where light intensity is greatest. Many of the phytoplanktonic organisms, particularly diatoms cannot move independently and so tend to sink. Those with a high density will, therefore, remain below the level of high production. Photosynthesis requires an optimal light intensity. The light intensity at superficial layer may have strongly light, and UV (ultra-violet) may damage some biological molecules and affect the process of photosynthesis
From the examples above, we can see: phytoplankton must have adequate light for photosynthesis and can develop only in the upper layers (photic zone). Phytoplankton is not most abundant in the superficial water, where light intensity is greatest. Many of the phytoplanktonic organisms, particularly diatoms cannot move independently and so tend to sink. Those with a high density will, therefore, remain below the level of high production. Photosynthesis requires an optimal light intensity. The light intensity at superficial layer may have strongly light, and UV (ultra-violet) may damage some biological molecules and affect the process of photosynthesis

Vertical distribution in zooplankton The distribution of the Euphausiacea in the North Atlantic sets an excellent example of vertical distribution in zooplankton. § 16.2
Vertical distribution in zooplankton The distribution of the Euphausiacea in the North Atlantic sets an excellent example of vertical distribution in zooplankton. § 16.2
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第15章 geographic distribution.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第14章 seasonal distribution.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第13章 Adaptation of pelagic life.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第12章 浮游幼体.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第11章 其他浮游生物.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第10章 被囊动物.pdf
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 传染与免疫.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 微生物的生态.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 微生物的遗传变异与育种.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 微生物的生长与控制.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 微生物的代谢.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 微生物的营养和培养基.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 病毒(Viruses)和亚病毒(virusoid).ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学实验指导书(共十一个实验).doc
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 真核微生物的形态和构造.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学实验室主要设备.doc
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 原核微生物的形态和构造.ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学实验常用基本操作技术.doc
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)微生物学实验(讲稿,主讲:王振河).ppt
- 河南科技学院:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 微生物的分类和鉴定.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第17章 Diurnal vertical migration(DVM).ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第18章 Plankton and Fishery.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第01章 硅藻门.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第02章 甲藻门.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第03章 其他海洋浮游植物.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第04章 原生动物.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第05章 腔肠动物.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第06章 栉水母.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第1节 绪论.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第2节 枝角类.ppt
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第3节 桡足类 1/2.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第3节 桡足类 2/2.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第4节 磷虾类.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第5节 糠虾类.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第6节 端足类.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07章 浮游甲壳动物 Planktonic Crustacea 第7节 樱虾类.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第08章 浮游软体动物.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第09章 毛颚动物.pdf
- 厦门大学:《海洋浮游生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)绪论 Marine Planktology(主讲:曹文清、郭东晖).pdf
- 齐鲁工业大学(山东轻工业学院):《生物工艺学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 生物工艺学概论 biotechnologh.ppt
